A STRAIGHTFORWARD SET UP OF
... Schrodinger Equation. In other words, the RHS of Eq.(31) or Eq.(32-b) represents the corrected Schrodinger eigenvalue based on only the relativistic effect due to the motion of the electron. Recall yet that, along the line we pursue, Eq.(31) is incorrect, since Eq.(30-a) should be considered togethe ...
... Schrodinger Equation. In other words, the RHS of Eq.(31) or Eq.(32-b) represents the corrected Schrodinger eigenvalue based on only the relativistic effect due to the motion of the electron. Recall yet that, along the line we pursue, Eq.(31) is incorrect, since Eq.(30-a) should be considered togethe ...
Physics AP B- Scope
... 1. Students should understand the uniform circular motion of a particle so they can: a) Relate the radius of the circle and the speed or rate of revolution of the particle to the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration. b) Describe the direction of the particle's velocity and acceleration at any i ...
... 1. Students should understand the uniform circular motion of a particle so they can: a) Relate the radius of the circle and the speed or rate of revolution of the particle to the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration. b) Describe the direction of the particle's velocity and acceleration at any i ...
same horizontal velocity.
... A truck is moving at constant speed. Inside the storage compartment, a rock is dropped from the midpoint of the ceiling and strikes the floor below. Does it strike the floor behind where it was dropped, in front of where it was dropped, or directly below? ...
... A truck is moving at constant speed. Inside the storage compartment, a rock is dropped from the midpoint of the ceiling and strikes the floor below. Does it strike the floor behind where it was dropped, in front of where it was dropped, or directly below? ...
File - Carroll`s Cave of Knowledge
... point. This point is called the “center of mass” or “center of gravity”. For a uniform object this point is the middle of the object. (Provided you do not go inside a planet or object, this assumption is valid.) Ex 2: What is the gravitational force between a 120 kg person and the earth. Calculate t ...
... point. This point is called the “center of mass” or “center of gravity”. For a uniform object this point is the middle of the object. (Provided you do not go inside a planet or object, this assumption is valid.) Ex 2: What is the gravitational force between a 120 kg person and the earth. Calculate t ...
GRADE 12A: Physics 4
... have the same period, and the shadows on the screen oscillate in phase and with similar amplitude. Students should observe that SHM can be treated as a projection of circular motion. Ask each student to draw, on graph paper, a circle with a radius of a few centimetres, centred on an intersection of ...
... have the same period, and the shadows on the screen oscillate in phase and with similar amplitude. Students should observe that SHM can be treated as a projection of circular motion. Ask each student to draw, on graph paper, a circle with a radius of a few centimetres, centred on an intersection of ...
10 Circular Motion - Aurora City Schools
... • It revolves around the sun once every 365 ¼ days. • It rotates around an axis passing through its geographical poles once every 24 hours. ...
... • It revolves around the sun once every 365 ¼ days. • It rotates around an axis passing through its geographical poles once every 24 hours. ...
4 Newton’s Second Law Experiment 4.1
... 9. Using the ruler permanently affixed to the air track, record the locations of X0 , X1 and X2 in your spreadsheet and assign a reasonable uncertainty to these positions ( X). It is very important that your glider always starts from the same location X0 and that the two photogates are not moved. If ...
... 9. Using the ruler permanently affixed to the air track, record the locations of X0 , X1 and X2 in your spreadsheet and assign a reasonable uncertainty to these positions ( X). It is very important that your glider always starts from the same location X0 and that the two photogates are not moved. If ...
AP1 Gravity - APlusPhysics
... Answer: (B) toward the right of the page To increase the radius of its orbit, the ship must attain a higher velocity, which requires an acceleration in the direction of its current velocity, or to the right of the page as depicted in this diagram. This will shift the orbit from a circular orbit to a ...
... Answer: (B) toward the right of the page To increase the radius of its orbit, the ship must attain a higher velocity, which requires an acceleration in the direction of its current velocity, or to the right of the page as depicted in this diagram. This will shift the orbit from a circular orbit to a ...
