AP C UNIT 4 - student handout
... Total acceleration, Direction for ω and α RHR: direction is along axis of rotation - curl fingers along direction of spin and direction of thumb is direction of ω and α. Explanation is in your book as to why…it stems from mathematical definition of vector in rotation. If object is speeding up, α is ...
... Total acceleration, Direction for ω and α RHR: direction is along axis of rotation - curl fingers along direction of spin and direction of thumb is direction of ω and α. Explanation is in your book as to why…it stems from mathematical definition of vector in rotation. If object is speeding up, α is ...
True or False - Hauserphysics
... 15. Which of the following is not true about the car in # 14 a. The magnitude of the displacement is 70 mi b. The displacements direction is to the northeast c. The magnitude of the displacement is something less that 70 mi 16. Suppose a car is moving in a straight line and its speed is increasing ...
... 15. Which of the following is not true about the car in # 14 a. The magnitude of the displacement is 70 mi b. The displacements direction is to the northeast c. The magnitude of the displacement is something less that 70 mi 16. Suppose a car is moving in a straight line and its speed is increasing ...
physics_11_review_be.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
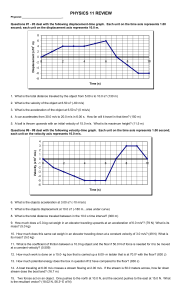
... 21. An object is thrown directly upwards with an initial velocity of 25 m/s. (A) What is the maximum height the object will travel? (32 m) (B) How long will it take to return to its starting point? (5.15 s) (C) What will its velocity be when it is 2.0 meters above its starting point as it travels do ...
... 21. An object is thrown directly upwards with an initial velocity of 25 m/s. (A) What is the maximum height the object will travel? (32 m) (B) How long will it take to return to its starting point? (5.15 s) (C) What will its velocity be when it is 2.0 meters above its starting point as it travels do ...
Force
... • Newton’s Second Law of motion – This law is also called the law of acceleration. • The 2nd law was actually developed first by Newton, but since it is slightly more complicated, it is discussed second. • The second law states that “When an object has a net force, Fnet, acting upon it, it will expe ...
... • Newton’s Second Law of motion – This law is also called the law of acceleration. • The 2nd law was actually developed first by Newton, but since it is slightly more complicated, it is discussed second. • The second law states that “When an object has a net force, Fnet, acting upon it, it will expe ...
Ch 9 HW Day 1
... Picture the Problem We’ll solve this problem for the general case in which the mass of the block on the ledge is M, the mass of the hanging block is m, the mass of the pulley is Mp, and R is the radius of the pulley. Let the zero of gravitational potential energy be 2.5 m below the initial position ...
... Picture the Problem We’ll solve this problem for the general case in which the mass of the block on the ledge is M, the mass of the hanging block is m, the mass of the pulley is Mp, and R is the radius of the pulley. Let the zero of gravitational potential energy be 2.5 m below the initial position ...
Motion
... closely related to Newton’s 2nd law • Includes effects of both motion (velocity) and inertia (mass) ...
... closely related to Newton’s 2nd law • Includes effects of both motion (velocity) and inertia (mass) ...
Energy Mom Plan (red)
... taken into consideration when collisions take place. Its’ units are Ns. Because the force during such collisions is rarely constant, the average force is used. Or...if you are given a plot of force vs. time, impulse is the area under the curve in that time interval (integral). ...
... taken into consideration when collisions take place. Its’ units are Ns. Because the force during such collisions is rarely constant, the average force is used. Or...if you are given a plot of force vs. time, impulse is the area under the curve in that time interval (integral). ...
Power is the rate at which work is done or is the amount energy
... Conservation of momentum The principle of conservation of momentum If no external force acts on a system, the total momentum of the system remains constant, i.e. momentum before the collision is equal to the momentum after the collision. We will only be concerned with cases where momenta are along o ...
... Conservation of momentum The principle of conservation of momentum If no external force acts on a system, the total momentum of the system remains constant, i.e. momentum before the collision is equal to the momentum after the collision. We will only be concerned with cases where momenta are along o ...
Newton`s Three Laws
... Newton’s First Law of Motion • An object at rest remains at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. • An object in motion continues in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • This law is often called “the law of inertia". ...
... Newton’s First Law of Motion • An object at rest remains at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. • An object in motion continues in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • This law is often called “the law of inertia". ...
Chap7Class2
... (a) Determine the work a hiker must do on a 15.0-kg backpack to carry it up a hill of height h = 10.0 m, as shown. Determine also (b) the work done by gravity on the backpack, and (c) the net work done on the backpack. For simplicity, assume the motion is smooth and at constant velocity (i.e., accel ...
... (a) Determine the work a hiker must do on a 15.0-kg backpack to carry it up a hill of height h = 10.0 m, as shown. Determine also (b) the work done by gravity on the backpack, and (c) the net work done on the backpack. For simplicity, assume the motion is smooth and at constant velocity (i.e., accel ...
Ch4-Force newton
... a force of 10 N, what is the force applied to the book by the Earth? What force is exerted on the scale? C) You now lift the book with a force of 20 N, what is the force exerted on the ...
... a force of 10 N, what is the force applied to the book by the Earth? What force is exerted on the scale? C) You now lift the book with a force of 20 N, what is the force exerted on the ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 7
... cannon ball is exactly equal in magnitude and opposite in direction 2. Must consider Newton’s Second law ...
... cannon ball is exactly equal in magnitude and opposite in direction 2. Must consider Newton’s Second law ...
Chapter 7 Force ppt
... • Like velocity and acceleration, a force is described by its strength and by the direction in which it acts. • Arrows are used to show the direction of the force. The length of the arrow shows the strength of the force. ...
... • Like velocity and acceleration, a force is described by its strength and by the direction in which it acts. • Arrows are used to show the direction of the force. The length of the arrow shows the strength of the force. ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.