The Physics, Chemistry and Perception of Colored Flames
... “sodium”; Cu in CuCl is “copper”. The nonmetal name has its ending changed to “ide”. Thus fluorine in NaF is “fluoride”, chlorine in CuCl is “chloride” and oxygen in FeO is “oxide”. When a metal, like copper, is capable of combining in different proportions with the same non-metal elements, like chl ...
... “sodium”; Cu in CuCl is “copper”. The nonmetal name has its ending changed to “ide”. Thus fluorine in NaF is “fluoride”, chlorine in CuCl is “chloride” and oxygen in FeO is “oxide”. When a metal, like copper, is capable of combining in different proportions with the same non-metal elements, like chl ...
Starter S-30
... The key moles can be converted to grams grams can be converted to moles Volume – remember that one mole of gas at STP is 22.4L ...
... The key moles can be converted to grams grams can be converted to moles Volume – remember that one mole of gas at STP is 22.4L ...
10/18/11 - Note: Once it is downloaded, click SET
... What’s involved? Periodic table, electron, atomic number Electrons are arranged in orbitals around the nucleus Things to know: -Hund’s Rule, Aufbau Principle, Pauli’s Exclusion Principle -Electron Dot- shows how many valence electrons it has. -SPDF (orbitals) S- 1- up to 2 electrons P- 3- up to 6 el ...
... What’s involved? Periodic table, electron, atomic number Electrons are arranged in orbitals around the nucleus Things to know: -Hund’s Rule, Aufbau Principle, Pauli’s Exclusion Principle -Electron Dot- shows how many valence electrons it has. -SPDF (orbitals) S- 1- up to 2 electrons P- 3- up to 6 el ...
Chapter 3
... atoms are very very small particles and we can not count it or weight it easily that because it contains huge number of atoms. For example the smallest thing we can see by our nicked eyes contains about 1016 atom, it is huge number is not?!!!! It is clear that we can not weight a single atom, but as ...
... atoms are very very small particles and we can not count it or weight it easily that because it contains huge number of atoms. For example the smallest thing we can see by our nicked eyes contains about 1016 atom, it is huge number is not?!!!! It is clear that we can not weight a single atom, but as ...
Module 9 Methods for Structure Determination Lecture 24 UV
... due to a similar fragmentation where one of the benzylic C-H is replaced by methyl group. Similarly, when an alkyl group attached to the benzene ring is a propyl group or larger, Mclafferty rearrangement occurs to give fragments. Using butyl benzene the effect of McLafferty rearrangement can be show ...
... due to a similar fragmentation where one of the benzylic C-H is replaced by methyl group. Similarly, when an alkyl group attached to the benzene ring is a propyl group or larger, Mclafferty rearrangement occurs to give fragments. Using butyl benzene the effect of McLafferty rearrangement can be show ...
chapter 4 review_package
... When 51.0 grams of NH3 is burned in an excess of oxygen, 52.65 g of water are produced. i. Calculate the theoretical yield of H2O. ...
... When 51.0 grams of NH3 is burned in an excess of oxygen, 52.65 g of water are produced. i. Calculate the theoretical yield of H2O. ...
Unit 2 – Quantities Review
... b. sulfanilamide: 41.86% carbon, 4.65% hydrogen, 16.28% nitrogen,18.60% oxygen, and 18.60% sulfur. 23. Phosphorus combines with oxygen to form two oxides. Find the empirical formula for each oxide of phosphorus if the percentage composition for each is: a. 43.6% oxygen b. 56.6% oxygen 24. Propane is ...
... b. sulfanilamide: 41.86% carbon, 4.65% hydrogen, 16.28% nitrogen,18.60% oxygen, and 18.60% sulfur. 23. Phosphorus combines with oxygen to form two oxides. Find the empirical formula for each oxide of phosphorus if the percentage composition for each is: a. 43.6% oxygen b. 56.6% oxygen 24. Propane is ...
Multiple Pathways To Success Quarter 3 Learning Module
... Students will identify five types of balanced equations including synthesis,decomposition, single replacement, double replacement and combustion. Students will balance equations and identify types of reactions including including synthesis,decomposition, single replacement, double replacement and co ...
... Students will identify five types of balanced equations including synthesis,decomposition, single replacement, double replacement and combustion. Students will balance equations and identify types of reactions including including synthesis,decomposition, single replacement, double replacement and co ...
Chapter 12 Stoichiometry - Ponder Independent School District
... Stoichiometry is… Greek for “measuring elements” Pronounced “stoy kee ahm uh tree” Defined ...
