Ch. 02 - HCC Learning Web
... • The chemical behavior of an atom is determined by the distribution of electrons in electron shells • The periodic table of the elements shows the electron distribution for each element ...
... • The chemical behavior of an atom is determined by the distribution of electrons in electron shells • The periodic table of the elements shows the electron distribution for each element ...
contents 2002 MAY
... cumulenes using RHF wave functions with 31-G basis set using Gaussian –94. Semi-empirical calculations(CNDO/2) are performed to elicit the trend of chlorination. Chlorination of cumulenes brings out some interesting properties such as lowering of energy, redistribution of charge density, stability o ...
... cumulenes using RHF wave functions with 31-G basis set using Gaussian –94. Semi-empirical calculations(CNDO/2) are performed to elicit the trend of chlorination. Chlorination of cumulenes brings out some interesting properties such as lowering of energy, redistribution of charge density, stability o ...
Honors Mid-Term Review Sheet
... Honors Chemistry Mid-Term Review Sheet **You must complete the entire review sheet to receive credit, and you must answer the questions on your own paper. Do not put your answers on this sheet! You do not need to write the questions, but you must SHOW YOUR WORK for any math problem. Chapter 1 1. Def ...
... Honors Chemistry Mid-Term Review Sheet **You must complete the entire review sheet to receive credit, and you must answer the questions on your own paper. Do not put your answers on this sheet! You do not need to write the questions, but you must SHOW YOUR WORK for any math problem. Chapter 1 1. Def ...
INERT GASES -
... contribution. The net force operating on the represel ktative molecule can be expressed as a "two-body" force, acting between the molecule on one hand and its neighbors on the oth er. The bulk property is then obtained by adding up these effects for all the molecules which are present, assuming that ...
... contribution. The net force operating on the represel ktative molecule can be expressed as a "two-body" force, acting between the molecule on one hand and its neighbors on the oth er. The bulk property is then obtained by adding up these effects for all the molecules which are present, assuming that ...
Chapter 3 – Stoichiometry of Formulas and Equations This chapter
... By convention, percent composition is almost always reported to a maximum accuracy of hundredths of a percent, even though the calculation may be more accurate. This is because percent composition calculations are usually used in the determination of the identity of unknown materials. It is quite di ...
... By convention, percent composition is almost always reported to a maximum accuracy of hundredths of a percent, even though the calculation may be more accurate. This is because percent composition calculations are usually used in the determination of the identity of unknown materials. It is quite di ...
Low-Angle Light Scattering (LALS) for Molecular Weight
... weight in gel permeation chromatography (GPC) experiments is now commonplace. The attraction for most users is that the molecular weight is measured from the light-scattering (LS) detector signal directly, avoiding the need to use polymer or protein standards to calibrate the GPC elution volume. In ...
... weight in gel permeation chromatography (GPC) experiments is now commonplace. The attraction for most users is that the molecular weight is measured from the light-scattering (LS) detector signal directly, avoiding the need to use polymer or protein standards to calibrate the GPC elution volume. In ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... The density of liquid ethanol (C2H5OH) is 0.790 g/mL. Calculate the number of molecules in a 35.0 mL sample of liquid ethanol. (NOTE: You CAN’T use 22.4 L/mol since this is NOT a ...
... The density of liquid ethanol (C2H5OH) is 0.790 g/mL. Calculate the number of molecules in a 35.0 mL sample of liquid ethanol. (NOTE: You CAN’T use 22.4 L/mol since this is NOT a ...
Chapter 2
... When two atoms that differ in electronegativity bond, they do not share the electron pair equally and they form a polar covalent bond. o The bonds between oxygen and hydrogen in water are polar covalent because oxygen has a much higher electronegativity than does hydrogen. o Compounds with a polar c ...
... When two atoms that differ in electronegativity bond, they do not share the electron pair equally and they form a polar covalent bond. o The bonds between oxygen and hydrogen in water are polar covalent because oxygen has a much higher electronegativity than does hydrogen. o Compounds with a polar c ...
Chapter 5 - U of L Class Index
... e.g. Elemental analysis of an unknown sample was found to contain 24.27% C, 4.075% H, and 71.65% Cl. What is the empirical formula of the unknown sample? Given that the unknown sample has a molar mass of 98.95 g/mol, what is its molecular formula? ...
... e.g. Elemental analysis of an unknown sample was found to contain 24.27% C, 4.075% H, and 71.65% Cl. What is the empirical formula of the unknown sample? Given that the unknown sample has a molar mass of 98.95 g/mol, what is its molecular formula? ...
N5 Chemistry Course Specification 2017-18 session
... Isotopes are defined as atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers, or as atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Nuclide notation is used to show the atomic number, mass number (and charge) of atoms (ions) from which the number of protons, electron ...
... Isotopes are defined as atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers, or as atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Nuclide notation is used to show the atomic number, mass number (and charge) of atoms (ions) from which the number of protons, electron ...
Unit 1 Review, pages 138–145
... 79. (a) Hydrogen is included in the same column of the periodic table as the alkali metals because it contains one valence electron, as alkali metals do. (b) Hydrogen is not considered to be an alkali metal because it does not have the same physical properties as the alkali metals. 80. (a) The peri ...
... 79. (a) Hydrogen is included in the same column of the periodic table as the alkali metals because it contains one valence electron, as alkali metals do. (b) Hydrogen is not considered to be an alkali metal because it does not have the same physical properties as the alkali metals. 80. (a) The peri ...
