02_LectureOutline
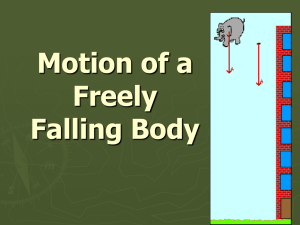
... Galileo’s Concept of Inertia Galileo demolished Aristotle’s assertions in the early 1500s. Galileo’s discovery: • Objects of different weight fall to the ground at the same time in the absence of air resistance. • A moving object needs no force to keep it moving in the absence of friction. ...
... Galileo’s Concept of Inertia Galileo demolished Aristotle’s assertions in the early 1500s. Galileo’s discovery: • Objects of different weight fall to the ground at the same time in the absence of air resistance. • A moving object needs no force to keep it moving in the absence of friction. ...
Torque, Atwood Machines, Angular M.
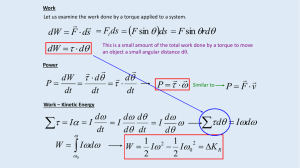
... words, the FORCE and DISPLACEMENT (lever arm) are in the X/Y plane, but the actual displacement of the BOLT is on the "Z“ axis. We therefore have what is called, CROSS PRODUCT. Counterclockwise rotation is considered to be POSITIVE and OUT OF THE PAGE Clockwise rotation is considered to be NEGATIV ...
... words, the FORCE and DISPLACEMENT (lever arm) are in the X/Y plane, but the actual displacement of the BOLT is on the "Z“ axis. We therefore have what is called, CROSS PRODUCT. Counterclockwise rotation is considered to be POSITIVE and OUT OF THE PAGE Clockwise rotation is considered to be NEGATIV ...
L m T L/2 L = 0.8m m = 2kg R T A T L θ L/2 L/2 L/2cosθ T v mgsinθ h
... bob can be resolved into components mgsinθ and mgcosθ. Tension T in the string acts as shown in the fig.. Net force acting on the bob towards pin A = (T - mgcosθ). This force provides the required centripetal force. Hence, (T - mgcosθ) = mv2/(L/2) = 2mv2/L Substituting for mv2 from (2) we get : (T - ...
... bob can be resolved into components mgsinθ and mgcosθ. Tension T in the string acts as shown in the fig.. Net force acting on the bob towards pin A = (T - mgcosθ). This force provides the required centripetal force. Hence, (T - mgcosθ) = mv2/(L/2) = 2mv2/L Substituting for mv2 from (2) we get : (T - ...
d = 0.5 gt 2
... As such, if an object travels for twice the time, it will cover four times (22) the distance; the total distance traveled after two seconds is four times the total distance traveled after one second. If an object travels for three times the time, then it will cover nine times (32) the distance; the ...
... As such, if an object travels for twice the time, it will cover four times (22) the distance; the total distance traveled after two seconds is four times the total distance traveled after one second. If an object travels for three times the time, then it will cover nine times (32) the distance; the ...
Unit 8 Momentum 6 lessons - science-b
... Before the collision, the baseball moves toward the bat. During the collision, the baseball is squashed against the bat. After the collision, however, the baseball moves at a higher velocity away from the bat, and the bat continues in its path, but at a slower velocity. How are the velocities of th ...
... Before the collision, the baseball moves toward the bat. During the collision, the baseball is squashed against the bat. After the collision, however, the baseball moves at a higher velocity away from the bat, and the bat continues in its path, but at a slower velocity. How are the velocities of th ...
Chapter 6
... 1. The greatest deceleration (of magnitude a) is provided by the maximum friction force (Eq. 6-1, with FN = mg in this case). Using Newton’s second law, we find a = fs,max /m = sg. Eq. 2-16 then gives the shortest distance to stop: |x| = v2/2a = 36 m. In this calculation, it is important to first ...
... 1. The greatest deceleration (of magnitude a) is provided by the maximum friction force (Eq. 6-1, with FN = mg in this case). Using Newton’s second law, we find a = fs,max /m = sg. Eq. 2-16 then gives the shortest distance to stop: |x| = v2/2a = 36 m. In this calculation, it is important to first ...
ppt - Physics | SIU
... • We saw that Newton’s second law can be written in terms of the linear momentum. ...
... • We saw that Newton’s second law can be written in terms of the linear momentum. ...
Lecture Notes
... Objects in orbit are said to experience weightlessness. They do have a gravitational force acting on them, though! The satellite and all its contents are in free fall, so there is no normal force. This is what leads to the experience of weightlessness. ...
... Objects in orbit are said to experience weightlessness. They do have a gravitational force acting on them, though! The satellite and all its contents are in free fall, so there is no normal force. This is what leads to the experience of weightlessness. ...
Honors Physics Unit 4 Notes
... • The action-reaction forces are equal and opposite, but either object may still have a net force on it. Consider driving a nail into wood with a hammer. The force that the nail exerts on the hammer is equal and opposite to the force that the hammer exerts on the nail. But there is a net force actin ...
... • The action-reaction forces are equal and opposite, but either object may still have a net force on it. Consider driving a nail into wood with a hammer. The force that the nail exerts on the hammer is equal and opposite to the force that the hammer exerts on the nail. But there is a net force actin ...