Physics 121 Exam Sheet - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... Chapter 8 - Conservation of Energy If a physical quantity X is conserved for an isolated system, then ...
... Chapter 8 - Conservation of Energy If a physical quantity X is conserved for an isolated system, then ...
4.1 Force
... reduction in the force of friction between the body and the surface. • Galileo considered that, in principle, friction between the surface and the puck might be eliminated altogether. In such a situation no unbalanced force acted on the body, which would then maintain its motion with constant veloci ...
... reduction in the force of friction between the body and the surface. • Galileo considered that, in principle, friction between the surface and the puck might be eliminated altogether. In such a situation no unbalanced force acted on the body, which would then maintain its motion with constant veloci ...
IPC Force Momentum Freefall Newtons Law Test Review
... a. a book on a smooth table being pulled rightward with constant velocity ...
... a. a book on a smooth table being pulled rightward with constant velocity ...
Review for Intro. Physics Part A Final Exam
... bicycle goes from rest to 5km/h which has a a) car greater b) bike acceleration? c) same same d) I don’t know ...
... bicycle goes from rest to 5km/h which has a a) car greater b) bike acceleration? c) same same d) I don’t know ...
R07
... State the assumptions for forces in members of a perfect frame and also explain the method of sections for finding the forces in a cantilever then with help of an example. ...
... State the assumptions for forces in members of a perfect frame and also explain the method of sections for finding the forces in a cantilever then with help of an example. ...
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
... force F1 counteracts the friction force on m1 and prevents m1 from moving right. You may wonder why F1 has no vertical component. This is because the statement of the problem sets N = m1g, and no other vertical forces are present. Thus, the axle of m1 can only provide horizontal forces, and can hold ...
... force F1 counteracts the friction force on m1 and prevents m1 from moving right. You may wonder why F1 has no vertical component. This is because the statement of the problem sets N = m1g, and no other vertical forces are present. Thus, the axle of m1 can only provide horizontal forces, and can hold ...
Blank Jeopardy
... What is the force of the rocket on the gas in one direction and the force of the gas on the rocket in the ...
... What is the force of the rocket on the gas in one direction and the force of the gas on the rocket in the ...
Chp+12+Quest REVISED 2012
... 5. What measurement determines the amount of inertia an object has? 6. According to the first law, why are seat belts needed in cars? 7. Why are car seats placed backwards and how does this make it safer for the baby? 8. What is Newton’s Second law of motion? 9. What is the formula for the second la ...
... 5. What measurement determines the amount of inertia an object has? 6. According to the first law, why are seat belts needed in cars? 7. Why are car seats placed backwards and how does this make it safer for the baby? 8. What is Newton’s Second law of motion? 9. What is the formula for the second la ...
Chapter 6 HW 2
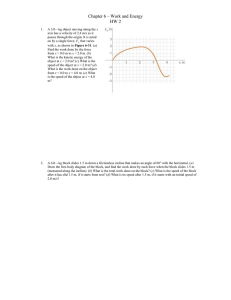
... A 3.0—kg object moving along the x axis has a velocity of 2.4 m/s as it passes through the origin. It is acted on by a single force, Fx, that varies with x, as shown in Figure 6-31. (a) Find the work done by the force from x = 0.0 m to x = 2.0 m. (b) What is the kinetic energy of the object at x = 2 ...
... A 3.0—kg object moving along the x axis has a velocity of 2.4 m/s as it passes through the origin. It is acted on by a single force, Fx, that varies with x, as shown in Figure 6-31. (a) Find the work done by the force from x = 0.0 m to x = 2.0 m. (b) What is the kinetic energy of the object at x = 2 ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.