Chemistry - Bulletin < Brown
... How does life work at the molecular level? This question is at the core of the concentration program Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. In earlier years of this discipline, the focus was on structure and function of proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates and small molecules such as vitamins ...
... How does life work at the molecular level? This question is at the core of the concentration program Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. In earlier years of this discipline, the focus was on structure and function of proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates and small molecules such as vitamins ...
Chapter
... found in the compound, the numbers of their atoms, order of atom attachment, and the kind of attachment – they do not directly describe the 3-dimensional shape, but an experienced chemist can make a good guess at it – use lines to represent covalent bonds – each line describes the number of electron ...
... found in the compound, the numbers of their atoms, order of atom attachment, and the kind of attachment – they do not directly describe the 3-dimensional shape, but an experienced chemist can make a good guess at it – use lines to represent covalent bonds – each line describes the number of electron ...
Chapter 3
... Begin with what you are given. You have 4.8 mol H2 4.8 mol H2 x 2 mol NH3 = 3.2 mol NH3 3 mol H2 3.2 mol NH3 x 17.0 g NH3 = 54.4 g NH3 ...
... Begin with what you are given. You have 4.8 mol H2 4.8 mol H2 x 2 mol NH3 = 3.2 mol NH3 3 mol H2 3.2 mol NH3 x 17.0 g NH3 = 54.4 g NH3 ...
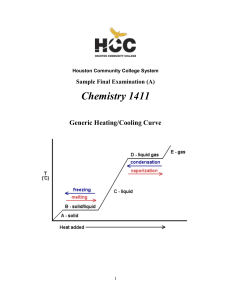
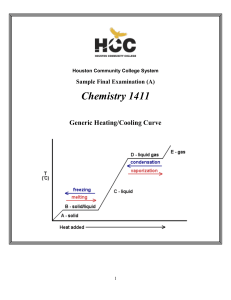
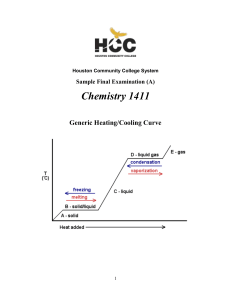
1411FINALSAMPLE+KEY - Houston Community College
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
CHEM-1411 Final Practice Exam
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
chemistry - Textbooks Online
... and Marie Lavoisier and by John Dalton on the chemistry of air and the atomic nature of matter paved the way for modern chemistry. During the nineteenth century chemists worked steadily towards an understanding of the relationships between the different chemical elements and the way they react toget ...
... and Marie Lavoisier and by John Dalton on the chemistry of air and the atomic nature of matter paved the way for modern chemistry. During the nineteenth century chemists worked steadily towards an understanding of the relationships between the different chemical elements and the way they react toget ...
CP - Supplemental Activities
... http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/Physical_Chemistry/Quantum_Mechanics/05.5%3A_Particle_in_Boxes/3.5%3A_Quan tum_Mechanics_of_Some_Simple_Systems! ...
... http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/Physical_Chemistry/Quantum_Mechanics/05.5%3A_Particle_in_Boxes/3.5%3A_Quan tum_Mechanics_of_Some_Simple_Systems! ...
CHEMISTRY 123-07 Midterm #1 – Answer key October 14, 2010
... PART II: SHORT ANSWER (Each short answer question has a 1-point value!!) 31. Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per volume of solution in liters. 32. Ions that contain atoms of more than one element are called polyatomic ions. 33. Proton donors are known as Brønsted acids. 34. A co ...
... PART II: SHORT ANSWER (Each short answer question has a 1-point value!!) 31. Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per volume of solution in liters. 32. Ions that contain atoms of more than one element are called polyatomic ions. 33. Proton donors are known as Brønsted acids. 34. A co ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Compounds
... electrical conductors (the flow of electricity is simply the flow of charged particles, like ions or electrons). Examples include H2(g), CO2(g), H2O( l ), C6H14( l ), and C12H22O11(s). ...
... electrical conductors (the flow of electricity is simply the flow of charged particles, like ions or electrons). Examples include H2(g), CO2(g), H2O( l ), C6H14( l ), and C12H22O11(s). ...
Chapter 12
... The formula of ethanol is therefore C0.50H1.5O0.25 We divide the subscripts by 0.25 (the smallest subscript) The empirical formula will be C2H6O To calculate the actual, molecular formula we must know the approximate molar mass of the compound in addition to its empirical formula. Example: 3.11. ...
... The formula of ethanol is therefore C0.50H1.5O0.25 We divide the subscripts by 0.25 (the smallest subscript) The empirical formula will be C2H6O To calculate the actual, molecular formula we must know the approximate molar mass of the compound in addition to its empirical formula. Example: 3.11. ...
Chapter 12
... The formula of ethanol is therefore C0.50H1.5O0.25 We divide the subscripts by 0.25 (the smallest subscript) The empirical formula will be C2H6O To calculate the actual, molecular formula we must know the approximate molar mass of the compound in addition to its empirical formula. Example: 3.11. ...
... The formula of ethanol is therefore C0.50H1.5O0.25 We divide the subscripts by 0.25 (the smallest subscript) The empirical formula will be C2H6O To calculate the actual, molecular formula we must know the approximate molar mass of the compound in addition to its empirical formula. Example: 3.11. ...