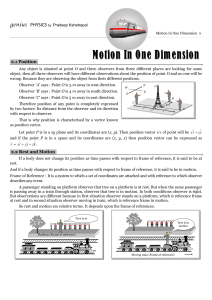
Introduction - PRADEEP KSHETRAPAL PHYSICS
... (zero displacement means that body after motion has came back to initial position) i.e., Distance > 0 but Displacement > = or < 0 (iii) For motion between two points displacement is single valued while distance depends on actual path and so can have many values. (iv) For a moving particle distance c ...
... (zero displacement means that body after motion has came back to initial position) i.e., Distance > 0 but Displacement > = or < 0 (iii) For motion between two points displacement is single valued while distance depends on actual path and so can have many values. (iv) For a moving particle distance c ...
Coriolis Force
... Coriolis force The Coriolis force is an "apparent force," arising because of the complicated frame of reference from which we observe the atmosphere. The laws of Newtonian physics are formulated in the absolute, or inertial, frame of reference, but we observe the atmosphere and oceans within a nonin ...
... Coriolis force The Coriolis force is an "apparent force," arising because of the complicated frame of reference from which we observe the atmosphere. The laws of Newtonian physics are formulated in the absolute, or inertial, frame of reference, but we observe the atmosphere and oceans within a nonin ...
Semester Exam Review
... 2.0 m/s2, how fast will she be running after 4.0 s? the pebble falls for 1.20 s, what is its velocity when it hits the water? A. 8.0 m/s A. 8.17 m/s B. 4.0 m/s B. 8.40 m/s C. 2.0 m/s C. 11.0 m/s D. 0.5 m/s D. 11.8 m/s ...
... 2.0 m/s2, how fast will she be running after 4.0 s? the pebble falls for 1.20 s, what is its velocity when it hits the water? A. 8.0 m/s A. 8.17 m/s B. 4.0 m/s B. 8.40 m/s C. 2.0 m/s C. 11.0 m/s D. 0.5 m/s D. 11.8 m/s ...
Forces and acceleration Newton`s 2nd Law
... When we let the cart go, being careful not to push it upon release, it will immediately trigger the photogate timer. The timer will stop when the cart gets through. Since the initial velocity is zero, we can use the formula x ...
... When we let the cart go, being careful not to push it upon release, it will immediately trigger the photogate timer. The timer will stop when the cart gets through. Since the initial velocity is zero, we can use the formula x ...
File - singhscience
... 3.6 Interpret velocity/time graphs to: a compare acceleration from gradients qualitatively b calculate the acceleration from the gradient (for uniform acceleration only) H c determine the distance travelled using the area between the graph line and the time axis (for uniform acceleration only) HSW 1 ...
... 3.6 Interpret velocity/time graphs to: a compare acceleration from gradients qualitatively b calculate the acceleration from the gradient (for uniform acceleration only) H c determine the distance travelled using the area between the graph line and the time axis (for uniform acceleration only) HSW 1 ...
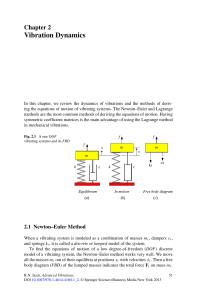
Vibration Dynamics
... in which, x is a column array of describing coordinates of the system, and f is a column array of the associated applied forces. The square matrices [m], [c], [k] are the mass, damping, and stiffness matrices. Example 30 (The one, two, and three DOF model of vehicles) The one, two, and three DOF mod ...
... in which, x is a column array of describing coordinates of the system, and f is a column array of the associated applied forces. The square matrices [m], [c], [k] are the mass, damping, and stiffness matrices. Example 30 (The one, two, and three DOF model of vehicles) The one, two, and three DOF mod ...
PS-5
... The object will accelerate at a constant rate of 9.8m/s2 or m/s/s. ○ This means that the object will speed up at a constant rate of 9.8 m/sec every second it is falling in the absence of air resistance. The value, 9.8m/s per s, is called the acceleration of gravity and has the symbol ag. Since the o ...
... The object will accelerate at a constant rate of 9.8m/s2 or m/s/s. ○ This means that the object will speed up at a constant rate of 9.8 m/sec every second it is falling in the absence of air resistance. The value, 9.8m/s per s, is called the acceleration of gravity and has the symbol ag. Since the o ...