02PCYQW_2016_Lagrange_approach - LaDiSpe
... A multibody system is considered as a system in which the dynamic equations derive from a unifying principle. This principle is based on the fact that, in order to describe the motion of a system, it is sufficient to consider some scalar quantities. These quantities were in origin called vis viva an ...
... A multibody system is considered as a system in which the dynamic equations derive from a unifying principle. This principle is based on the fact that, in order to describe the motion of a system, it is sufficient to consider some scalar quantities. These quantities were in origin called vis viva an ...
Introduction to Circular Motion
... But what about centrifugal forces? • There is no such thing! The sensation of an outward force and an outward acceleration is a false sensation. • For example, if you are in a car make a right turn, while the car is accelerating inward, your body continues in a __________________ line. If you are s ...
... But what about centrifugal forces? • There is no such thing! The sensation of an outward force and an outward acceleration is a false sensation. • For example, if you are in a car make a right turn, while the car is accelerating inward, your body continues in a __________________ line. If you are s ...
m2_FM
... Choose the X axis parallel to the include and the Y axis at right angle to the incline as shown in figure 6. The object is represented as a dot. Show all the forces which act only on the box. Resolve all these forces into components parallel and at right angles to the incline. Apply Newton’s 2nd Law ...
... Choose the X axis parallel to the include and the Y axis at right angle to the incline as shown in figure 6. The object is represented as a dot. Show all the forces which act only on the box. Resolve all these forces into components parallel and at right angles to the incline. Apply Newton’s 2nd Law ...
Vectors and Scalars
... A 100 N force acts on a cart in the direction shown. This force can be resolved into a horizontal component ( x ) and a vertical component ( y ). Each component represents the complete effect of the100 N in its direction. To prevent the cart from moving horizontally a force of 86.6 N acting to the ...
... A 100 N force acts on a cart in the direction shown. This force can be resolved into a horizontal component ( x ) and a vertical component ( y ). Each component represents the complete effect of the100 N in its direction. To prevent the cart from moving horizontally a force of 86.6 N acting to the ...
File - Phy 2048-0002
... Translation: body’s movement described by x(t). Rotation: body’s movement given by θ(t) = angular position of the body’s reference line as function of time. Angular displacement: body’s rotation about its axis changing the angular position from θ1 to θ2. ...
... Translation: body’s movement described by x(t). Rotation: body’s movement given by θ(t) = angular position of the body’s reference line as function of time. Angular displacement: body’s rotation about its axis changing the angular position from θ1 to θ2. ...
Wednesday, Oct. 29, 2008
... The principle of energy conservation can be used to solve problems that are harder to solve just using Newton’s laws. It is used to describe motion of an object or a system of objects. A new concept of linear momentum can also be used to solve physical problems, especially the problems involving col ...
... The principle of energy conservation can be used to solve problems that are harder to solve just using Newton’s laws. It is used to describe motion of an object or a system of objects. A new concept of linear momentum can also be used to solve physical problems, especially the problems involving col ...
FanCartPhysicsSE-1
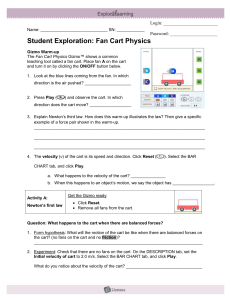
... 2. Suppose several more horses were hitched up to the same cart. How would this affect the speed of the cart? __________________________________________________ Although these questions may seem simple, they form the basis of Newton’s second law of motion. The Fan Cart Physics Gizmo™ can be used to ...
... 2. Suppose several more horses were hitched up to the same cart. How would this affect the speed of the cart? __________________________________________________ Although these questions may seem simple, they form the basis of Newton’s second law of motion. The Fan Cart Physics Gizmo™ can be used to ...
Table of Contents
... central point which is called the axis or center of spin. If the axis is within the body, we say it is rotating. If the axis is outside the body, then the object is revolving. The earth rotates around its axis, which causes day and night. The earth revolves around the sun, which causes the four seas ...
... central point which is called the axis or center of spin. If the axis is within the body, we say it is rotating. If the axis is outside the body, then the object is revolving. The earth rotates around its axis, which causes day and night. The earth revolves around the sun, which causes the four seas ...
module p1: energy for the home
... that for some quantities (e.g. force), direction is important, whereas for other quantities (e.g. mass), direction is not important ...
... that for some quantities (e.g. force), direction is important, whereas for other quantities (e.g. mass), direction is not important ...
Physical Science
... starting point, at a velocity slower than the motion from 0 to 3 seconds. From 13 to 15 seconds the object is not moving relative to the starting point. From 15 to 21 seconds the object is accelerating (speeding up) as it moves away from the starting point. You do NOT need to construct or analyze v ...
... starting point, at a velocity slower than the motion from 0 to 3 seconds. From 13 to 15 seconds the object is not moving relative to the starting point. From 15 to 21 seconds the object is accelerating (speeding up) as it moves away from the starting point. You do NOT need to construct or analyze v ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... 3. Explain Newton’s third law. How does this warm-up illustrates the law? Then give a specific example of a force pair shown in the warm-up. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
... 3. Explain Newton’s third law. How does this warm-up illustrates the law? Then give a specific example of a force pair shown in the warm-up. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
Velocity and Acceleration PowerPoint
... magnetism as major kinds of forces acting in nature. • a. Recognize that every object exerts gravitational force on every other object and that the force exerted depends on how much mass the objects have and how far apart they are. ...
... magnetism as major kinds of forces acting in nature. • a. Recognize that every object exerts gravitational force on every other object and that the force exerted depends on how much mass the objects have and how far apart they are. ...
2008 Quarter-Final Exam Solutions
... (a) Consider an axis perpendicular to the initial impulse and coplanar with the table. (Throughout this solution we consider only torques and angular momenta with respect to this axis.) After the initial impulse, the torque about this axis is always zero, so angular momentum is conserved. The initia ...
... (a) Consider an axis perpendicular to the initial impulse and coplanar with the table. (Throughout this solution we consider only torques and angular momenta with respect to this axis.) After the initial impulse, the torque about this axis is always zero, so angular momentum is conserved. The initia ...
Chapter 6 - AstroStop
... Simple Examples of Head-On Collisions (Energy and Momentum are Both Conserved) Collision between two objects of the same mass. One mass is at rest. ...
... Simple Examples of Head-On Collisions (Energy and Momentum are Both Conserved) Collision between two objects of the same mass. One mass is at rest. ...