lecture2.pdf
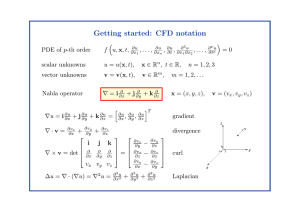
... It is important to understand the meaning and significance of each equation in order to develop a good numerical method and properly interpret the results ...
... It is important to understand the meaning and significance of each equation in order to develop a good numerical method and properly interpret the results ...
What is force? - cashmerephysics
... with a force of 1500 N. The friction between the truck and the road is 600N. a) Sketch a vector diagram to show the net force. b) Calculate the car’s acceleration. c) Once the car starts moving, what would happen if the two truck pulls with a smaller force of only 600N? ...
... with a force of 1500 N. The friction between the truck and the road is 600N. a) Sketch a vector diagram to show the net force. b) Calculate the car’s acceleration. c) Once the car starts moving, what would happen if the two truck pulls with a smaller force of only 600N? ...
Lec4
... The displacements, velocities, and accelerations have positive values in the direction of the coordinate axes. 1b. Write the equation describing the constraint: When particles are connected with a cable, its length which remains constant is ...
... The displacements, velocities, and accelerations have positive values in the direction of the coordinate axes. 1b. Write the equation describing the constraint: When particles are connected with a cable, its length which remains constant is ...
Net force = 0 Net force = 0 - University of Iowa Physics
... • This is Newton’s second law • It is the law which explains how things move • If a net force is applied to an object it will accelerate – change its velocity • It includes the law of inertia Æ if there is no force, F = 0, then the acceleration = 0 Æ the velocity doesn’t change Æ no force is needed ...
... • This is Newton’s second law • It is the law which explains how things move • If a net force is applied to an object it will accelerate – change its velocity • It includes the law of inertia Æ if there is no force, F = 0, then the acceleration = 0 Æ the velocity doesn’t change Æ no force is needed ...
Motion & Forces
... be the difference between the two forces because they are in opposite directions. They are considered to be unbalanced forces. ...
... be the difference between the two forces because they are in opposite directions. They are considered to be unbalanced forces. ...
The branch of mechanics dealing withy the cause of motion is called
... surface). An object at rest on the ground feels the force of gravity W down and a normal force N up. The normal force comes from the ground pushing up on the object and is really the sum of electrical forces between atoms of the ground. We can draw a diagram of this situation. If we clearly show the ...
... surface). An object at rest on the ground feels the force of gravity W down and a normal force N up. The normal force comes from the ground pushing up on the object and is really the sum of electrical forces between atoms of the ground. We can draw a diagram of this situation. If we clearly show the ...
net force
... • Force can also be described by intuitive concepts such as a push or pull that can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (which includes to begin moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform. A force has both magnitude and direction, ...
... • Force can also be described by intuitive concepts such as a push or pull that can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (which includes to begin moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform. A force has both magnitude and direction, ...
forces
... determine distance, velocity, speed, or acceleration from a reference point. 2. Describe how the various balanced and unbalanced forces can have an effect on an object’s motion. 3. Apply Newton’s Laws to real world examples. 4. Analyze the methods by which machines make ...
... determine distance, velocity, speed, or acceleration from a reference point. 2. Describe how the various balanced and unbalanced forces can have an effect on an object’s motion. 3. Apply Newton’s Laws to real world examples. 4. Analyze the methods by which machines make ...
UNIT 2 REVIEW SHEET Answers sp 10
... acceleration due to gravity is 25 m/s2, that same object would weigh what on Earth and on Jupiter? On Jupiter it would have a mass of ? Weight on Earth Fw = mg 120(10) = Weight on Jupiter Fw = mg 120 (25)= The object would have the same mass on Jupiter as it does on Earth. Mass doesn’t change. 2. Wh ...
... acceleration due to gravity is 25 m/s2, that same object would weigh what on Earth and on Jupiter? On Jupiter it would have a mass of ? Weight on Earth Fw = mg 120(10) = Weight on Jupiter Fw = mg 120 (25)= The object would have the same mass on Jupiter as it does on Earth. Mass doesn’t change. 2. Wh ...
Forces
... wants to establish that things “don’t move by themselves”. If isolated and object experience no force and it follows the first law. Of course Newton also needed to recognize that being at rest fr ...
... wants to establish that things “don’t move by themselves”. If isolated and object experience no force and it follows the first law. Of course Newton also needed to recognize that being at rest fr ...
Friction, Work, and Energy in the Inclined Plane
... is non-conservative (or dissipative) if the work it does on an object moving between two points depends on the path of the motion between the points. Useful work is always lost to the kinetic frictional force because it dissipates into heat, which is un-recoverable in our system to do useful work. T ...
... is non-conservative (or dissipative) if the work it does on an object moving between two points depends on the path of the motion between the points. Useful work is always lost to the kinetic frictional force because it dissipates into heat, which is un-recoverable in our system to do useful work. T ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.