Balance this equation:
... The diagram shows iron oxide, Fe2O3, and carbon monoxide, CO reacting to form iron and carbon dioxide. Which of the following is the correct full balanced chemical equation for the reaction depicted? ...
... The diagram shows iron oxide, Fe2O3, and carbon monoxide, CO reacting to form iron and carbon dioxide. Which of the following is the correct full balanced chemical equation for the reaction depicted? ...
Chemistry 1a Fall 2005
... The grade for the lecture component will be based on the following: first midterm (125 points), the remaining two midterms (175 points per exam) and the final exam (275 points). The grade for the laboratory component will be based on your lab reports and a short lab final given at the end of the sem ...
... The grade for the lecture component will be based on the following: first midterm (125 points), the remaining two midterms (175 points per exam) and the final exam (275 points). The grade for the laboratory component will be based on your lab reports and a short lab final given at the end of the sem ...
Chapter 3
... – how much reactant is consumed and how much product is formed – coefficients must be consistent with the Law of Conservation of Mass; atoms are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. – i.e. chemical equation must be balanced ...
... – how much reactant is consumed and how much product is formed – coefficients must be consistent with the Law of Conservation of Mass; atoms are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. – i.e. chemical equation must be balanced ...
Optimization_2016_JS
... What is optimization? • Optimization = Finding the best way of doing something • The overall problem usually consists of a multitude of decisions that are made simultaneously (decision variables) • The “goodness” of a certain set of decisions is measured by a numerical value called the objective fu ...
... What is optimization? • Optimization = Finding the best way of doing something • The overall problem usually consists of a multitude of decisions that are made simultaneously (decision variables) • The “goodness” of a certain set of decisions is measured by a numerical value called the objective fu ...
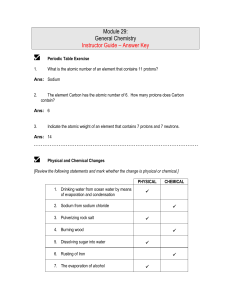
Module 29: General Chemistry Instructor Guide – Answer Key
... area away from sources of heat, moisture and incompatibilities. Always add the caustic to water while stirring; never the reverse. Containers of this material may be hazardous when empty since they retain product residues (dust, solids); observe all warnings and precautions listed for the product. D ...
... area away from sources of heat, moisture and incompatibilities. Always add the caustic to water while stirring; never the reverse. Containers of this material may be hazardous when empty since they retain product residues (dust, solids); observe all warnings and precautions listed for the product. D ...
Chapter 3 Review: Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions Will
... The coefficients of a chemical equation can represent the relationship of molecules or moles. These coefficients DO NOT in any way show mass relationships. 13. Distinguish between products and reactants in a chemical equation The products are on the right side of the chemical equation. These a ...
... The coefficients of a chemical equation can represent the relationship of molecules or moles. These coefficients DO NOT in any way show mass relationships. 13. Distinguish between products and reactants in a chemical equation The products are on the right side of the chemical equation. These a ...
... summarised below (see also Refs 7,8). Natta and co-workers prepared polyacetylene in 1958 by polymerising acetylene in hexane using Et3Al/Ti(OPr)4 (Et= ethyl, Pr=propyl) as a catalyst. Though the resulting material was highly crystalline and of regular structure, it was a black, air-sensitive, infus ...
SOL Review Part 3 Nomenclature reactions
... ► If the anion is an element, change its ending to -ide; if the anion is a polyatomic ion, simply write the name of the polyatomic ion. ► If the cation can have more than one possible charge, write the charge as a Roman numeral in parentheses. ...
... ► If the anion is an element, change its ending to -ide; if the anion is a polyatomic ion, simply write the name of the polyatomic ion. ► If the cation can have more than one possible charge, write the charge as a Roman numeral in parentheses. ...
Honors Chemistry / SAT II
... particles and electrons arranged in concentric shells around the nucleus.” This description most clearly fits the atomic theory proposed by (D) Thomson (A) Bohr (B) Rutherford (E) Avogadro (C) Dalton 2487. The maximum number of electrons possible in the second energy level of an atom is (D) 18 (A) 8 ...
