F - Cloudfront.net
... Ex. #8: A mass of 44.0 kg is pulled towards the top of a ramp at a constant speed by an applied force. The applied force is parallel to the ramp, and points towards the top of the ramp. The coefficient of friction between the ramp and the surface is 0.400 and the block is pulled a distance of 5.00 ...
... Ex. #8: A mass of 44.0 kg is pulled towards the top of a ramp at a constant speed by an applied force. The applied force is parallel to the ramp, and points towards the top of the ramp. The coefficient of friction between the ramp and the surface is 0.400 and the block is pulled a distance of 5.00 ...
Newton`s Law of Motion
... • However, for a typical mission, the shuttle orbits Earth at an altitude of about 400 km. • According to the law of universal gravitation, at 400-km altitude the force of Earth’s gravity is about 90 percent as strong as it is at Earth’s surface. • So an astronaut with a mass of 80 kg still would we ...
... • However, for a typical mission, the shuttle orbits Earth at an altitude of about 400 km. • According to the law of universal gravitation, at 400-km altitude the force of Earth’s gravity is about 90 percent as strong as it is at Earth’s surface. • So an astronaut with a mass of 80 kg still would we ...
Lab for October 14: acceleration due to gravity and Newton`s second
... Follow the computer instructions for Newton’s Second Law at the end of this lab. Attach a mass holder to a string about 3.0 m long and pass it over the pulley, tying the other end to the hook on the glider. Place the assigned number of grams on the glider and use the scale provided to determine the ...
... Follow the computer instructions for Newton’s Second Law at the end of this lab. Attach a mass holder to a string about 3.0 m long and pass it over the pulley, tying the other end to the hook on the glider. Place the assigned number of grams on the glider and use the scale provided to determine the ...
Learning Outcomes
... Understand force and Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion. Apply these laws (especially the 2nd Law) to problems with objects subjected to constant forces. Understand frictional forces. Apply Newton’s 2nd Law to problems with objects moving in the presence of friction. Understand the basics of motion on an inc ...
... Understand force and Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion. Apply these laws (especially the 2nd Law) to problems with objects subjected to constant forces. Understand frictional forces. Apply Newton’s 2nd Law to problems with objects moving in the presence of friction. Understand the basics of motion on an inc ...
Newton`s Law of Gravitation - Swift
... curved surface of the Earth at each point. However, the force of the Earth’s gravity on Swift is “vertical” – pointed towards the center of the Earth. Why then does Swift not fall to Earth immediately? The answer is that Swift moves horizontally at just the right rate so that as it falls vertically, ...
... curved surface of the Earth at each point. However, the force of the Earth’s gravity on Swift is “vertical” – pointed towards the center of the Earth. Why then does Swift not fall to Earth immediately? The answer is that Swift moves horizontally at just the right rate so that as it falls vertically, ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... and turn it on by clicking the ON/OFF button below. 1. Look at the blue lines coming from the fan. In which direction is the air pushed? ____________________ ...
... and turn it on by clicking the ON/OFF button below. 1. Look at the blue lines coming from the fan. In which direction is the air pushed? ____________________ ...
an sh (SOLVED) CBSE SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER (THEORY)
... Ans. Law of conservation of momentum : The sum of momenta of the objects before collision is equal to the sum of momenta after collision, provided there is no external unbalanced force is acting on them. When a person falls on the hard floor, he is brought to rest in a very short interval of time so ...
... Ans. Law of conservation of momentum : The sum of momenta of the objects before collision is equal to the sum of momenta after collision, provided there is no external unbalanced force is acting on them. When a person falls on the hard floor, he is brought to rest in a very short interval of time so ...
Modeling a Rocket in Orbit Around the Earth
... from the origin starting from the position of the rocket. To find the acceleration of an object the force and mass must be known. Because rockets use a masspropellant system, their mass will decrease over the duration of the flight. For the purposes of this model the rocket engine will be simplified ...
... from the origin starting from the position of the rocket. To find the acceleration of an object the force and mass must be known. Because rockets use a masspropellant system, their mass will decrease over the duration of the flight. For the purposes of this model the rocket engine will be simplified ...
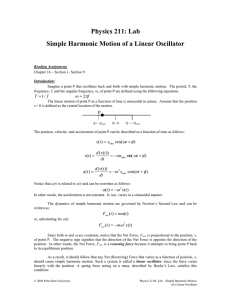
Lab #11: Simple Harmonic Motion of a Linear Oscillator
... There are many examples of resonance in everyday life. Engineers must be extremely careful not to design a structure that has a natural frequency that matches a potential driving force. The Tacoma Narrows Bridge disaster is an example of such an error. Troops usually march in step with each other as ...
... There are many examples of resonance in everyday life. Engineers must be extremely careful not to design a structure that has a natural frequency that matches a potential driving force. The Tacoma Narrows Bridge disaster is an example of such an error. Troops usually march in step with each other as ...
0BJECTIVES 7
... ____ 13. The average acceleration of a car that goes from 0 m/s to 25 m/s in 8.0s is a. 0.32 m/s c. 3.1 m/s b. 0.32 m/s2 d. 3.1 m/s2 ____ 14. Which of the following does not indicate velocity? a. 14 m/s SSE b. 40 km/h toward the town square along the main street c. 80 km/h going from New York toward ...
... ____ 13. The average acceleration of a car that goes from 0 m/s to 25 m/s in 8.0s is a. 0.32 m/s c. 3.1 m/s b. 0.32 m/s2 d. 3.1 m/s2 ____ 14. Which of the following does not indicate velocity? a. 14 m/s SSE b. 40 km/h toward the town square along the main street c. 80 km/h going from New York toward ...
Chapter 10 PowerPoint - Derry Area School District
... Through the process of doing work, energy can move between the external world and the system. The direction of energy transfer can go both ways. If the external world does work on a system, then W is positive and the energy of the system increases. If, however, a system does work on the external wor ...
... Through the process of doing work, energy can move between the external world and the system. The direction of energy transfer can go both ways. If the external world does work on a system, then W is positive and the energy of the system increases. If, however, a system does work on the external wor ...
Name - Mrs. Henderson`s Science Site
... 64. When would the momentum of a system not be conserved? 65. If you were stranded in the middle of a frozen pond where there is no friction between your feet and the ice, what could you do to get off the ice? 66. If you are in space (frictionless) and you throw an object that is less massive than y ...
... 64. When would the momentum of a system not be conserved? 65. If you were stranded in the middle of a frozen pond where there is no friction between your feet and the ice, what could you do to get off the ice? 66. If you are in space (frictionless) and you throw an object that is less massive than y ...
newton`s second law - Otterbein University
... the harder you push on a cart, the faster it goes. However, according to Newton, the force merely changes the velocity. It is the acceleration, not the velocity, that is proportional to the force. Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a mu ...
... the harder you push on a cart, the faster it goes. However, according to Newton, the force merely changes the velocity. It is the acceleration, not the velocity, that is proportional to the force. Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a mu ...
Newton`s Laws PPT
... Static and Kinetic Frictional Forces When an object is in contact with a surface there is a force acting on that object. Frictional force is the component of this force that is parallel to the surface. ...
... Static and Kinetic Frictional Forces When an object is in contact with a surface there is a force acting on that object. Frictional force is the component of this force that is parallel to the surface. ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.