Unit 1
... associated with heat • It is the energy of the random motion of individual atoms within an object. • What you perceive as heat on a stovetop is the energy of the individual atoms in the heating element striking ...
... associated with heat • It is the energy of the random motion of individual atoms within an object. • What you perceive as heat on a stovetop is the energy of the individual atoms in the heating element striking ...
How many laws did Newton create?
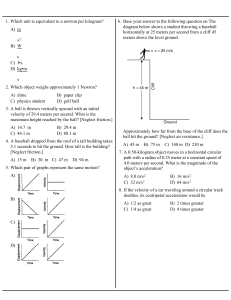
... 6. In the absence of air resistance, describe the acceleration of a 1.5 kg book compared to the acceleration of a 15 kg rock if the objects were dropped from the same height? 7. What happens to the gravitation force on an object as it gets closer to another object? 8. There are 2 rocks. Rock A has ...
... 6. In the absence of air resistance, describe the acceleration of a 1.5 kg book compared to the acceleration of a 15 kg rock if the objects were dropped from the same height? 7. What happens to the gravitation force on an object as it gets closer to another object? 8. There are 2 rocks. Rock A has ...
2nd or 3rd law inquiry lab makeup work
... the direction of the force, and the size of the arrow represents the strength of the force. Look at the skateboarders in the Figure below. In the top row, the arrows represent the forces with which the skateboarders push against each other. This is the action. In the bottom row, the arrows represent ...
... the direction of the force, and the size of the arrow represents the strength of the force. Look at the skateboarders in the Figure below. In the top row, the arrows represent the forces with which the skateboarders push against each other. This is the action. In the bottom row, the arrows represent ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion - U
... Things don’t keep moving forever because there’s almost always an unbalanced force acting upon it. A book sliding across a table slows down and stops because of the force of friction. ...
... Things don’t keep moving forever because there’s almost always an unbalanced force acting upon it. A book sliding across a table slows down and stops because of the force of friction. ...
PhysCh7.78
... • Acceleration directed toward the center of a circular path • Although an object is moving at a constant speed, it can still have an acceleration. • Velocity is a vector, which has both magnitude and DIRECTION. • In circular motion, velocity is constantly ...
... • Acceleration directed toward the center of a circular path • Although an object is moving at a constant speed, it can still have an acceleration. • Velocity is a vector, which has both magnitude and DIRECTION. • In circular motion, velocity is constantly ...
Lunar Base Supply Egg Drop - NSTA Learning Center
... Discussion Questions What do we call the path that the tray moves in? If the strings are held at a shorter distance to the tray, shortening the tray’s orbit, what happens to the speed of the tray? ...
... Discussion Questions What do we call the path that the tray moves in? If the strings are held at a shorter distance to the tray, shortening the tray’s orbit, what happens to the speed of the tray? ...
Physics 11 Final Exam Outline
... -Apply Newton's laws of motion to explain inertia and the relationships among force, mass, and acceleration -Analyze natural and technological systems to interpret and explain their structure and dynamics state Newton’s 1st law of motion illustrate Newton’s 1st law with examples define inertia diffe ...
... -Apply Newton's laws of motion to explain inertia and the relationships among force, mass, and acceleration -Analyze natural and technological systems to interpret and explain their structure and dynamics state Newton’s 1st law of motion illustrate Newton’s 1st law with examples define inertia diffe ...
Lecture 3 - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... Example: Free Fall. (“Free fall” means the only force is gravity; the motion can be in any direction). All objects in free fall move with constant downward acceleration: ...
... Example: Free Fall. (“Free fall” means the only force is gravity; the motion can be in any direction). All objects in free fall move with constant downward acceleration: ...
HP UNIT 5 work & energy - student handout
... property that the work done in moving a particle between two points is independent of the path taken…only matters on initial and final positions. ie; Gravity & spring force. A non-conservative force is a force with the property that the work done in moving a particle between two points DOES depend o ...
... property that the work done in moving a particle between two points is independent of the path taken…only matters on initial and final positions. ie; Gravity & spring force. A non-conservative force is a force with the property that the work done in moving a particle between two points DOES depend o ...
File
... State the 2 definitions, one in terms of force and the other in terms of acceleration. State the 2 key components. State the formula produced by each of the definitions. State the units of force, providing the special name given to this unit. Explain direct and indirect proportion as it relates to N ...
... State the 2 definitions, one in terms of force and the other in terms of acceleration. State the 2 key components. State the formula produced by each of the definitions. State the units of force, providing the special name given to this unit. Explain direct and indirect proportion as it relates to N ...
StudyGuideForcesAP2016
... Force is the same; acceleration depends on the mass; more mass is less acceleration according to Newton’s 2nd Law (F=ma) Coefficient of static friction: Increase incline until the box just starts to slip. Solve for the force of gravity parallel to the incline at that angle. This is equal to static f ...
... Force is the same; acceleration depends on the mass; more mass is less acceleration according to Newton’s 2nd Law (F=ma) Coefficient of static friction: Increase incline until the box just starts to slip. Solve for the force of gravity parallel to the incline at that angle. This is equal to static f ...
F r i c t i o n - Southgate Community School District
... • Ex. You accelerated at 4 m/s2 eastbound this morning on Eureka Rd • Can be positive or negative, accels = positive, decels = negative • Uniform Acceleration=constant acceleration Ex. g=9.8 m/s2 ...
... • Ex. You accelerated at 4 m/s2 eastbound this morning on Eureka Rd • Can be positive or negative, accels = positive, decels = negative • Uniform Acceleration=constant acceleration Ex. g=9.8 m/s2 ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.



![[force and motion]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006065207_1-8bff05158caa0c6fdea67b84566f5781-300x300.png)