Ecology Word Search
... 1. This is a type of organism that goes through photosynthesis to produce it’s own source of energy. ...
... 1. This is a type of organism that goes through photosynthesis to produce it’s own source of energy. ...
Biological Classification / Biomes
... Classification is the process of grouping things by their shared traits. At least 1.7 million different organisms identified on Earth. Taxonomy Taxonomy is the scientific study of how things are classified. Carolus Linneaus Swedish scientist who came up with classification system for living thin ...
... Classification is the process of grouping things by their shared traits. At least 1.7 million different organisms identified on Earth. Taxonomy Taxonomy is the scientific study of how things are classified. Carolus Linneaus Swedish scientist who came up with classification system for living thin ...
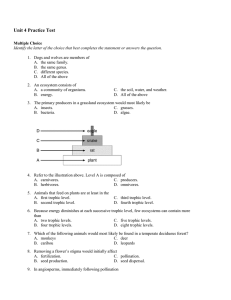
Unit 4 Practice Test - Kirkwood Community College
... A. is a feature of most invertebrates, including the sponges. B. is characterized by the concentration of sensory organs in the anterior end. C. occurs in marine protozoa. D. results when the brain does not develop properly. 12. Hermaphroditic organisms A. reproduce only by asexual means. B. produce ...
... A. is a feature of most invertebrates, including the sponges. B. is characterized by the concentration of sensory organs in the anterior end. C. occurs in marine protozoa. D. results when the brain does not develop properly. 12. Hermaphroditic organisms A. reproduce only by asexual means. B. produce ...
chapter 5 learning objectives
... 1.1.4. Define and describe examples of evolution by artificial selection (examples to know: dog domestication, edible plants from mustard, herbicide/antibiotic resistant organisms). 1.1.5. Explain evolution by natural selection and include Darwin’s 5 key ideas. 1.1.6. Define fitness and adaptations ...
... 1.1.4. Define and describe examples of evolution by artificial selection (examples to know: dog domestication, edible plants from mustard, herbicide/antibiotic resistant organisms). 1.1.5. Explain evolution by natural selection and include Darwin’s 5 key ideas. 1.1.6. Define fitness and adaptations ...
Unit6 StudyGuide
... energy (autotrophic) - Consumers – organisms that consume other living things for energy (heterotrophic) - Herbivore – consumer that eats plants - Carnivore – consumer that eats animals - Omnivore – comsumer that eats both plants and animals - Decomposer – consumer that breaks down living/dead organ ...
... energy (autotrophic) - Consumers – organisms that consume other living things for energy (heterotrophic) - Herbivore – consumer that eats plants - Carnivore – consumer that eats animals - Omnivore – comsumer that eats both plants and animals - Decomposer – consumer that breaks down living/dead organ ...
1. Living Things - The Physics Teacher.ie
... Sensitivity is the ability to detect and respond to stimuli or changes in the environment. 4. Growth All living things can grow/increase in size. This happens through cell division where cells have the ability to make copies of themselves. 5. Reproduction Reproduction is the formation of new individ ...
... Sensitivity is the ability to detect and respond to stimuli or changes in the environment. 4. Growth All living things can grow/increase in size. This happens through cell division where cells have the ability to make copies of themselves. 5. Reproduction Reproduction is the formation of new individ ...
Chapter 30 Study Guide:
... 7. How does gas exchange take place in the lungs and in the cells? 8. How are the respiratory and circulatory system connected? 9. What is the heart’s natural pacemaker and what happens if this is damaged? 10. What are the functions of the circulatory and respiratory systems? 11. Why is heart muscle ...
... 7. How does gas exchange take place in the lungs and in the cells? 8. How are the respiratory and circulatory system connected? 9. What is the heart’s natural pacemaker and what happens if this is damaged? 10. What are the functions of the circulatory and respiratory systems? 11. Why is heart muscle ...
What is Life?
... The transmission of genetic information from parent to offspring is heredity ...
... The transmission of genetic information from parent to offspring is heredity ...
