IB Physics 11 Assess.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... A brother and sister take the same time to run up a set of steps. The sister has a greater mass than her brother. Which of the following is correct? Has done the most work ...
... A brother and sister take the same time to run up a set of steps. The sister has a greater mass than her brother. Which of the following is correct? Has done the most work ...
dynamics
... Net Force (or Resultant Force): is the vector sum of all forces acting on that object. Fnet=F1+F2+F3+… (vector sum) ...
... Net Force (or Resultant Force): is the vector sum of all forces acting on that object. Fnet=F1+F2+F3+… (vector sum) ...
Study Notes Lesson 10 Newton`s Third Law of Motion
... a. View the system in 3 different ways. The cart system, the horse system, and the horse-cart system. b. The cart system is only concerned with accelerating. The net force of the cart divided by the mass of the cart is the cart’s acceleration. c. In the horse system, the opposite reaction force by t ...
... a. View the system in 3 different ways. The cart system, the horse system, and the horse-cart system. b. The cart system is only concerned with accelerating. The net force of the cart divided by the mass of the cart is the cart’s acceleration. c. In the horse system, the opposite reaction force by t ...
Linear Momentum
... moving at 45 mph than to stop a car moving at 45 mph, even though they both have the same speed. • Both mass and velocity are important factors when considering the force needed to change the motion of an object. ...
... moving at 45 mph than to stop a car moving at 45 mph, even though they both have the same speed. • Both mass and velocity are important factors when considering the force needed to change the motion of an object. ...
PS03H - willisworldbio
... falling object in free fall is about _____. • This acceleration is given the symbol _ and is sometimes called the acceleration of gravity. • By Newton’s second law of motion, the force of Earth’s gravity on a falling object is the object’s ____ times the _______ of gravity. ...
... falling object in free fall is about _____. • This acceleration is given the symbol _ and is sometimes called the acceleration of gravity. • By Newton’s second law of motion, the force of Earth’s gravity on a falling object is the object’s ____ times the _______ of gravity. ...
Dynamics Multiple Choice Homework
... C. turn right D. move with constant velocity E. turn left 2. When a cat sleeps on a table, the net force on it is A. zero B. directed upward C. directed downward D. directed in the horizontal direction E. more information is required 3. When the engines on a rocket ship in deep space, far from any o ...
... C. turn right D. move with constant velocity E. turn left 2. When a cat sleeps on a table, the net force on it is A. zero B. directed upward C. directed downward D. directed in the horizontal direction E. more information is required 3. When the engines on a rocket ship in deep space, far from any o ...
Unit 4 vocabulary - Riverdale Middle School
... 26. Newton’s first law of motion – states that an object at rest tends to stay at rest, and an object in constant motion tends to stay in motion, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. 27. Newton’s second law of motion – states that acceleration depends on the object’s mass and the amount of net ...
... 26. Newton’s first law of motion – states that an object at rest tends to stay at rest, and an object in constant motion tends to stay in motion, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. 27. Newton’s second law of motion – states that acceleration depends on the object’s mass and the amount of net ...
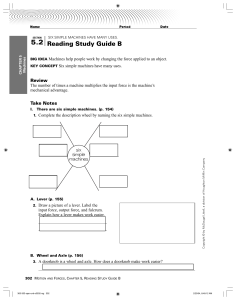
ACTIVITY: Objective 1: Identifying Common Simple and Compound
... refer to this outward force as ___________________________ force. Centrifugal means __________________________________ or away from the center. When the string breaks, the whirling can moves in a __________________, tangent to—NOT _____________________ from the center of—its circular path. The pictu ...
... refer to this outward force as ___________________________ force. Centrifugal means __________________________________ or away from the center. When the string breaks, the whirling can moves in a __________________, tangent to—NOT _____________________ from the center of—its circular path. The pictu ...
Chapter 4 Motion
... Are you hurt because you hit the wall? No—you can't feel the force on the wall. You can feel forces only on your body. You're hurt because the wall hit you. The wall didn't reach out and hit you, of course. But it did push you with the same amount of force with which you pushed it. If it hadn't, you ...
... Are you hurt because you hit the wall? No—you can't feel the force on the wall. You can feel forces only on your body. You're hurt because the wall hit you. The wall didn't reach out and hit you, of course. But it did push you with the same amount of force with which you pushed it. If it hadn't, you ...
V 1
... • For any conservative force F we can define a potential energy function U in the following way: W = ...
... • For any conservative force F we can define a potential energy function U in the following way: W = ...
pp\NewtonLaws - Dr. Robert MacKay
... Law of inertia (1st Law) • Inertia (The intrinsic tendency of an object to resist changes in motion) • Mass is a measure of an object’s inertia • Mass is also a measure of the amount of an object’s matter content. (i.e. protons, neutrons, and electrons) • Weight is the force upon an object due to ...
... Law of inertia (1st Law) • Inertia (The intrinsic tendency of an object to resist changes in motion) • Mass is a measure of an object’s inertia • Mass is also a measure of the amount of an object’s matter content. (i.e. protons, neutrons, and electrons) • Weight is the force upon an object due to ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.