
GRADE 6 SCIENCE NOTES
... Plant tends to bend towards the direction from where the light is coming in. This is called phototropism. Roots tend to grow towards the earth and stems grow against it .This is called geotropism. Animals also show response to light, for example, cockroach and earthworm move away from light. 6. Expl ...
... Plant tends to bend towards the direction from where the light is coming in. This is called phototropism. Roots tend to grow towards the earth and stems grow against it .This is called geotropism. Animals also show response to light, for example, cockroach and earthworm move away from light. 6. Expl ...
Interdependence and adaptation
... Animals that kill and eat other animals are called predators. The animals that they eat are called prey. Predators are usually bigger and fewer in number than their prey. List five things that make a good predator: List five ways prey have adapted escape ...
... Animals that kill and eat other animals are called predators. The animals that they eat are called prey. Predators are usually bigger and fewer in number than their prey. List five things that make a good predator: List five ways prey have adapted escape ...
Available - Ggu.ac.in
... In order to be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the same time and belong to a panmictic population (one with random mating). Polymorphism as described here involves morphs of the phenotype. Polymorphism is common in nature; it is related to biodiversity, genetic variation a ...
... In order to be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the same time and belong to a panmictic population (one with random mating). Polymorphism as described here involves morphs of the phenotype. Polymorphism is common in nature; it is related to biodiversity, genetic variation a ...
The Scientific Study of Life
... Heritable variations are exposed to environmental factors that favor the reproductive success of some individuals over others ...
... Heritable variations are exposed to environmental factors that favor the reproductive success of some individuals over others ...
What is Ecology? - MsHollandScience
... and human disturbances – Primary Succession- succession on land where no soil exists or on newly exposed surfaces – Example: where these was a volcano and lava flowed ...
... and human disturbances – Primary Succession- succession on land where no soil exists or on newly exposed surfaces – Example: where these was a volcano and lava flowed ...
A - My CCSD
... which an animal becomes inactive and all body processes slow down. homeostasis: the regulation of steady, lifemaintaining conditions inside an organism or cell, despite changes in its environment. homologous: body parts in different species that are similar in origin and structure. homozygous: an or ...
... which an animal becomes inactive and all body processes slow down. homeostasis: the regulation of steady, lifemaintaining conditions inside an organism or cell, despite changes in its environment. homologous: body parts in different species that are similar in origin and structure. homozygous: an or ...
Great Barrier Reef
... still inhabit the earth and its oceans and their ancestors may have represented the predecessors for the shelled invertebrates that are found in the fossil records. These softbodied animals belong to the phylum Platyhelminthes. The most basic of these animals is the flatworm, a flat-leaf shaped worm ...
... still inhabit the earth and its oceans and their ancestors may have represented the predecessors for the shelled invertebrates that are found in the fossil records. These softbodied animals belong to the phylum Platyhelminthes. The most basic of these animals is the flatworm, a flat-leaf shaped worm ...
I. Anatomy and Physiology
... A. ANATOMY: _________ (morphology), form and how the parts are organized B. PHYSIOLOGY: _____________, what the parts do and how they work C. ______________ and ____________ are closely associated and hard to separate in the human body. How a part is put together (Anatomy) effects how that part will ...
... A. ANATOMY: _________ (morphology), form and how the parts are organized B. PHYSIOLOGY: _____________, what the parts do and how they work C. ______________ and ____________ are closely associated and hard to separate in the human body. How a part is put together (Anatomy) effects how that part will ...
UNIT 6 PART 1 ORGANIZATION IN THE BIOSPHERE
... • Interspecific competition occurs between members of different species. – Squirrels and chipmunks both eat pine seeds. ...
... • Interspecific competition occurs between members of different species. – Squirrels and chipmunks both eat pine seeds. ...
Chapter 6 - Cloudfront.net
... Endocrine glands that produce hormones that control growth and digestion… ...
... Endocrine glands that produce hormones that control growth and digestion… ...
Chapter 6 - Cloudfront.net
... Endocrine glands that produce hormones that control growth and digestion… ...
... Endocrine glands that produce hormones that control growth and digestion… ...