... Stoichiometry is… Greek for “measuring elements” Pronounced “stoy kee ahm uh tree” Defined ...
AP Chemistry - luckyscience
... Mercury poisoning is a debilitating disease that is often fatal. In the human body, mercury reacts with essential enzymes leading to irreversible inactivity of these enzymes. If the amount of mercury in a polluted lake is 00.4000 micrograms Hg per milliliter, what is the total mass in kilograms of ...
... Mercury poisoning is a debilitating disease that is often fatal. In the human body, mercury reacts with essential enzymes leading to irreversible inactivity of these enzymes. If the amount of mercury in a polluted lake is 00.4000 micrograms Hg per milliliter, what is the total mass in kilograms of ...
NCERT Solution - Mywayteaching
... Lattice energy is directly proportional to the charge carried by an ion. When a metal combines with oxygen, the lattice energy of the oxide involving O2− ion is much more than the oxide involving O− ion. Hence, the oxide having O2− ions are more stable than oxides having O−. Hence, we can say that f ...
... Lattice energy is directly proportional to the charge carried by an ion. When a metal combines with oxygen, the lattice energy of the oxide involving O2− ion is much more than the oxide involving O− ion. Hence, the oxide having O2− ions are more stable than oxides having O−. Hence, we can say that f ...
Numerical analysis of Richards` problem for water penetration in
... was then effectively used to solve the resulting equations. Ross (2003) introduced an efficient non-iterative solution for Richards’ equation using soil property descriptions as proposed by Brooks and Corey (1964). In his method, Ross used a space and time discretization scheme in order to derive a ...
... was then effectively used to solve the resulting equations. Ross (2003) introduced an efficient non-iterative solution for Richards’ equation using soil property descriptions as proposed by Brooks and Corey (1964). In his method, Ross used a space and time discretization scheme in order to derive a ...
2 - Ponder ISD
... Stoichiometry is… Greek for “measuring elements” Pronounced “stoy kee ahm uh tree” Defined as: calculations of the quantities in chemical reactions, based on a balanced equation. ...
... Stoichiometry is… Greek for “measuring elements” Pronounced “stoy kee ahm uh tree” Defined as: calculations of the quantities in chemical reactions, based on a balanced equation. ...
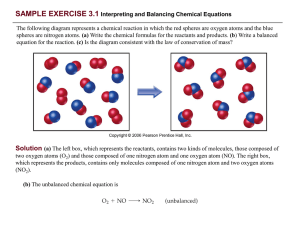
PRACTICE EXERCISE - Needham.K12.ma.us
... Comment: Notice that in balancing this equation, we moved back and forth placing a coefficient in front of H2O then NaOH, and finally Na. In balancing equations, we often find ourselves following this pattern of moving back and forth from one side of the arrow to the other, placing coefficients firs ...
... Comment: Notice that in balancing this equation, we moved back and forth placing a coefficient in front of H2O then NaOH, and finally Na. In balancing equations, we often find ourselves following this pattern of moving back and forth from one side of the arrow to the other, placing coefficients firs ...
James Ruse with Solutions
... Use balanced ionic equations to demonstrate how one of the above compounds can behave as an amphiprotic substance. ...
... Use balanced ionic equations to demonstrate how one of the above compounds can behave as an amphiprotic substance. ...
AP Chemistry Syllabus - Old Mill High School
... understanding of fundamentals and competence in dealing with chemical problems. Course Description AP Chemistry is a year-long course designed to prepare students to perform well on the AP Chemistry exam and to be equivalent to the general chemistry course usually taken during the first year of coll ...
... understanding of fundamentals and competence in dealing with chemical problems. Course Description AP Chemistry is a year-long course designed to prepare students to perform well on the AP Chemistry exam and to be equivalent to the general chemistry course usually taken during the first year of coll ...
Tutorial – Mass mole conversions Std 3e
... This tells you how many moles of O2 will be needed for each mole of H2 you have. But, we were given grams of H2 so we have to change from grams to moles before we can use the mole ratio. So we use the gmw (gram molecular weight) of H2 to do that. The gmw of H2 can be retrieved from the periodic tabl ...
... This tells you how many moles of O2 will be needed for each mole of H2 you have. But, we were given grams of H2 so we have to change from grams to moles before we can use the mole ratio. So we use the gmw (gram molecular weight) of H2 to do that. The gmw of H2 can be retrieved from the periodic tabl ...