PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 1
... force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the speed (not a vector, just a positive number) increases. So answer c is correct. PHY 231 ...
... force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the speed (not a vector, just a positive number) increases. So answer c is correct. PHY 231 ...
Name - Deans Community High School
... 4. A car travels a distance of 2 000 metres in a time of 160 seconds. Calculate the average speed of the car in metres per second. 5. Jane jogs to work every day at an average speed of 4 m/s. Most days it takes her 600 seconds to reach work. Calculate how far she jogs. 6. Describe a method of findin ...
... 4. A car travels a distance of 2 000 metres in a time of 160 seconds. Calculate the average speed of the car in metres per second. 5. Jane jogs to work every day at an average speed of 4 m/s. Most days it takes her 600 seconds to reach work. Calculate how far she jogs. 6. Describe a method of findin ...
S2-3-06 - In Motion - Lesson Sequence
... a) Contact Forces – involving actual contact between two objects. e.g. Normal forces, Frictional forces, Tensional forces, Spring forces, Air Resistance forces, etc. b) Action at a Distance Forces – forces that affect an object without it. e.g. Gravitational forces, Electrical forces, Magnetic force ...
... a) Contact Forces – involving actual contact between two objects. e.g. Normal forces, Frictional forces, Tensional forces, Spring forces, Air Resistance forces, etc. b) Action at a Distance Forces – forces that affect an object without it. e.g. Gravitational forces, Electrical forces, Magnetic force ...
NewtonsLaws
... between all objects that have mass. • Objects fall to the ground because Earth exerts gravity on them. • Earth’s gravitational force pulls objects towards Earth’s surface. • Mass is the amount of matter in an object. • Mass is often measured in kilograms (kg). ...
... between all objects that have mass. • Objects fall to the ground because Earth exerts gravity on them. • Earth’s gravitational force pulls objects towards Earth’s surface. • Mass is the amount of matter in an object. • Mass is often measured in kilograms (kg). ...
Thompkins: AP Physics Simple Harmonic Motion Whiteboarding
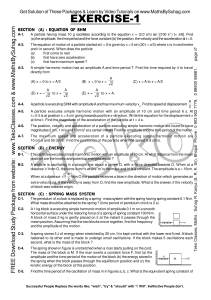
... 4) A 5-kilogram block is fastened to a vertical spring that has a spring constant of 1,000 newtons per meter. A 3-kilogram block rests on top of the 5-kilogram block, as shown above. a. When the blocks are at rest, how much is the spring compressed from its original length? The blocks are now pushe ...
... 4) A 5-kilogram block is fastened to a vertical spring that has a spring constant of 1,000 newtons per meter. A 3-kilogram block rests on top of the 5-kilogram block, as shown above. a. When the blocks are at rest, how much is the spring compressed from its original length? The blocks are now pushe ...
Introduction to Circular Motion
... Center of gravity is the same thing as the center of mass, except specifically referring to an object under the influence of gravity. The terms are effectively synonymous and we will use the abbreviation COG or CG for short, when consideration of this position is necessary. The COG of a uniform obje ...
... Center of gravity is the same thing as the center of mass, except specifically referring to an object under the influence of gravity. The terms are effectively synonymous and we will use the abbreviation COG or CG for short, when consideration of this position is necessary. The COG of a uniform obje ...
Force Tension Compression Shear and Torsion
... B. If twice the force is applied, there will be twice the acceleration. C. If the same force is applied to an object with twice the mass, there will be only half the acceleration ...
... B. If twice the force is applied, there will be twice the acceleration. C. If the same force is applied to an object with twice the mass, there will be only half the acceleration ...
Solutions - Brown University
... 4. In this problem we will set up a more accurate calculation of Felix Baumgartner’s space jump. We made two crude approximations in our earlier calculation: (i) the first phase of the jump was approximated using a rough guess for the variation of acceleration with time; and (ii) the variation of ai ...
... 4. In this problem we will set up a more accurate calculation of Felix Baumgartner’s space jump. We made two crude approximations in our earlier calculation: (i) the first phase of the jump was approximated using a rough guess for the variation of acceleration with time; and (ii) the variation of ai ...
What is Newton`s Third Law
... that is falling. Inside the elevator you and the scale are both in a free fall. The only force acting upon you is gravity, the scale is no longer pushing up on you. ...
... that is falling. Inside the elevator you and the scale are both in a free fall. The only force acting upon you is gravity, the scale is no longer pushing up on you. ...
Lesson 1 - Physical Quantities and units - science
... take the gradient of the line. But if the acceleration is non-uniform it is, by definition, changing. So we can only work out the acceleration at specific points, or instants. We call this taking the instantaneous acceleration. Graph A shows the V-T graph of an object with non-uniform acceleration. ...
... take the gradient of the line. But if the acceleration is non-uniform it is, by definition, changing. So we can only work out the acceleration at specific points, or instants. We call this taking the instantaneous acceleration. Graph A shows the V-T graph of an object with non-uniform acceleration. ...
Newton`s Second Law for Rotation Newton`s First Law for Rotation
... • Assignment 9 has been posted on WebAssign. • The grades for Test 2 have been posted on WebAssign. ...
... • Assignment 9 has been posted on WebAssign. • The grades for Test 2 have been posted on WebAssign. ...
Newton`s Law of Gravitation - Swift
... the curved surface of the Earth at each point. However, the force of the Earth’s gravity on Swift is “vertical” – pointed towards the center of the Earth. Why then does Swift not fall to Earth immediately? The answer is that Swift moves horizontally at just the right rate so that as it falls vertica ...
... the curved surface of the Earth at each point. However, the force of the Earth’s gravity on Swift is “vertical” – pointed towards the center of the Earth. Why then does Swift not fall to Earth immediately? The answer is that Swift moves horizontally at just the right rate so that as it falls vertica ...
CST Review - cloudfront.net
... B There is an oscillating magnetic field inside the loop. C There is a fixed current running in a separate wire along the axis of the loop. D There is a static configuration of positive charge external to the loop. ...
... B There is an oscillating magnetic field inside the loop. C There is a fixed current running in a separate wire along the axis of the loop. D There is a static configuration of positive charge external to the loop. ...
Chapter 12 - FIA Science
... Acceleration also depends upon the mass of the object (inversely proportional) Mass is a measure of inertia of an object and depends on the amount of matter the object contains. ...
... Acceleration also depends upon the mass of the object (inversely proportional) Mass is a measure of inertia of an object and depends on the amount of matter the object contains. ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.