Chapter 2
... • Population – A group of organisms, all of one species, which can interbreed and live in the same place at the same time • Organism – An individual living thing that is made of cells, uses energy, reproduces, responds, grows and develops ...
... • Population – A group of organisms, all of one species, which can interbreed and live in the same place at the same time • Organism – An individual living thing that is made of cells, uses energy, reproduces, responds, grows and develops ...
Lecture 01 Ecology Ecology as a Science
... Populations – single organisms – basic unit in ecology - fill a niche (‘job’ or function) communities - populations of many types of organisms ecosystems: All organisms living in an area, and the physical environment (habitat) with which these organisms interact. ...
... Populations – single organisms – basic unit in ecology - fill a niche (‘job’ or function) communities - populations of many types of organisms ecosystems: All organisms living in an area, and the physical environment (habitat) with which these organisms interact. ...
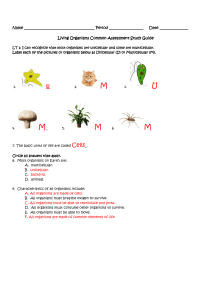
Living Organisms unit test study guide - Answer Key - Parkway C-2
... 15. Pick one organism you identified above and describe how you made your decision. -An animal is made of many complex cells, and must eat other organisms to survive. -A bacteria is made of individual simple cells, and can reproduce on its own. -A fungus can be made of either one or many complex cel ...
... 15. Pick one organism you identified above and describe how you made your decision. -An animal is made of many complex cells, and must eat other organisms to survive. -A bacteria is made of individual simple cells, and can reproduce on its own. -A fungus can be made of either one or many complex cel ...
Chapter 11 New
... and an adult stage, in which the insect reproduces. This separation of life stages has contributed to the enormous ecological diversity of insects. It has also produced remarkable specializations among the nearly 1 million species of insects that have been named. ...
... and an adult stage, in which the insect reproduces. This separation of life stages has contributed to the enormous ecological diversity of insects. It has also produced remarkable specializations among the nearly 1 million species of insects that have been named. ...
File
... What is a trophic level? Any class of organisms that occupy the same position in a food chain, such as primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumer. ...
... What is a trophic level? Any class of organisms that occupy the same position in a food chain, such as primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumer. ...
Symbiosis Resource Mutualism Parasitism
... B. the change in an abiotic factor in its environment. C. its need to find a new habitat. D. the change in a biotic factor in its environment. ____ 2. An organism’s niche is A. the range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which it uses those conditions. B ...
... B. the change in an abiotic factor in its environment. C. its need to find a new habitat. D. the change in a biotic factor in its environment. ____ 2. An organism’s niche is A. the range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which it uses those conditions. B ...
Human Body Test 12/16 [1388442]
... A. They do not need any substance from outside of the cell. B. They are able to perform all necessary functions within one cell. C. They do not need to perform more than one function to survive. 14. Fish are multi-celled organisms with specialized cells. What would most ...
... A. They do not need any substance from outside of the cell. B. They are able to perform all necessary functions within one cell. C. They do not need to perform more than one function to survive. 14. Fish are multi-celled organisms with specialized cells. What would most ...
Ecology Word Search
... 1. This is a type of organism that goes through photosynthesis to produce it’s own source of energy. ...
... 1. This is a type of organism that goes through photosynthesis to produce it’s own source of energy. ...
Components of an Ecosystem.b
... What would happen to an ecosystem if there were no more bugs? S7L4 ...
... What would happen to an ecosystem if there were no more bugs? S7L4 ...
Chapter 9 Sponges, Cnidarians, and Worms - RubygirlScience6-7-8
... Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ 31. Most animals are invertebrates. _________________________ ____ 32. The body parts of animals with radial symmetry are arranged in a circle. _________________________ _ ...
... Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ 31. Most animals are invertebrates. _________________________ ____ 32. The body parts of animals with radial symmetry are arranged in a circle. _________________________ _ ...



















![Human Body Test 12/16 [1388442]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/020444861_1-5f310fa9844f0b2fa5e006a0adbe59b7-300x300.png)


