ICNS 132 : Rotational Motion and Equilibrium
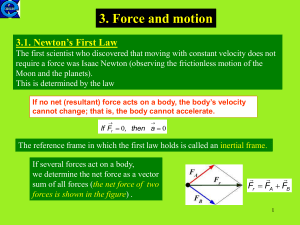
... •Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial reference ...
... •Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial reference ...
02-5-net-force-with
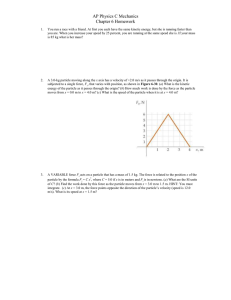
... Model the motion of a BASE jumper who falls from rest, if his total mass (with chute) is 100 kg and his drag constant is 0.31. Graph y vs. t and vy vs. t. What is the BASE jumper’s terminal speed and approximately how long does he fall until he reaches this speed? ...
... Model the motion of a BASE jumper who falls from rest, if his total mass (with chute) is 100 kg and his drag constant is 0.31. Graph y vs. t and vy vs. t. What is the BASE jumper’s terminal speed and approximately how long does he fall until he reaches this speed? ...
Work is a force that moves through a distance
... How much work is done when a force of 1000N is used to slide a 20kg crate a distance of 4.0m across a floor? W= F·D W= 1000N 4.0m W= 4000J How much power is required when a force of 1000N is used to slide a 20kg crate a distance of 4.0m across a floor in 20s? Power is the rate at which work is done. ...
... How much work is done when a force of 1000N is used to slide a 20kg crate a distance of 4.0m across a floor? W= F·D W= 1000N 4.0m W= 4000J How much power is required when a force of 1000N is used to slide a 20kg crate a distance of 4.0m across a floor in 20s? Power is the rate at which work is done. ...
MCA PPT Review - Math On Monday
... Collisions are often classified according to whether the total kinetic energy changes during the collision: 1.Elastic collision—One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision. 2.Inelastic collision—One in which the to ...
... Collisions are often classified according to whether the total kinetic energy changes during the collision: 1.Elastic collision—One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision. 2.Inelastic collision—One in which the to ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... When an object accelerates, the size of that acceleration is directly proportional to the force applied, and inversely proportional to the mass of the body. Further, the acceleration will take place in the same direction as the applied force. Expressed mathematically this is: ...
... When an object accelerates, the size of that acceleration is directly proportional to the force applied, and inversely proportional to the mass of the body. Further, the acceleration will take place in the same direction as the applied force. Expressed mathematically this is: ...
Chapter 4 Motion
... 14. CAUSE AND EFFECT If you walk on a 0 log floating in water, the log moves backward. Which of the following explains this? F. Newton's first law G. Newton's second law H. Newton's third law J. friction ...
... 14. CAUSE AND EFFECT If you walk on a 0 log floating in water, the log moves backward. Which of the following explains this? F. Newton's first law G. Newton's second law H. Newton's third law J. friction ...
BEZOUT IDENTITIES WITH INEQUALITY CONSTRAINTS
... WORK-KINETIC ENERGY THEOREM Consider a net force that is applied to an object having mass m that is moving along the x-axis The work done is ...
... WORK-KINETIC ENERGY THEOREM Consider a net force that is applied to an object having mass m that is moving along the x-axis The work done is ...
Lecture_2 - Department of Mathematics
... WORK-KINETIC ENERGY THEOREM Consider a net force that is applied to an object having mass m that is moving along the x-axis The work done is ...
... WORK-KINETIC ENERGY THEOREM Consider a net force that is applied to an object having mass m that is moving along the x-axis The work done is ...
Print Newton`s Laws problem set #1
... 4) A boat moves through the water with two forces acting on it. One is a 2100N forward push by the motor and the other is an 1800N resistive force due to the water. a. What is the acceleration of the 1200kg boat? b. If it starts from rest, how far will it move in 10 sec? 5) A 75 kg person escapes fr ...
... 4) A boat moves through the water with two forces acting on it. One is a 2100N forward push by the motor and the other is an 1800N resistive force due to the water. a. What is the acceleration of the 1200kg boat? b. If it starts from rest, how far will it move in 10 sec? 5) A 75 kg person escapes fr ...
PHY820 Homework Set 13
... PHY820 Homework Set 13 1. [10 pts] For the system in problem 6-12 in Goldstein, determine the particle positions as a function of time, if, at t = 0, (a) the displacements and the velocity of the second particle are zero while the first particle moves at a velocity v, (b) the velocities and the disp ...
... PHY820 Homework Set 13 1. [10 pts] For the system in problem 6-12 in Goldstein, determine the particle positions as a function of time, if, at t = 0, (a) the displacements and the velocity of the second particle are zero while the first particle moves at a velocity v, (b) the velocities and the disp ...
Laws of Motion
... gravity in a law now known as the law of universal gravitation. Mathematically, the law of universal gravitation is stated as: F = G (m1m2 ÷ d2) ...
... gravity in a law now known as the law of universal gravitation. Mathematically, the law of universal gravitation is stated as: F = G (m1m2 ÷ d2) ...
11.2 Questions Force and Mass Determine Acceleration 1. What 3
... 8. A mass is 2kg. What other information do you need to calculate acceleration? 2. Look at the picture on page 354. What do the arrows in the diagrams show? 9. If an object moves at a constant speed, but it accelerates, what changes? 3. What happens to the acceleration of an object when the force on ...
... 8. A mass is 2kg. What other information do you need to calculate acceleration? 2. Look at the picture on page 354. What do the arrows in the diagrams show? 9. If an object moves at a constant speed, but it accelerates, what changes? 3. What happens to the acceleration of an object when the force on ...
105old Exam2 solutio..
... passes over a hill of radius 15 m, as shown. At the top of the hill, the car has a speed of 8.0 m/s. What is the force of the track on the car at the top of the hill? ...
... passes over a hill of radius 15 m, as shown. At the top of the hill, the car has a speed of 8.0 m/s. What is the force of the track on the car at the top of the hill? ...
Momentum and Energy
... where v1 and v2 are the velocities of the objects before the collision and v3 and v4 new velocities after the collision. Notice the masses haven’t changed. ...
... where v1 and v2 are the velocities of the objects before the collision and v3 and v4 new velocities after the collision. Notice the masses haven’t changed. ...
Practice - People Server at UNCW
... b) The average and instantaneous speeds of an object are equal when the object a. has uniform velocity. b. has uniform acceleration. c. moves in a straight line. d. covers twice as much distance in each second. e. none of the above. _____ c) When an object is thrown vertically upward from ground lev ...
... b) The average and instantaneous speeds of an object are equal when the object a. has uniform velocity. b. has uniform acceleration. c. moves in a straight line. d. covers twice as much distance in each second. e. none of the above. _____ c) When an object is thrown vertically upward from ground lev ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.