BSc Honours chemistry CBCS Syllabus 2016-17
... (i) Ionic bond: General characteristics, types of ions, size effects, radius ratio rule and its limitations. Packing of ions in crystals.Born-Landé equation with derivation and importance of Kapustinskii expression for lattice energy.Madelung constant, Born-Haber cycle and its application, Solvation ...
... (i) Ionic bond: General characteristics, types of ions, size effects, radius ratio rule and its limitations. Packing of ions in crystals.Born-Landé equation with derivation and importance of Kapustinskii expression for lattice energy.Madelung constant, Born-Haber cycle and its application, Solvation ...
IChO 35 Theoretical Exam
... The muon () is a subatomic particle of the lepton family which has same charge and magnetic behavior as the electron, but has a different mass and is unstable, i.e., it disintegrates into other particles within microseconds after its creation. Here you will attempt to determine the mass of the muon ...
... The muon () is a subatomic particle of the lepton family which has same charge and magnetic behavior as the electron, but has a different mass and is unstable, i.e., it disintegrates into other particles within microseconds after its creation. Here you will attempt to determine the mass of the muon ...
1411FINALSAMPLEs and Key
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
CP Chemistry - Final Exam Review KEY
... A chemical change results in a new, different substance, while a physical change does not. Chemical changes are shown with bubbling, color change, precipitate formation, temperature change and a substance “disappearing.” What is the law of conservation of mass? Give an example to explain it. The ...
... A chemical change results in a new, different substance, while a physical change does not. Chemical changes are shown with bubbling, color change, precipitate formation, temperature change and a substance “disappearing.” What is the law of conservation of mass? Give an example to explain it. The ...
department of pure and applied chemistry
... of English for academic purposes. The focus of this course is academic writing and information literacy skills. Broadly, the course covers the use of English for academic discourse, use of library skills with particular reference to information literacy skills for academic success. The use of Englis ...
... of English for academic purposes. The focus of this course is academic writing and information literacy skills. Broadly, the course covers the use of English for academic discourse, use of library skills with particular reference to information literacy skills for academic success. The use of Englis ...
Ceramics for catalysis
... Commercial catalysts must possess sufficient mechanical strength to resist losses as a result of crushing (in packed bed operation) or attrition (in reactors involving vigorous agitation). High surface areas can be attained either by fabricating small particles or clusters where the surface-to-volum ...
... Commercial catalysts must possess sufficient mechanical strength to resist losses as a result of crushing (in packed bed operation) or attrition (in reactors involving vigorous agitation). High surface areas can be attained either by fabricating small particles or clusters where the surface-to-volum ...
Chapter 6 - Sites @ Suffolk University
... : When hydrogen molecules and oxygen molecules react to form water molecules, the atoms form different bonds to make new molecules. The total number of atoms remains the same because the same atoms are present before and after the reaction. But this equation as we have written it is an unbalanced eq ...
... : When hydrogen molecules and oxygen molecules react to form water molecules, the atoms form different bonds to make new molecules. The total number of atoms remains the same because the same atoms are present before and after the reaction. But this equation as we have written it is an unbalanced eq ...
wiley_ch6_Chemical_Equilibrium
... Almost all systems come to equilibrium Where equilibrium lies depends on system Some systems’ equilibrium hard to detect Essentially no reactants or no products present Jespersen/Brady/Hyslop ...
... Almost all systems come to equilibrium Where equilibrium lies depends on system Some systems’ equilibrium hard to detect Essentially no reactants or no products present Jespersen/Brady/Hyslop ...
SUPPLEMENTAL PROBLEMS FOR CHEM 110
... The reaction is exothermic with ΔH = −46.2 kJ. The reaction is endothermic with ΔH = −92.4 kJ. The reaction is exothermic with ΔH = 92.4 kJ. The reaction is endothermic with ΔH = 92.4 kJ. The reaction is endothermic with ΔH = 46.2 kJ. ...
... The reaction is exothermic with ΔH = −46.2 kJ. The reaction is endothermic with ΔH = −92.4 kJ. The reaction is exothermic with ΔH = 92.4 kJ. The reaction is endothermic with ΔH = 92.4 kJ. The reaction is endothermic with ΔH = 46.2 kJ. ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry
... Physical versus Chemical Changes Physical changes- changes that do not change the original composition of the substance. Changes in state such as boiling or melting are physical changes. Changes involving an alteration in the form of the substance such as grinding or tearing are physical changes. Bo ...
... Physical versus Chemical Changes Physical changes- changes that do not change the original composition of the substance. Changes in state such as boiling or melting are physical changes. Changes involving an alteration in the form of the substance such as grinding or tearing are physical changes. Bo ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry
... Physical versus Chemical Changes Physical changes- changes that do not change the original composition of the substance. Changes in state such as boiling or melting are physical changes. Changes involving an alteration in the form of the substance such as grinding or tearing are physical changes. Bo ...
... Physical versus Chemical Changes Physical changes- changes that do not change the original composition of the substance. Changes in state such as boiling or melting are physical changes. Changes involving an alteration in the form of the substance such as grinding or tearing are physical changes. Bo ...