Forces Test I
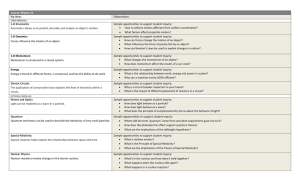
... 16. A sheet of paper can be withdrawn from under a container of milk without falling over if the paper is jerked quickly. The reason this can be done is that ___. a) the milk carton has no acceleration. c) the gravitational field pulls on the milk carton. b) there is an action-reaction pair operatin ...
... 16. A sheet of paper can be withdrawn from under a container of milk without falling over if the paper is jerked quickly. The reason this can be done is that ___. a) the milk carton has no acceleration. c) the gravitational field pulls on the milk carton. b) there is an action-reaction pair operatin ...
Course: Physics 11 Big Ideas Elaborations: CORE MODULES: 1
... Second: free body diagrams (FBD); the net force from two or more forces Third: demonstrate that actions happen at the same time and in pairs the relationship between variables: Refer to the formula sheet Aboriginal knowledge: the application of Newton’s laws in various Aboriginal technologies 1- ...
... Second: free body diagrams (FBD); the net force from two or more forces Third: demonstrate that actions happen at the same time and in pairs the relationship between variables: Refer to the formula sheet Aboriginal knowledge: the application of Newton’s laws in various Aboriginal technologies 1- ...
and y - Cloudfront.net
... 2. Calculate the x and y components of a displacement, velocity, and force vector. 3. Write a velocity vector in polar and x-y coordinates. 4. Calculate the range of a projectile given the initial velocity vector. 5. Use force vectors to solve two-dimensional equilibrium problems with up to three fo ...
... 2. Calculate the x and y components of a displacement, velocity, and force vector. 3. Write a velocity vector in polar and x-y coordinates. 4. Calculate the range of a projectile given the initial velocity vector. 5. Use force vectors to solve two-dimensional equilibrium problems with up to three fo ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter 2.6
... means that the direction of the total momentum also will change, which cannot be true since the direction is constant. The only way out is to have the stars move at diametrically opposite positions, so that the momenta are equal and opposite. This means that the constant value of the total momentum ...
... means that the direction of the total momentum also will change, which cannot be true since the direction is constant. The only way out is to have the stars move at diametrically opposite positions, so that the momenta are equal and opposite. This means that the constant value of the total momentum ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... you hit each of these balls with a full swing of a baseball bat, which ball will change its motion by the greater amount? 3. In the absence of friction and other forces, if you exert a force, F, on a mass, m, the mass will accelerate. If you exert the same force on a mass of 2m, would you expect the ...
... you hit each of these balls with a full swing of a baseball bat, which ball will change its motion by the greater amount? 3. In the absence of friction and other forces, if you exert a force, F, on a mass, m, the mass will accelerate. If you exert the same force on a mass of 2m, would you expect the ...
Document
... 4-7 Solving Problems with Newton’s Laws: FreeBody Diagrams Example 4-13: Elevator and counterweight (Atwood’s machine). A system of two objects suspended over a pulley by a flexible cable is sometimes referred to as an Atwood’s machine. Here, let the mass of the counterweight be 1000 kg. Assume the ...
... 4-7 Solving Problems with Newton’s Laws: FreeBody Diagrams Example 4-13: Elevator and counterweight (Atwood’s machine). A system of two objects suspended over a pulley by a flexible cable is sometimes referred to as an Atwood’s machine. Here, let the mass of the counterweight be 1000 kg. Assume the ...
Lecture Notes for Sections 14.1
... energy! In the SI system, the unit for energy is called a joule (J), where 1 J = 1 N·m. In the FPS system, units are ft·lb. The principle of work and energy cannot be used, in general, to determine forces directed normal to the path, since these forces do no work. The principle of work and energy ca ...
... energy! In the SI system, the unit for energy is called a joule (J), where 1 J = 1 N·m. In the FPS system, units are ft·lb. The principle of work and energy cannot be used, in general, to determine forces directed normal to the path, since these forces do no work. The principle of work and energy ca ...
Two-Dimensional Motion
... object in motion stays in motion, in a straight line, at a constant speed unless acted on by an outside force. 2nd Law…an outside force causes an object to accelerate…a= F/m THEREFORE, circular motion is caused by a force that causes an object to travel contrary to its inertial path ...
... object in motion stays in motion, in a straight line, at a constant speed unless acted on by an outside force. 2nd Law…an outside force causes an object to accelerate…a= F/m THEREFORE, circular motion is caused by a force that causes an object to travel contrary to its inertial path ...
3rd Law: Force every action force there is an equal and opposite
... a larger force must be exerted on an object with greater mass in order for it to have the same acceleration as an object with less mass. What is a force? A force is a push or pull that can change the motion of an object 3. How does the force acting on an object affect its tendency to remain at rest? ...
... a larger force must be exerted on an object with greater mass in order for it to have the same acceleration as an object with less mass. What is a force? A force is a push or pull that can change the motion of an object 3. How does the force acting on an object affect its tendency to remain at rest? ...
1.35 Gravitation AP C
... times, that is, the rate dA/dt at which it sweeps out area A is constant.” THE LAW OF PERIODS - "The square of the period of any planet is proportional to the cube of the semi major axis of its orbit." ...
... times, that is, the rate dA/dt at which it sweeps out area A is constant.” THE LAW OF PERIODS - "The square of the period of any planet is proportional to the cube of the semi major axis of its orbit." ...
Work and Power - Broadneck High School
... A rope is used to pull a metal box 15.0 m across the floor. The rope is held at an angle of 30.0o with the floor using a force of 628 N. • How much work does the force on the rope do? W = F d (cos θ) W = (628 N) (15.0 m) (cos 30o) W = 8157.96 J ~ 8160 J ...
... A rope is used to pull a metal box 15.0 m across the floor. The rope is held at an angle of 30.0o with the floor using a force of 628 N. • How much work does the force on the rope do? W = F d (cos θ) W = (628 N) (15.0 m) (cos 30o) W = 8157.96 J ~ 8160 J ...
Dynamic forces - Physics Champion
... accelerating the applied force making it accelerate has to overcome the inertia. This is the force which resists the acceleration (or deceleration) and is equal and opposite to the applied force. This means that the total force acting on the body is zero ...
... accelerating the applied force making it accelerate has to overcome the inertia. This is the force which resists the acceleration (or deceleration) and is equal and opposite to the applied force. This means that the total force acting on the body is zero ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.