Forces acting on a particle in a concentration gradient under an
... monitored through an oscilloscope (2205GN, Tektronics, OR). An epifluorescence microscope (FN1; Nikon, Japan) equipped with a mercury lamp (100 W) and a high-speed camera (Phantom, Vision Research, NJ) was used to capture and transfer images to a computer for the subsequent analysis. Fig. 2 presents ...
... monitored through an oscilloscope (2205GN, Tektronics, OR). An epifluorescence microscope (FN1; Nikon, Japan) equipped with a mercury lamp (100 W) and a high-speed camera (Phantom, Vision Research, NJ) was used to capture and transfer images to a computer for the subsequent analysis. Fig. 2 presents ...
Momentum
... Impulse and Collision • In a collision, an object experiences a force for a specific amount of time, which results in a change in momentum. The mass either speeds up or slows down. • This means that during a collision an object experiences IMPULSE! ...
... Impulse and Collision • In a collision, an object experiences a force for a specific amount of time, which results in a change in momentum. The mass either speeds up or slows down. • This means that during a collision an object experiences IMPULSE! ...
doc
... from one object in the to another. Internal and External Forces Internal forces act between objects in system. External forces are exerted by objects the system. The total momentum of a system is conserved only when there are no forces acting on the system. Conservation of Momentum in Two Dimensions ...
... from one object in the to another. Internal and External Forces Internal forces act between objects in system. External forces are exerted by objects the system. The total momentum of a system is conserved only when there are no forces acting on the system. Conservation of Momentum in Two Dimensions ...
Chapter 7 - Muddassir
... small metallic bob suspended from a frictionless rigid support by means of long, weighless and inextensible string. These conditions are impossible to attain in nature. So ideal simple pendulum can’t be realized. Q # 4. What is total distance travelled by an object moving with SHM in a time equal to ...
... small metallic bob suspended from a frictionless rigid support by means of long, weighless and inextensible string. These conditions are impossible to attain in nature. So ideal simple pendulum can’t be realized. Q # 4. What is total distance travelled by an object moving with SHM in a time equal to ...
Symbols and Units
... be characterized by both its magnitude and direction. Scalars are any quantity in physics that can be characterized by magnitude only. ...
... be characterized by both its magnitude and direction. Scalars are any quantity in physics that can be characterized by magnitude only. ...
Internal And External Forces: Every body of finite size is made of
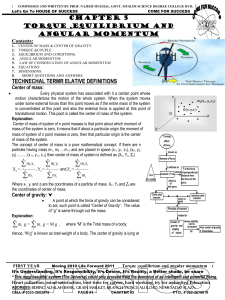
... for e.g. as shown in the figure the rod is pivoted at point O as shown in the figure and two forces F1 and F2 acts on it in downward direction. The system will be in rotational equilibrium if the moment of forces about point O is zero F1 x l1 = F2 x l2 This also basically implies that net torque is ...
... for e.g. as shown in the figure the rod is pivoted at point O as shown in the figure and two forces F1 and F2 acts on it in downward direction. The system will be in rotational equilibrium if the moment of forces about point O is zero F1 x l1 = F2 x l2 This also basically implies that net torque is ...
document
... The amount of air resistance depends upon the speed of the object. A falling object will continue to accelerate to higher speeds until they encounter an amount of air resistance that is equal to their weight. Since the 150-kg skydiver weighs more (experiences a greater force of gravity), it will acc ...
... The amount of air resistance depends upon the speed of the object. A falling object will continue to accelerate to higher speeds until they encounter an amount of air resistance that is equal to their weight. Since the 150-kg skydiver weighs more (experiences a greater force of gravity), it will acc ...
ID_newton4_060706 - Swift Education and Public Outreach
... the same velocity (if they both drop from the same height). This is counter-intuitive to most people, including, most likely, your students. Our intuition tells us that more massive objects fall faster, but that is not correct. Students may be confused by this, because they know that more massive o ...
... the same velocity (if they both drop from the same height). This is counter-intuitive to most people, including, most likely, your students. Our intuition tells us that more massive objects fall faster, but that is not correct. Students may be confused by this, because they know that more massive o ...
Circular Motion Review
... a horizontal circle at a constant speed of 10. meters per second. If the magnitude of the force applied to the string by the student's hand is increased, the magnitude of the acceleration of the ball in its circular path will A. decrease B. increase C. remain the same ...
... a horizontal circle at a constant speed of 10. meters per second. If the magnitude of the force applied to the string by the student's hand is increased, the magnitude of the acceleration of the ball in its circular path will A. decrease B. increase C. remain the same ...
systems of particles
... • Principle of work and energy can be applied to the entire system by adding the kinetic energies of all particles and considering the work done by all external and internal forces. ...
... • Principle of work and energy can be applied to the entire system by adding the kinetic energies of all particles and considering the work done by all external and internal forces. ...
Document
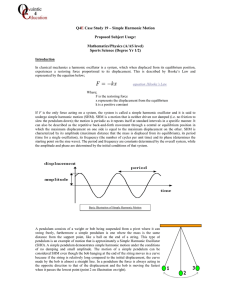
... particles make one revolution in the same amount of time. i.e., they all have the same angular speed. Moment of Inertia: A rigid body rotating about a fixed axis AB, a particle 'p' of mass is rotating in a circle of radius 'r'. Law of conservation of angular momentum: The total angular momentum of ...
... particles make one revolution in the same amount of time. i.e., they all have the same angular speed. Moment of Inertia: A rigid body rotating about a fixed axis AB, a particle 'p' of mass is rotating in a circle of radius 'r'. Law of conservation of angular momentum: The total angular momentum of ...
Work and Energy - Uplift North Hills
... The same work is done if the object is pulled along a ramp or vertically upward. ▪ minimum force needed to pull an object along a ramp is F2 = mg sinθ. the work done against gravitational force is: W = F2 d cos 00 = mg sinθ d = mg h is the same as before and is stored as PE of the object at height h ...
... The same work is done if the object is pulled along a ramp or vertically upward. ▪ minimum force needed to pull an object along a ramp is F2 = mg sinθ. the work done against gravitational force is: W = F2 d cos 00 = mg sinθ d = mg h is the same as before and is stored as PE of the object at height h ...
Impulse and Momentum
... objects after collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy before collision. The two object experience a permanent deformation in their original shape P1i + P2i = P1f + P2f ...
... objects after collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy before collision. The two object experience a permanent deformation in their original shape P1i + P2i = P1f + P2f ...
Sample
... 10) A 300-kg bear grasping a vertical tree slides down at constant velocity. The friction force between the tree and the bear is A) 30 N. B) 300 N. C) 3000 N. D) more than 3000 N. Answer: C Diff: 3 Topic: Friction 11) A package falls off a truck that is moving at 30 m/s. Neglecting air resistance, ...
... 10) A 300-kg bear grasping a vertical tree slides down at constant velocity. The friction force between the tree and the bear is A) 30 N. B) 300 N. C) 3000 N. D) more than 3000 N. Answer: C Diff: 3 Topic: Friction 11) A package falls off a truck that is moving at 30 m/s. Neglecting air resistance, ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.