Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology II BY 32
... stimulates GH release in response to low blood sugar, increased levels of stress i.e. exercise and increases in levels of some amino acids. • GH: causes cells in the liver, muscle, cartilage, bones and other tissues to release (IGF’s): • Insulin like growth factors. (Anabolic) – Skeletal muscle: inc ...
... stimulates GH release in response to low blood sugar, increased levels of stress i.e. exercise and increases in levels of some amino acids. • GH: causes cells in the liver, muscle, cartilage, bones and other tissues to release (IGF’s): • Insulin like growth factors. (Anabolic) – Skeletal muscle: inc ...
Chapter 25 The Endocrine Glands
... Panhypopituitarism: failure of secretion of all hormones. Secondary hypofunction of all target organs. Pituitary dwarfism: deficiency of growth hormone. Diabetes insipidus: lack of ADH causes excretion of large volume of extremely dilute urine. Pituitary tumors. Overproduction of growth hormone: cau ...
... Panhypopituitarism: failure of secretion of all hormones. Secondary hypofunction of all target organs. Pituitary dwarfism: deficiency of growth hormone. Diabetes insipidus: lack of ADH causes excretion of large volume of extremely dilute urine. Pituitary tumors. Overproduction of growth hormone: cau ...
Endocrine System
... Classification of Hormones Peptide hormones Formed from chains of amino acids Most of out body’s hormones are peptide hormones Longer chains are called protein hormones Example is growth hormone Steroid hormones Type of lipid derived from cholesterol Example is testosterone Biogen ...
... Classification of Hormones Peptide hormones Formed from chains of amino acids Most of out body’s hormones are peptide hormones Longer chains are called protein hormones Example is growth hormone Steroid hormones Type of lipid derived from cholesterol Example is testosterone Biogen ...
CHAPTER 1 3
... Glands that controi the rate ofchemical reactions, help transport substances through cell membranes, and help reguiate fluid and electrolye balance ...
... Glands that controi the rate ofchemical reactions, help transport substances through cell membranes, and help reguiate fluid and electrolye balance ...
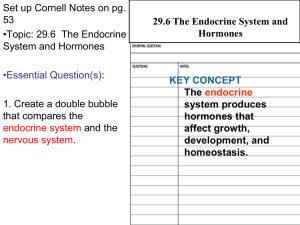
29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones
... collection of physically disconnected organs • Control growth, development, and responds to your environment ...
... collection of physically disconnected organs • Control growth, development, and responds to your environment ...
Endocrine Lecture Test Questions – Set 5
... Abnormal fat distribution, muscle atrophy, hyperglycemia, hypertension and immune suppression, would indicate: a. myxedema b. diabetes mellitus c. hypoadrenalism (Addison’s disease) d. hyperadrenalism (Cushing’s syndrome) e. hyperthyroidism (Graves disease) ...
... Abnormal fat distribution, muscle atrophy, hyperglycemia, hypertension and immune suppression, would indicate: a. myxedema b. diabetes mellitus c. hypoadrenalism (Addison’s disease) d. hyperadrenalism (Cushing’s syndrome) e. hyperthyroidism (Graves disease) ...
Endocrine System
... Hypothyroidism- deficiency of thyroid secretion Hyperthyroidism- Excess of thyroid secretion Hashimoto’s thyroiditis- Autoimmune disorder, immune system attacks thyroid can lead to Goiter’s Grave’s disease- Autoimmune disorder, hyperthyroidism. ...
... Hypothyroidism- deficiency of thyroid secretion Hyperthyroidism- Excess of thyroid secretion Hashimoto’s thyroiditis- Autoimmune disorder, immune system attacks thyroid can lead to Goiter’s Grave’s disease- Autoimmune disorder, hyperthyroidism. ...
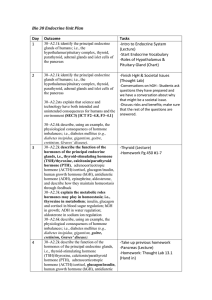
Bio 30 Endocrine Unit Plan Day Outcome Tasks 1 30–A2.1k identify
... 30–A2.2sts explain that science and technology have both intended and unintended consequences for humans and the environment (SEC3) [ICT F2–4.8, F3–4.1] ...
... 30–A2.2sts explain that science and technology have both intended and unintended consequences for humans and the environment (SEC3) [ICT F2–4.8, F3–4.1] ...
Chapter 11 The Endocrine System - Linn
... • Explain how negative and positive feedback mechanisms regulate secretion of endocrine hormones • Mechanisms of endocrine disorders • Identify the principal functions of each major endocrine hormone and describe the conditions that may result from hyposecretion or hypersecretion ...
