PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... If you grab onto a pole while running, your body will rotate about the pole, gaining angular momentum. We’ve used the linear momentum to solve physical problems with linear motions, the angular momentum will do the same for rotational motions. Let’s consider a point-like object ( particle) with mass ...
... If you grab onto a pole while running, your body will rotate about the pole, gaining angular momentum. We’ve used the linear momentum to solve physical problems with linear motions, the angular momentum will do the same for rotational motions. Let’s consider a point-like object ( particle) with mass ...
Impulse and Momentum
... Momentum: mv, or the product of the object’s mass and the objects velocity Impulse-momentum Theorem: FΔt= pf –pi ; The impulse on an object is equal to the object’s final momentum mines the object’s initial momentum (p= momentum) ...
... Momentum: mv, or the product of the object’s mass and the objects velocity Impulse-momentum Theorem: FΔt= pf –pi ; The impulse on an object is equal to the object’s final momentum mines the object’s initial momentum (p= momentum) ...
Monday, April 27, 2009
... If you grab onto a pole while running, your body will rotate about the pole, gaining angular momentum. We’ve used the linear momentum to solve physical problems with linear motions, the angular momentum will do the same for rotational motions. Let’s consider a point-like object ( particle) with mass ...
... If you grab onto a pole while running, your body will rotate about the pole, gaining angular momentum. We’ve used the linear momentum to solve physical problems with linear motions, the angular momentum will do the same for rotational motions. Let’s consider a point-like object ( particle) with mass ...
Normal Reaction force
... Question 4 Solution Emma is correct and Frank is incorrect. The book is at rest, so, the resultant force on the book is zero. As a result N and mg are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. N and mg both act on the book and therefore cannot be action and reaction in the sense of Newton's 3 rd ...
... Question 4 Solution Emma is correct and Frank is incorrect. The book is at rest, so, the resultant force on the book is zero. As a result N and mg are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. N and mg both act on the book and therefore cannot be action and reaction in the sense of Newton's 3 rd ...
2.1.1
... Determine his weight on the Moon where the acceleration due to gravity is 1.62 meters per ...
... Determine his weight on the Moon where the acceleration due to gravity is 1.62 meters per ...
Monday, February 25, 2008
... once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of net external force, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in moti ...
... once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of net external force, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in moti ...
FRICTION
... FRICTION - the force that present whenever two surfaces are in contact and always acts opposite to the direction of motion. Depends on: • Type of materials in contact • Surfaces of materials ...
... FRICTION - the force that present whenever two surfaces are in contact and always acts opposite to the direction of motion. Depends on: • Type of materials in contact • Surfaces of materials ...
Packet I - North Allegheny School District
... B) velocity change of the object C) impulse acting on it D) objects mass times the force acting on it E) force acting on it times its velocity. 47) Momentum is conserved in all collisions where no external forces are acting, except A) when heat is generated. B) in elastic collisions. C) in inelastic ...
... B) velocity change of the object C) impulse acting on it D) objects mass times the force acting on it E) force acting on it times its velocity. 47) Momentum is conserved in all collisions where no external forces are acting, except A) when heat is generated. B) in elastic collisions. C) in inelastic ...
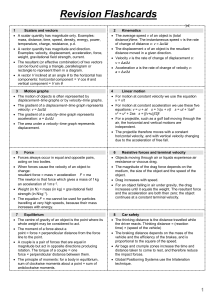
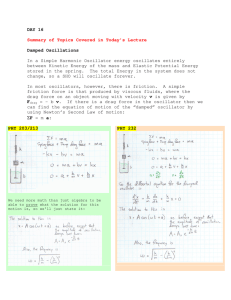
AS Revision Flash Cards File
... Series and parallel circuits Kirchhoff’s first law: at any circuit junction, total current in = total current out. This is a consequence of the conservation of charge. It follows that the current is constant round any series circuit. Kirchhoff’s second law: round any circuit loop, the sum of the ...
... Series and parallel circuits Kirchhoff’s first law: at any circuit junction, total current in = total current out. This is a consequence of the conservation of charge. It follows that the current is constant round any series circuit. Kirchhoff’s second law: round any circuit loop, the sum of the ...
Laws of Motion Test Name_________________________________
... because its mass and acceleration is so large. d. Both b and c. 22. Pick the best example of Newton’s First Law in action. a. A rocket taking off from earth which pushes gasses in one direction and the rocket in the other. b. A rocket sitting on the ground preparing for takeoff but it needs an outsi ...
... because its mass and acceleration is so large. d. Both b and c. 22. Pick the best example of Newton’s First Law in action. a. A rocket taking off from earth which pushes gasses in one direction and the rocket in the other. b. A rocket sitting on the ground preparing for takeoff but it needs an outsi ...
Student Review Sheet Physics Semester A Examination
... describe the forces that act on a conical pendulum. identify appropriate units for quantities. describe the effect of a force on an object in space. describe the relationship between mass and velocity in elastic collisions. identify factors that limit the acceleration of an object in free fall. use ...
... describe the forces that act on a conical pendulum. identify appropriate units for quantities. describe the effect of a force on an object in space. describe the relationship between mass and velocity in elastic collisions. identify factors that limit the acceleration of an object in free fall. use ...
Energy And SHM
... the max velocity d) the velocity when .050 m from equilibrium e) the max acceleration f) the total energy ...
... the max velocity d) the velocity when .050 m from equilibrium e) the max acceleration f) the total energy ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.