Chapter 5 HW – Conservation of Energy… and Springs
... 15. A sling shot, which uses an elastic band to propel and object, has an elastic constant of 40 N/m. If a metal ball with a mass of 200g is pulled back 10 cm, a) how fast will it be moving when it leaves the sling shot? b) If the sling shot is held 1.5 m above the ground, what will its velocity be ...
... 15. A sling shot, which uses an elastic band to propel and object, has an elastic constant of 40 N/m. If a metal ball with a mass of 200g is pulled back 10 cm, a) how fast will it be moving when it leaves the sling shot? b) If the sling shot is held 1.5 m above the ground, what will its velocity be ...
1. In the absence of air friction, an object dropped near the surface of
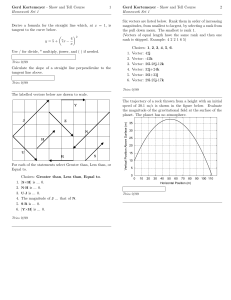
... 15. A conservative force has the potential energy function U(x), shown by the graph above. A particle moving in one dimension under the influence of this force has kinetic energy 1.0 joule when it is at position x 1 Which of the following is a correct statement about the motion of the particle? (A) ...
... 15. A conservative force has the potential energy function U(x), shown by the graph above. A particle moving in one dimension under the influence of this force has kinetic energy 1.0 joule when it is at position x 1 Which of the following is a correct statement about the motion of the particle? (A) ...
same horizontal velocity.
... For 4000 points An object in motion will stay in motion and an object at rest will stay at rest unless acted on by an outside force. ...
... For 4000 points An object in motion will stay in motion and an object at rest will stay at rest unless acted on by an outside force. ...
NEWTON`S LESSON 9
... Note that the vertical forces balance but the horizontal forces do not. The net force is Fnet = 129.9 N, right - 60 N, left = 69.9 N, right The mass is m = (Fgrav / g) = 20 kg So the acceleration is a = (69.9 N) / (20 kg) =3.50 m/s/s. ...
... Note that the vertical forces balance but the horizontal forces do not. The net force is Fnet = 129.9 N, right - 60 N, left = 69.9 N, right The mass is m = (Fgrav / g) = 20 kg So the acceleration is a = (69.9 N) / (20 kg) =3.50 m/s/s. ...
Force
... argument. Questions concerning the workings of the natural world were posed, answers in the form of theory were supplied, and elegant arguments were also proposed to lend support to theory. In the Aristotelian worldview, experimentation was perceived to be “unnatural” and therefore not appropriate f ...
... argument. Questions concerning the workings of the natural world were posed, answers in the form of theory were supplied, and elegant arguments were also proposed to lend support to theory. In the Aristotelian worldview, experimentation was perceived to be “unnatural” and therefore not appropriate f ...
Class26
... •It is essential that these axes are parallel; as you can see from table 10-2, the moments of inertia can be different for different axes. ...
... •It is essential that these axes are parallel; as you can see from table 10-2, the moments of inertia can be different for different axes. ...
Simple Harmonic Motion and Elastic Energy
... In mechanical systems, energy can be stored in springs. For example a compressed spring on a popgun can provide energy to a pellet and shoot it from the gun. Even a simple slingshot uses the elastic energy stored in a rubber band to shoot it projectile. When two balls collide it is as if a spring is ...
... In mechanical systems, energy can be stored in springs. For example a compressed spring on a popgun can provide energy to a pellet and shoot it from the gun. Even a simple slingshot uses the elastic energy stored in a rubber band to shoot it projectile. When two balls collide it is as if a spring is ...