Chapters 42
... functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Effector Cells- the muscle cells or gland cells that actually carry out the body’s responses to stimuli Neuron-the functional unity of the nervous system specialized for transmitting sig ...
... functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Effector Cells- the muscle cells or gland cells that actually carry out the body’s responses to stimuli Neuron-the functional unity of the nervous system specialized for transmitting sig ...
Characteristic and Interactions of Living Organisms
... All populations living together within a community interact with one another and with their environment in order to survive and maintain a balanced ecosystem That the diversity of species within an ecosystem is affected by changes in the environment, which can be caused by other organisms or outside ...
... All populations living together within a community interact with one another and with their environment in order to survive and maintain a balanced ecosystem That the diversity of species within an ecosystem is affected by changes in the environment, which can be caused by other organisms or outside ...
chapter 12 study guide rev9-22
... 1. Describe the lifestyles of plankton, nekton, and benthos. Why is it true that plankton account for a much larger percentage of the ocean’s biomass than benthos and nekton? 2. Discuss some adaptations other than size that are used by organisms to increase their resistance to sinking. 3. List the d ...
... 1. Describe the lifestyles of plankton, nekton, and benthos. Why is it true that plankton account for a much larger percentage of the ocean’s biomass than benthos and nekton? 2. Discuss some adaptations other than size that are used by organisms to increase their resistance to sinking. 3. List the d ...
Ecological Pyramids
... Only 10% of the overall movement of potential energy is transferred to the next tropic level ...
... Only 10% of the overall movement of potential energy is transferred to the next tropic level ...
Human Body Systems
... • Fill in the missing labels in the diagram to show how a thermostat uses feedback inhibition to maintain a stable temperature in a house. ...
... • Fill in the missing labels in the diagram to show how a thermostat uses feedback inhibition to maintain a stable temperature in a house. ...
Human Body Systems - Hamilton Township High School
... • Fill in the missing labels in the diagram to show how a thermostat uses feedback inhibition to maintain a stable temperature in a house. ...
... • Fill in the missing labels in the diagram to show how a thermostat uses feedback inhibition to maintain a stable temperature in a house. ...
Unit 5, Module 14 Animals - rev 2012
... 1. A behavior that is beneficial to an organism has adaptive value – it allows the organism to survive and reproduce better that those organism’s that do NOT display this behavior. 2. These behaviors may be directed by genes (DNA) and can therefore be inherited by organisms from their parents 3. Mos ...
... 1. A behavior that is beneficial to an organism has adaptive value – it allows the organism to survive and reproduce better that those organism’s that do NOT display this behavior. 2. These behaviors may be directed by genes (DNA) and can therefore be inherited by organisms from their parents 3. Mos ...
40animal homeostasis
... • Smaller animals have higher metabolic rates per gram than larger animals! • The higher metabolic rate of smaller animals leads to a higher oxygen delivery rate, breathing rate, heart rate, and greater (relative) blood volume, compared with a larger animal ...
... • Smaller animals have higher metabolic rates per gram than larger animals! • The higher metabolic rate of smaller animals leads to a higher oxygen delivery rate, breathing rate, heart rate, and greater (relative) blood volume, compared with a larger animal ...
Ecology Notes - Rochester Century High School
... substance enters living organisms such as trees from the atmosphere, water, or soil; stays for a time in the living organism; then returns to the nonliving environment. ...
... substance enters living organisms such as trees from the atmosphere, water, or soil; stays for a time in the living organism; then returns to the nonliving environment. ...
worksheet interaction between species
... 5. An organism that derives nutrition from a host causing harm to the host 6. Living together Across 4. An animal that a predator kills and eats 5. An animal that eats another animal 7. A close relationship between two organisms in which both organisms benefit 8. A living thing Word Bank: ...
... 5. An organism that derives nutrition from a host causing harm to the host 6. Living together Across 4. An animal that a predator kills and eats 5. An animal that eats another animal 7. A close relationship between two organisms in which both organisms benefit 8. A living thing Word Bank: ...