File
... The plum pudding model of the atom by J. J. Thomson, who discovered the electron in 1897, was proposed in 1904 before the discovery of the atomic nucleus in order to add the electron to the atomic model. In this model, the atom is composed of electrons (which Thomson still called "corpuscles", thoug ...
... The plum pudding model of the atom by J. J. Thomson, who discovered the electron in 1897, was proposed in 1904 before the discovery of the atomic nucleus in order to add the electron to the atomic model. In this model, the atom is composed of electrons (which Thomson still called "corpuscles", thoug ...
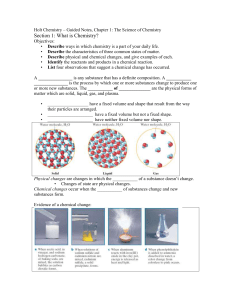
Holt Chemistry – Guided Notes, Chapter 1
... • Describe ways in which chemistry is a part of your daily life. • Describe the characteristics of three common states of matter. • Describe physical and chemical changes, and give examples of each. • Identify the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. • List four observations that suggest a ...
... • Describe ways in which chemistry is a part of your daily life. • Describe the characteristics of three common states of matter. • Describe physical and chemical changes, and give examples of each. • Identify the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. • List four observations that suggest a ...
Eperimental studies of V.Ostwald and J.van Hoff
... although the basic chemistry had been patented some 64 years earlier by Kuhlmann, when it was probably of only academic interest due to the lack of a significant source of ammonia. That may have still been the state of affairs in 1902, although things were due to change dramatically in the second ha ...
... although the basic chemistry had been patented some 64 years earlier by Kuhlmann, when it was probably of only academic interest due to the lack of a significant source of ammonia. That may have still been the state of affairs in 1902, although things were due to change dramatically in the second ha ...
Document
... There are three significant reasons to study chemistry. First chemistry has important practical application in the society. The development of life saving drugs in one and a complete list would touch upon most areas of modern technology. Second chemistry is an intellectual enterprise, a way of expl ...
... There are three significant reasons to study chemistry. First chemistry has important practical application in the society. The development of life saving drugs in one and a complete list would touch upon most areas of modern technology. Second chemistry is an intellectual enterprise, a way of expl ...
urbano, mariajose
... Emergent properties, such as the kinds and number of bonds carbon will form, are determined by their tetravalent electron configuration. • It makes large, complex molecules possible. The carbon atom is a central point from which the molecule branches off into four directions. • It gives carbon coval ...
... Emergent properties, such as the kinds and number of bonds carbon will form, are determined by their tetravalent electron configuration. • It makes large, complex molecules possible. The carbon atom is a central point from which the molecule branches off into four directions. • It gives carbon coval ...
Presentation Maths Curriculum Evening 2017 final version
... Can you see any issues with these calculations? ...
... Can you see any issues with these calculations? ...
Algebra 2
... Find the value of the discriminant “D”, and then tell how many solutions equation has and what type of solutions (rational, irrational, or imaginary) 13. 2x2 – 8x + 9 = 0 ...
... Find the value of the discriminant “D”, and then tell how many solutions equation has and what type of solutions (rational, irrational, or imaginary) 13. 2x2 – 8x + 9 = 0 ...
Unit 3: Bonding and Nomenclature Content Outline: Chemical
... A. These are forces or attractions between molecules of solids or liquids mainly, but can be gases too. B. They vary in strength; but are generally weaker than chemical bonds, as there is no real physical interaction like there is in bonds…hence the term forces. C. These forces usually affect the bo ...
... A. These are forces or attractions between molecules of solids or liquids mainly, but can be gases too. B. They vary in strength; but are generally weaker than chemical bonds, as there is no real physical interaction like there is in bonds…hence the term forces. C. These forces usually affect the bo ...
51 Draw a Lewis electron-dot diagram for a
... Many breads are made by adding yeast to dough, causing the dough to rise. Yeast is a type of microorganism that produces the catalyst zymase, which converts glucose, C6H12O6, to ethanol and carbon dioxide gas. The balanced equation for this reaction is shown below. ...
... Many breads are made by adding yeast to dough, causing the dough to rise. Yeast is a type of microorganism that produces the catalyst zymase, which converts glucose, C6H12O6, to ethanol and carbon dioxide gas. The balanced equation for this reaction is shown below. ...
ap chemistry chapter 8 bonding
... by much research data. However, some data suggests that electrons are delocalized. That is, they are not associated with a particular atom in a molecule. ...
... by much research data. However, some data suggests that electrons are delocalized. That is, they are not associated with a particular atom in a molecule. ...
Chemistry - Sanskriti School
... Unit X : s-Block Elements (Alkali and Alkaline earth metals) Group 1 and Group 2 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, anomalous properties of the first element of each group, diagonal relationship, trends in the variation of properties (such as ionization enthalpy, a ...
... Unit X : s-Block Elements (Alkali and Alkaline earth metals) Group 1 and Group 2 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, anomalous properties of the first element of each group, diagonal relationship, trends in the variation of properties (such as ionization enthalpy, a ...
Carefully detach the last page. It is the Data Sheet.
... carbon dioxide and water are the only products. What is the coefficient of O2 when the chemical equation 17 When the hydrides of the group 16 elements are representing the combustion reaction is balanced using arranged in order of increasing boiling point, the order is the smallest whole number coef ...
... carbon dioxide and water are the only products. What is the coefficient of O2 when the chemical equation 17 When the hydrides of the group 16 elements are representing the combustion reaction is balanced using arranged in order of increasing boiling point, the order is the smallest whole number coef ...
Review for Final Exam - Short Answer and Problems
... How many hydrogen atoms are there in this sample? ...
... How many hydrogen atoms are there in this sample? ...