Study Notes
... These are only some of the problems for the simplest possible problem (only 1 slow moving particle). Real problems may involve large numbers of particles whose interactions depend on the location of the particles (solving multiple couple differential equations), a finite object whose mass might chan ...
... These are only some of the problems for the simplest possible problem (only 1 slow moving particle). Real problems may involve large numbers of particles whose interactions depend on the location of the particles (solving multiple couple differential equations), a finite object whose mass might chan ...
Motion Unit Class Notes
... Force – a transfer of energy; a push or pull that starts, stops or changes the direction of an object Friction – force that happens when the surfaces of matter move past each other (Static, sliding, rolling, fluid) - depends on the surfaces and the force pushing them together Gravity – force that pu ...
... Force – a transfer of energy; a push or pull that starts, stops or changes the direction of an object Friction – force that happens when the surfaces of matter move past each other (Static, sliding, rolling, fluid) - depends on the surfaces and the force pushing them together Gravity – force that pu ...
Study Guide For Unit 6 Test
... 6. The same 30 kg object is being held by a string. It is being accelerated upwards at a rate of 4 m/s2. What is the Tension (force) in the string? Draw the FBD. Sum the forces. ...
... 6. The same 30 kg object is being held by a string. It is being accelerated upwards at a rate of 4 m/s2. What is the Tension (force) in the string? Draw the FBD. Sum the forces. ...
Exam 1 review solutions
... 9) You and your friend finally get the same speedometers. You both have another race. At the instant the traffic light turns green, you start ahead with a 3.20 m/s^2 acceleration. Your friend, underestimating the track distance, leaves with a constant 20 m/s. How far past the starting point do you o ...
... 9) You and your friend finally get the same speedometers. You both have another race. At the instant the traffic light turns green, you start ahead with a 3.20 m/s^2 acceleration. Your friend, underestimating the track distance, leaves with a constant 20 m/s. How far past the starting point do you o ...
Newtons Laws - Cardinal Newman High School
... If a car and a train are driving along the same path at the exact same speed, which will be harder to stop? Why? Train it has more momentum ...
... If a car and a train are driving along the same path at the exact same speed, which will be harder to stop? Why? Train it has more momentum ...
Free Body Diagram
... 60 N is applied to the block on the right at an angle of 30 degrees to the horizontal. What is the acceleration of the blocks? ...
... 60 N is applied to the block on the right at an angle of 30 degrees to the horizontal. What is the acceleration of the blocks? ...
INTRODUCTION TO FORCES WORKSHEET
... 4. A college student rests a backpack on his shoulder. The pack is suspended motionless by one strap from one shoulder. ...
... 4. A college student rests a backpack on his shoulder. The pack is suspended motionless by one strap from one shoulder. ...
Circular Motion A rotation of an object about some axis, whether
... Angular acceleration is also called radial accelration. This acceleration is always directed towards the center of the circular path. Objects moving in circular paths experience acceleration toward the center even if they are going with constant velocity sice the direction is constantly changing. ...
... Angular acceleration is also called radial accelration. This acceleration is always directed towards the center of the circular path. Objects moving in circular paths experience acceleration toward the center even if they are going with constant velocity sice the direction is constantly changing. ...
DYNAMICS
... motion of everything. • He very well may have been one of the most influential human beings to ever live. • And you thought he was just some dumb guy who got hit on the head with an apple. ...
... motion of everything. • He very well may have been one of the most influential human beings to ever live. • And you thought he was just some dumb guy who got hit on the head with an apple. ...
Morgan Rezer
... 14. John pulls a box with a force of 4 N, and Jason pulls the box from the opposite side with a force of 3 N. Ignore friction. In which direction, and with how much force would the box move? ...
... 14. John pulls a box with a force of 4 N, and Jason pulls the box from the opposite side with a force of 3 N. Ignore friction. In which direction, and with how much force would the box move? ...
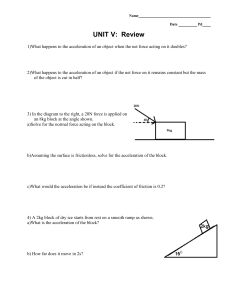
Unit 5 Review
... 2)What happens to the acceleration of an object if the net force on it remains constant but the mass of the object is cut in half? ...
... 2)What happens to the acceleration of an object if the net force on it remains constant but the mass of the object is cut in half? ...
Forces Test Review - Ms. Rousseau`s Classroom
... analyse, in qualitative and quantitative terms, the relationships between the force of gravity, normal force, applied force, force of friction, coefficient of static friction, and coefficient of kinetic friction, and solve related two-dimensional problems using free-body diagrams, vector component ...
... analyse, in qualitative and quantitative terms, the relationships between the force of gravity, normal force, applied force, force of friction, coefficient of static friction, and coefficient of kinetic friction, and solve related two-dimensional problems using free-body diagrams, vector component ...
Forces and Motion Learning Outcomes
... 2. Velocity tells us the speed of a moving object and its direction 3. Acceleration is an object’s change in velocity divided by the time it Takes for that change to occur. Forces 4. Gravity is the force that pulls everything around you towards the center of the Earth 5. Friction is a force that act ...
... 2. Velocity tells us the speed of a moving object and its direction 3. Acceleration is an object’s change in velocity divided by the time it Takes for that change to occur. Forces 4. Gravity is the force that pulls everything around you towards the center of the Earth 5. Friction is a force that act ...
1 Newton`s Laws
... A student of mass 55kg is standing on the surface of the earth. a)What is the force that the earth pulls the student with? b)What is the force with which the student pulls the earth? c)What is the acceleration of the earth because of the pull of the student? ...
... A student of mass 55kg is standing on the surface of the earth. a)What is the force that the earth pulls the student with? b)What is the force with which the student pulls the earth? c)What is the acceleration of the earth because of the pull of the student? ...
Some Introductory Concepts for Energy
... • How can there ever be an unbalanced force on an object if every action has an equal and opposite reaction? ...
... • How can there ever be an unbalanced force on an object if every action has an equal and opposite reaction? ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.