5.1 The First Law: The Law of Inertia
... The Atwood’s machine is driven by a net force equal in magnitude to the weight difference between the two mass hangers. You will vary the two masses, m1 and m2, but you will keep the total mass constant. As you move plastic washers from m2 to m1, you will use a photogate to measure the acceleration ...
... The Atwood’s machine is driven by a net force equal in magnitude to the weight difference between the two mass hangers. You will vary the two masses, m1 and m2, but you will keep the total mass constant. As you move plastic washers from m2 to m1, you will use a photogate to measure the acceleration ...
Chapter 4 Work and Energy
... You transfer energy to a machine, the machine transfers that energy to the object Energy is neither created nor destroyed, so the work done by the machine is never greater than the work done to the machine Because of energy losses due to friction, the work done by the machine is always less th ...
... You transfer energy to a machine, the machine transfers that energy to the object Energy is neither created nor destroyed, so the work done by the machine is never greater than the work done to the machine Because of energy losses due to friction, the work done by the machine is always less th ...
Explanation - Fort Bend ISD
... Masses attract one another about their centers with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them (whew!). ...
... Masses attract one another about their centers with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them (whew!). ...
1991B5 A polonium nucleus of atomic number 84
... What is the velocity of the alpha particle? (Neglect relativistic effects for this calculation.) c. Where does the kinetic energy of the alpha particle come from? Explain briefly. d. Suppose that the fermium-252 nucleus could undergo a decay in which a β- particle was produced. How would this affect ...
... What is the velocity of the alpha particle? (Neglect relativistic effects for this calculation.) c. Where does the kinetic energy of the alpha particle come from? Explain briefly. d. Suppose that the fermium-252 nucleus could undergo a decay in which a β- particle was produced. How would this affect ...
PPT - LSU Physics
... where W is the work required to move the ball from point P (at distance R) to infinity. Work can also be expressed in terms of potential energies as ...
... where W is the work required to move the ball from point P (at distance R) to infinity. Work can also be expressed in terms of potential energies as ...
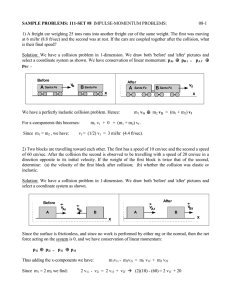
SAMPLE PROBLEMS: 111-SET #8 08-1
... That is, the Impulse produced by the net force during any time interval is equal to the change in the linear momentum during that time interval. Since we neglect all forces in the problem other than the force of bat on the ball, then the net force is the force of the bat on the ball, and we have: Im ...
... That is, the Impulse produced by the net force during any time interval is equal to the change in the linear momentum during that time interval. Since we neglect all forces in the problem other than the force of bat on the ball, then the net force is the force of the bat on the ball, and we have: Im ...
1. The potential energy stored by the spring is given by U kx = 1 2
... (measured downward so that it yields a positive value). Our reference point for the gravitational potential energy is the initial position of the block. The block drops a total distance h + x, and the final gravitational potential energy is –mg(h + x). The spring ...
... (measured downward so that it yields a positive value). Our reference point for the gravitational potential energy is the initial position of the block. The block drops a total distance h + x, and the final gravitational potential energy is –mg(h + x). The spring ...
Only external forces affect the motion of the center of mass
... table with velocity v0. It explodes into two pieces, one with mass m/3. The light piece flies off horizontally, perpendicular to the original direction of motion, with velocity 2v0. Find as many equations as you need to find the velocity of the heavy piece. ...
... table with velocity v0. It explodes into two pieces, one with mass m/3. The light piece flies off horizontally, perpendicular to the original direction of motion, with velocity 2v0. Find as many equations as you need to find the velocity of the heavy piece. ...
Test 3 Preparation Questions
... (B) If a charged object is placed at that point, it is the magnitude of the net electric force on that object. (C) If a charged object is placed at that point, it is the ratio of the charge on that object to its mass. (D) If a charged object is placed at that point, it is the magnitude of the net el ...
... (B) If a charged object is placed at that point, it is the magnitude of the net electric force on that object. (C) If a charged object is placed at that point, it is the ratio of the charge on that object to its mass. (D) If a charged object is placed at that point, it is the magnitude of the net el ...
Projectile Motion
... Is only acted upon by gravity No force in the x-direction, only in the ydirection (gravity) • Gravity ALWAYS acts in the y-direction, and ONLY the y-direction ...
... Is only acted upon by gravity No force in the x-direction, only in the ydirection (gravity) • Gravity ALWAYS acts in the y-direction, and ONLY the y-direction ...
Document
... 8. A constant force of 8.0 N is exerted for 8.0 s on a 16-kg object initially at rest. The change in speed of this object will be: A. 0.5m/s B. 2m/s C. 4m/s D. 8m/s E. 32m/s ans: C 9. Two forces are applied to a 1.0-kg crate; one is 6.0N to the north and the other is 8.0N to the west. The magnitude ...
... 8. A constant force of 8.0 N is exerted for 8.0 s on a 16-kg object initially at rest. The change in speed of this object will be: A. 0.5m/s B. 2m/s C. 4m/s D. 8m/s E. 32m/s ans: C 9. Two forces are applied to a 1.0-kg crate; one is 6.0N to the north and the other is 8.0N to the west. The magnitude ...
Gravity and Friction
... This diagram represents a star orbited by two planets—planet A and planet B. The star is also orbited by a mysterious object, object X, that entered into the star’s gravitational field. Directions: Use the diagram to answer each question or respond to each statement. ...
... This diagram represents a star orbited by two planets—planet A and planet B. The star is also orbited by a mysterious object, object X, that entered into the star’s gravitational field. Directions: Use the diagram to answer each question or respond to each statement. ...
Lecture 9.CircularMo..
... the circle. As q becomes smaller and smaller, v points directly to center. Therefore the acceleration points towards the center of the circle. ...
... the circle. As q becomes smaller and smaller, v points directly to center. Therefore the acceleration points towards the center of the circle. ...
Forces_and_Newtons_Laws_powerpoint
... Newton’s Second Law tells us what an object will do when it has UNBALANCED forces acting on it. A net force acting on an object will cause the object to accelerate (speed up, slow down, or change direction). The greater the net force acting on an object, the larger the acceleration of the object wil ...
... Newton’s Second Law tells us what an object will do when it has UNBALANCED forces acting on it. A net force acting on an object will cause the object to accelerate (speed up, slow down, or change direction). The greater the net force acting on an object, the larger the acceleration of the object wil ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.