Review Rotational Motion and Equilibrium and Elasticity
... long and initially at rest in the water. The child then slowly walks to the other end of the canoe. How far does the canoe move in the water, assuming water friction is negligible? A.) 1.0 m B.) 2.0 m C.) 3.0 m D.) 4.0 m E.) 5.0 m 10.) The center of mass (or center of gravity) of a two-particle syst ...
... long and initially at rest in the water. The child then slowly walks to the other end of the canoe. How far does the canoe move in the water, assuming water friction is negligible? A.) 1.0 m B.) 2.0 m C.) 3.0 m D.) 4.0 m E.) 5.0 m 10.) The center of mass (or center of gravity) of a two-particle syst ...
Midterm Review - MrStapleton.com
... 5. Suppose a 75kg world class sprinter accelerates at a rate of 3 m/s2. Starting from a standstill, he eventually reaches a speed of 12 m/s on a flat, horizontal surface. During this acceleration, the sprinter undergoes a change in potential and kinetic energy. This is because the runner is doing wo ...
... 5. Suppose a 75kg world class sprinter accelerates at a rate of 3 m/s2. Starting from a standstill, he eventually reaches a speed of 12 m/s on a flat, horizontal surface. During this acceleration, the sprinter undergoes a change in potential and kinetic energy. This is because the runner is doing wo ...
Chapter 4- The Equations of Motion Aircraft
... The three Equations of Motion are simply statements of Newton’s Second Law. The three Equations of Motion describe the translational motion of an airplane through three-dimensional space over a flat earth. There are three additional equations of motion that describe the rotational motion of the airc ...
... The three Equations of Motion are simply statements of Newton’s Second Law. The three Equations of Motion describe the translational motion of an airplane through three-dimensional space over a flat earth. There are three additional equations of motion that describe the rotational motion of the airc ...
Honors Physics S2 Final Exam Review 2013
... A person pulls on a door handle with 5N of force. Use a complete sentence to describe the reaction force (include direction and amount). ...
... A person pulls on a door handle with 5N of force. Use a complete sentence to describe the reaction force (include direction and amount). ...
physics - Regents
... (1) Sphere A is positive and sphere B is negative. (2) Sphere A is negative and sphere B is positive. (3) Both spheres are positive. ...
... (1) Sphere A is positive and sphere B is negative. (2) Sphere A is negative and sphere B is positive. (3) Both spheres are positive. ...
Lecture 21 - PhysicsGivesYouWings
... Momentum Conservation • Principle of momentum conservation: In the absence of external interactions, the total momentum of a system is constant in time. – “Absence of external interactions” means that the net external force is zero: ...
... Momentum Conservation • Principle of momentum conservation: In the absence of external interactions, the total momentum of a system is constant in time. – “Absence of external interactions” means that the net external force is zero: ...
Project1: Automation using Light Sensors
... Revitalizing Achievement by using Instrumentation in Science Education 2004-2007 ...
... Revitalizing Achievement by using Instrumentation in Science Education 2004-2007 ...
lecture 1 statics
... It the resultant force F acting on a particle of mass m is not zero, the particle will accelerate linearly in the direction of the force according to the law F=ma. It the resultant moment M acting on a body of mass moment of inertia I is not zero, the body will have an angular acceleration α, define ...
... It the resultant force F acting on a particle of mass m is not zero, the particle will accelerate linearly in the direction of the force according to the law F=ma. It the resultant moment M acting on a body of mass moment of inertia I is not zero, the body will have an angular acceleration α, define ...
FSN: Sport Science
... How many pounds of force did the sensors record when the hit occurred 12 inches from the boards? How many pounds of force did the sensors record when the hit occurred directly on the boards? What causes such a big difference between the force impacts from 12 inches to 0 inches along the boards? Whic ...
... How many pounds of force did the sensors record when the hit occurred 12 inches from the boards? How many pounds of force did the sensors record when the hit occurred directly on the boards? What causes such a big difference between the force impacts from 12 inches to 0 inches along the boards? Whic ...
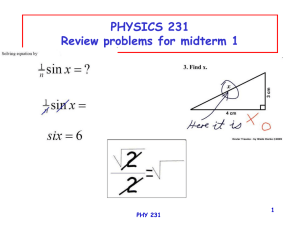
PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 1 1 PHY 231
... force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the speed (not a vector, just a positive number) increases. So answer c is correct. PHY 231 ...
... force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the speed (not a vector, just a positive number) increases. So answer c is correct. PHY 231 ...
Stacey Carpenter
... Isaac Newton is one of the most famous scientists. His formula, F = ma, is the most important formula in early physics and, along with Einstein's E = mc2, is one of the two best-known formulas in all of physics. Newton looked at the movement of objects, just as Galileo did. He started with inertia ...
... Isaac Newton is one of the most famous scientists. His formula, F = ma, is the most important formula in early physics and, along with Einstein's E = mc2, is one of the two best-known formulas in all of physics. Newton looked at the movement of objects, just as Galileo did. He started with inertia ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.