Forces_and_Newtons_Laws_powerpoint
... Newton’s Second Law tells us what an object will do when it has UNBALANCED forces acting on it. A net force acting on an object will cause the object to accelerate (speed up, slow down, or change direction). The greater the net force acting on an object, the larger the acceleration of the object wil ...
... Newton’s Second Law tells us what an object will do when it has UNBALANCED forces acting on it. A net force acting on an object will cause the object to accelerate (speed up, slow down, or change direction). The greater the net force acting on an object, the larger the acceleration of the object wil ...
kg·m
... Impulse Example An 8N force acts on a 5 kg object for 3 seconds. If the initial velocity of the object was 25 m/s, what is its final velocity? F= 8 N m= 5 kg t= 3 s v1 = 25 m/s v2 = ? J = Ft =(8N)(3s) = 24 N·s BUT we need to find v2 ……… ...
... Impulse Example An 8N force acts on a 5 kg object for 3 seconds. If the initial velocity of the object was 25 m/s, what is its final velocity? F= 8 N m= 5 kg t= 3 s v1 = 25 m/s v2 = ? J = Ft =(8N)(3s) = 24 N·s BUT we need to find v2 ……… ...
Problem CP2 Chapt 4 - My Solution PDF with thumbnails 2/29/04
... Basic Solution (Minimum Expected from the student) Ch4 CP2 A rope exerts a constant horizontal force of 250 N to pull a 60-kg crate across the floor. The velocity of the crate is observed to increase from 1 m/s to 3 m/s in a time of 2 seconds under the influence of this force and the frictional forc ...
... Basic Solution (Minimum Expected from the student) Ch4 CP2 A rope exerts a constant horizontal force of 250 N to pull a 60-kg crate across the floor. The velocity of the crate is observed to increase from 1 m/s to 3 m/s in a time of 2 seconds under the influence of this force and the frictional forc ...
lecture 3 pendulum and energy
... It has more mass than the other one. It has less mass than the other one. It is longer than the other one. It is shorter than the other one. It has slightly more energy than the other one. It has slightly less energy than the other one. It moves faster at the lowest point in its swing than the other ...
... It has more mass than the other one. It has less mass than the other one. It is longer than the other one. It is shorter than the other one. It has slightly more energy than the other one. It has slightly less energy than the other one. It moves faster at the lowest point in its swing than the other ...
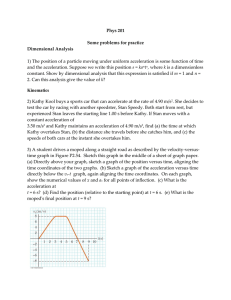
Phys 201 Some problems for practice Dimensional Analysis 1) The
... Some problems for practice Dimensional Analysis 1) The position of a particle moving under uniform acceleration is some function of time and the acceleration. Suppose we write this position s = kamtn, where k is a dimensionless constant. Show by dimensional analysis that this expression is satisfied ...
... Some problems for practice Dimensional Analysis 1) The position of a particle moving under uniform acceleration is some function of time and the acceleration. Suppose we write this position s = kamtn, where k is a dimensionless constant. Show by dimensional analysis that this expression is satisfied ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Dynamics continued
... The rotational kinetic energy of a rigid rotating object is ...
... The rotational kinetic energy of a rigid rotating object is ...
Form B
... A) When the object is just released. Mg B) When the object reaches the highest point. C) When moving downward the object passes the starting height. D) When the object is just about to hit the bottom of the hole. E) When the object is just released and when moving downward it passes its starting hei ...
... A) When the object is just released. Mg B) When the object reaches the highest point. C) When moving downward the object passes the starting height. D) When the object is just about to hit the bottom of the hole. E) When the object is just released and when moving downward it passes its starting hei ...
GRADE 10F: Physics 2
... Get pairs or small groups of students to use a forces board to measure forces acting on an object and draw the corresponding vector diagram. The diagram will probably show a (small) non-zero resultant force. Discuss the reasons for this (e.g. frictional forces, uncertainty in measurement of forces a ...
... Get pairs or small groups of students to use a forces board to measure forces acting on an object and draw the corresponding vector diagram. The diagram will probably show a (small) non-zero resultant force. Discuss the reasons for this (e.g. frictional forces, uncertainty in measurement of forces a ...
Kreutter/Costello: Linear Dynamics 6 Newton`s Second Law
... Newton’s Second Law: Qualitative 6.1 Observe and Find a Pattern Student A is on rollerblades and stands in front of a motion detector. The motion detector produces velocity-versus-time graphs. Student B (not on rollerblades) stands behind Student A and pushes her forward. Student A starts moving. Th ...
... Newton’s Second Law: Qualitative 6.1 Observe and Find a Pattern Student A is on rollerblades and stands in front of a motion detector. The motion detector produces velocity-versus-time graphs. Student B (not on rollerblades) stands behind Student A and pushes her forward. Student A starts moving. Th ...
Physics Toolkit - Effingham County Schools
... In order for a bolt to be tightened, a torque of 45.0 N•m is needed. You use a 0.341 m long wrench, and you exert a maximum force of 189 N. What is the smallest angle, with respect to the wrench, at which you can exert this force and still tighten the bolt? ...
... In order for a bolt to be tightened, a torque of 45.0 N•m is needed. You use a 0.341 m long wrench, and you exert a maximum force of 189 N. What is the smallest angle, with respect to the wrench, at which you can exert this force and still tighten the bolt? ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion
... Force is directly proportional to mass and acceleration. Imagine a ball of a certain mass moving at a certain acceleration. This ball has a certain force. Now imagine we make the ball twice as big (double the mass) but keep the acceleration constant. F = ma says that this new ball has twice the forc ...
... Force is directly proportional to mass and acceleration. Imagine a ball of a certain mass moving at a certain acceleration. This ball has a certain force. Now imagine we make the ball twice as big (double the mass) but keep the acceleration constant. F = ma says that this new ball has twice the forc ...
12 - UTSC
... zero at the equilibrium position x = 0. We have seen in other notes that eq[12-1] is an example of a central or restoring force. It is restoring in the sense that if the block is displaced to the right of the equilibrium position, then the force exerted by the spring on the block points to the left, ...
... zero at the equilibrium position x = 0. We have seen in other notes that eq[12-1] is an example of a central or restoring force. It is restoring in the sense that if the block is displaced to the right of the equilibrium position, then the force exerted by the spring on the block points to the left, ...
notebook- Universal Gravitation
... What we want to know… What is Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation? How does distance affect gravitational force between two objects? What is weight and how can something appear weightless? What are Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion? ...
... What we want to know… What is Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation? How does distance affect gravitational force between two objects? What is weight and how can something appear weightless? What are Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion? ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.