Newton`s Laws of Motion – In Sports
... Newton’s Second Law in (Insert Sport Name) Using complete sentences, explain how Newton’s Second Law of Motion applies in your sport. Make sure you have at least two examples. One example should include objects of equal mass meeting different forces. How do they accelerate? The second exampl ...
... Newton’s Second Law in (Insert Sport Name) Using complete sentences, explain how Newton’s Second Law of Motion applies in your sport. Make sure you have at least two examples. One example should include objects of equal mass meeting different forces. How do they accelerate? The second exampl ...
PHYSICS
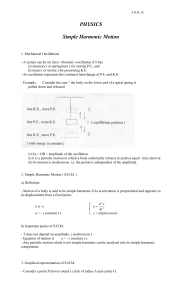
... (i) A body is said to be forced vibration (oscillation )if there is an external periodic driving force acting on it. (ii) In the early stages, beats will occur between the forced and natural vibration, giving rise to transient oscillations. (This stage is usually ignored since its time interval is s ...
... (i) A body is said to be forced vibration (oscillation )if there is an external periodic driving force acting on it. (ii) In the early stages, beats will occur between the forced and natural vibration, giving rise to transient oscillations. (This stage is usually ignored since its time interval is s ...
Chap.4 Conceptual Modules Fishbane
... After the cart is released, there is no longer a force in the x-direction. This does not mean that the cart stops moving!! It simply means that the cart will continue moving with the same velocity it had at the moment of release. The initial push got the cart moving, but that force is not needed to ...
... After the cart is released, there is no longer a force in the x-direction. This does not mean that the cart stops moving!! It simply means that the cart will continue moving with the same velocity it had at the moment of release. The initial push got the cart moving, but that force is not needed to ...
Slide 1
... And if you were at the edge of a Yo-yo that was falling under gravity? What would it feel like in both cases? ...
... And if you were at the edge of a Yo-yo that was falling under gravity? What would it feel like in both cases? ...
Chapter 6 and 7 Review
... a. The car and the tree mutually exert equal forces in the same direction. b. The car and the tree mutually exert different forces in the same direction. c. The car and the tree mutually exert equal and opposite forces on each other. d. The car and the tree mutually exert different and opposite forc ...
... a. The car and the tree mutually exert equal forces in the same direction. b. The car and the tree mutually exert different forces in the same direction. c. The car and the tree mutually exert equal and opposite forces on each other. d. The car and the tree mutually exert different and opposite forc ...
MANOEUVRING OF HIGH SPEED SHIPS
... Manoeuvring of High Speed Craft from Stability and Safety Point of View ...
... Manoeuvring of High Speed Craft from Stability and Safety Point of View ...
M - SCHOOLinSITES
... 7.1.2. As the name implies, the impulse-momentum theorem provides a relationship between impulse and momentum. Which one of the following statements correctly describes that relationship? a) An impulse is equal to the work done on an object when a net force acts on an object and it has a displaceme ...
... 7.1.2. As the name implies, the impulse-momentum theorem provides a relationship between impulse and momentum. Which one of the following statements correctly describes that relationship? a) An impulse is equal to the work done on an object when a net force acts on an object and it has a displaceme ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... rider alone becomes weightless at the top and has a speed v1. Now two additional passenger get in so that the total weight of the car (at rest) and people doubles. How fast must the car go so we are still weightless at the top ? Normal force is zero. ...
... rider alone becomes weightless at the top and has a speed v1. Now two additional passenger get in so that the total weight of the car (at rest) and people doubles. How fast must the car go so we are still weightless at the top ? Normal force is zero. ...
Chapter 5 - Physics@Brock
... if the units of each term of an equation match, the formula is not necessarily correct (some unitless factors might be missing), but if the units of each term are not the same then you can be sure the formula is incorrect. OK, that's good, but it would be better to have an intuitive feel for why the ...
... if the units of each term of an equation match, the formula is not necessarily correct (some unitless factors might be missing), but if the units of each term are not the same then you can be sure the formula is incorrect. OK, that's good, but it would be better to have an intuitive feel for why the ...
Potential field-based mobile node movement
... Global in the sense that it coordinates the agents and determines the distribution of the agents throughout the system. Local Control Force – The individual attractive and repulsive forces sensed by an agent. Leading Agents – Mobile agent with a preprogrammed path. Landmark Agents – Have a fixed pos ...
... Global in the sense that it coordinates the agents and determines the distribution of the agents throughout the system. Local Control Force – The individual attractive and repulsive forces sensed by an agent. Leading Agents – Mobile agent with a preprogrammed path. Landmark Agents – Have a fixed pos ...
Applied Sci. - Government Polytechnic Distance Learning Pune
... acceleration and uniform retardation, equations of motion for motion under gravity. 1.2 Angular Motion Definition of angular displacement, angular velocity, angular acceleration, Relation between angular velocity and linear velocity, Three equations of circular motion (no derivation) angular distanc ...
... acceleration and uniform retardation, equations of motion for motion under gravity. 1.2 Angular Motion Definition of angular displacement, angular velocity, angular acceleration, Relation between angular velocity and linear velocity, Three equations of circular motion (no derivation) angular distanc ...
File
... always come in pairs, are directed away from each other, are equal in magnitude, and opposite in direction. ...
... always come in pairs, are directed away from each other, are equal in magnitude, and opposite in direction. ...
solutions - UCSB C.L.A.S.
... 12) Two cars are moving toward an intersection. Car A is traveling East at 20 m/s, and Car B is traveling North at 12 m/s. The mass of Car A is 1000 kg and the mass of Car B is 2000 kg. Driver A is applying mascara to her eyelashes, and driver B is reading a text message, so neither of them slows d ...
... 12) Two cars are moving toward an intersection. Car A is traveling East at 20 m/s, and Car B is traveling North at 12 m/s. The mass of Car A is 1000 kg and the mass of Car B is 2000 kg. Driver A is applying mascara to her eyelashes, and driver B is reading a text message, so neither of them slows d ...
Potential Energy
... Then as the roller coaster reaches the top of the hill, all the potential energy is unloaded. The force of gravity does positive work (force and displacement vectors in line), and the roller coaster flies down the hill, converting all that potential energy into heart-in-your-throat kinetic energy. ...
... Then as the roller coaster reaches the top of the hill, all the potential energy is unloaded. The force of gravity does positive work (force and displacement vectors in line), and the roller coaster flies down the hill, converting all that potential energy into heart-in-your-throat kinetic energy. ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.