... particles and electrons arranged in concentric shells around the nucleus.” This description most clearly fits the atomic theory proposed by (D) Thomson (A) Bohr (B) Rutherford (E) Avogadro (C) Dalton 2487. The maximum number of electrons possible in the second energy level of an atom is (D) 18 (A) 8 ...
Accelerated Chemistry 6.2 Notes Teacher
... This is typically the only number given in the problem. This is your starting point. Write it down! Then write “x _________”. This will be the first conversion factor ratio. ...
... This is typically the only number given in the problem. This is your starting point. Write it down! Then write “x _________”. This will be the first conversion factor ratio. ...
Chemistry STAAR Review File
... Atoms combine in new ways during a chemical change. When elements react, their atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios. Two criteria are usually applied to any theory. First, does it agree with facts which are already known? Second, does it predict new relationships and stimulate additional obs ...
... Atoms combine in new ways during a chemical change. When elements react, their atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios. Two criteria are usually applied to any theory. First, does it agree with facts which are already known? Second, does it predict new relationships and stimulate additional obs ...
CHEMISTRY 101 Name Mock Final Exam Spring 2014 Signature Dr
... Ionization energies are generally endothermic. “Lower in energy” also means “more stable”. The ground state is the lowest energy state. In an exothermic chemical reaction, the products are more stable than the reactants. All of the above statements (a-d) are true. ...
... Ionization energies are generally endothermic. “Lower in energy” also means “more stable”. The ground state is the lowest energy state. In an exothermic chemical reaction, the products are more stable than the reactants. All of the above statements (a-d) are true. ...
Moles - University of Leicester
... 6) Look at the numbers in column 5. Check that they are all whole numbers. If so, copy them into column 6. If any of them are not whole numbers, multiply all of them by the lowest number needed to make them all whole numbers and write these in column 6. 7) Write out the empirical formula by using th ...
... 6) Look at the numbers in column 5. Check that they are all whole numbers. If so, copy them into column 6. If any of them are not whole numbers, multiply all of them by the lowest number needed to make them all whole numbers and write these in column 6. 7) Write out the empirical formula by using th ...
Summer_Assignment_AP_Chemistry_TW 2015
... Watch your stoichiometry. A lot of problems will be set up perfectly within the problem itself, so keep your eyes peeled. Memorize strong acids and bases. They ionize 100%, and are therefore very important. It's okay if you don't get something right the first time. Try again and again, until you can ...
... Watch your stoichiometry. A lot of problems will be set up perfectly within the problem itself, so keep your eyes peeled. Memorize strong acids and bases. They ionize 100%, and are therefore very important. It's okay if you don't get something right the first time. Try again and again, until you can ...
Ch1small - Rutgers University
... • Skim topics in the text before they are covered in lecture. Read the Intro and Summary first. • After lecture, carefully read the topics covered in class. Sample exercises (in the chapter) Practice exercises (at end of chapter) ...
... • Skim topics in the text before they are covered in lecture. Read the Intro and Summary first. • After lecture, carefully read the topics covered in class. Sample exercises (in the chapter) Practice exercises (at end of chapter) ...
Lecture Notes 1 - Rutgers University
... • Skim topics in the text before they are covered in lecture. Read the Intro and Summary first. Then match the next day’s lecture notes to the text. • After lecture, carefully re-read the topics covered in class. Sample exercises (in the chapter) Practice exercises (at end of chapter) ...
... • Skim topics in the text before they are covered in lecture. Read the Intro and Summary first. Then match the next day’s lecture notes to the text. • After lecture, carefully re-read the topics covered in class. Sample exercises (in the chapter) Practice exercises (at end of chapter) ...
15anespp
... topics at AS and A2 level Chemistry. It is based on the requirements of the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other examination boards. Individual students may use the material at home for revision purposes or it may be used for classroom teaching if an interactive white board is availa ...
... topics at AS and A2 level Chemistry. It is based on the requirements of the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other examination boards. Individual students may use the material at home for revision purposes or it may be used for classroom teaching if an interactive white board is availa ...