... • Explain how negative and positive feedback mechanisms regulate secretion of endocrine hormones • Mechanisms of endocrine disorders • Identify the principal functions of each major endocrine hormone and describe the conditions that may result from hyposecretion or hypersecretion ...
chapter 18 the endocrine system
... 31. Upon entering the blood, steroid and thyroid hormones a. circulate freely as separate molecules b. attach to specific transport proteins c. combine with lipid carrier molecules d. react chemically with carbohydrates to inactivate them 32. The toxin of the cholera bacteria is very damaging to th ...
... 31. Upon entering the blood, steroid and thyroid hormones a. circulate freely as separate molecules b. attach to specific transport proteins c. combine with lipid carrier molecules d. react chemically with carbohydrates to inactivate them 32. The toxin of the cholera bacteria is very damaging to th ...
Posterior Pituitary Disorders
... on the breath, marked dehydration from polyuria CO 2. Hyperosmolar Non-Ketotic Coma: NIDDM, in elderly patients, precipitated with infection, altered consciousness 3. Hypoglycemic Coma (insulin shock): IDDM, serum glucose due to: either insulin dosage or delay in ingestion of a meal or phy ...
... on the breath, marked dehydration from polyuria CO 2. Hyperosmolar Non-Ketotic Coma: NIDDM, in elderly patients, precipitated with infection, altered consciousness 3. Hypoglycemic Coma (insulin shock): IDDM, serum glucose due to: either insulin dosage or delay in ingestion of a meal or phy ...
January 2015 Newsletter - Endocrine System
... suppress the release of various hormone messages to the other glands. The pituitary gland is also responsible endocrine system. Eating fish twice for secreting growth hormones. a week will aid in keeping a balanced endocrine system. ...
... suppress the release of various hormone messages to the other glands. The pituitary gland is also responsible endocrine system. Eating fish twice for secreting growth hormones. a week will aid in keeping a balanced endocrine system. ...
Chapter 45. - RMC Science Home
... hormones made by the hypothalamus. Both hormones act directly on muscles and kidneys (rather than affecting other endocrine glands) Anterior Pituitary – produce their own hormones, several act on other endocrine glands ...
... hormones made by the hypothalamus. Both hormones act directly on muscles and kidneys (rather than affecting other endocrine glands) Anterior Pituitary – produce their own hormones, several act on other endocrine glands ...
The Endocrine System
... • And - if there is an in mineralocorticoids as well – A serious electolyte imbalance will occur due to the potassium excretion by the kidney, which results in hypokalemia. ...
... • And - if there is an in mineralocorticoids as well – A serious electolyte imbalance will occur due to the potassium excretion by the kidney, which results in hypokalemia. ...
Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... • Contracts muscles in uterine wall and those associated with milk-secreting glands • Produced by the hypothalamus and secreted by neurosecretory cells in the posterior pituitary in response to uterine and vaginal wall stretching and stimulation of breasts ...
... • Contracts muscles in uterine wall and those associated with milk-secreting glands • Produced by the hypothalamus and secreted by neurosecretory cells in the posterior pituitary in response to uterine and vaginal wall stretching and stimulation of breasts ...
File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... In this exercise, you will determine the identity of an unknown hormone by observing the effect it has on the organs of the male rat. The data for this lab were compiled from seven pairs of male rats; one pair was the control group and the remaining six pairs were experimental groups. In each set, t ...
... In this exercise, you will determine the identity of an unknown hormone by observing the effect it has on the organs of the male rat. The data for this lab were compiled from seven pairs of male rats; one pair was the control group and the remaining six pairs were experimental groups. In each set, t ...
Endocrine System Jeopardy - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... gland that develops from tissue in embryonic mouth and grows up toward brain is called… What is the anterior pituitary? ...
... gland that develops from tissue in embryonic mouth and grows up toward brain is called… What is the anterior pituitary? ...
Endocrine System Jeopardy
... gland that develops from tissue in embryonic mouth and grows up toward brain is called… What is the anterior pituitary? ...
... gland that develops from tissue in embryonic mouth and grows up toward brain is called… What is the anterior pituitary? ...
2,3,4-Anterior Pituitary 12017-02-05 00:361.9 MB
... mammary gland and milk synthesis (production) during lactation. PL inhibits GnRH, FSH and LH secretion. PL antagonizes the actions of FSH and LH. Thus, ovulation is often inhibited by breast feeding. Effects in males: In males, PL is involved in testicular function. ...
... mammary gland and milk synthesis (production) during lactation. PL inhibits GnRH, FSH and LH secretion. PL antagonizes the actions of FSH and LH. Thus, ovulation is often inhibited by breast feeding. Effects in males: In males, PL is involved in testicular function. ...
45_InstGuide_AR
... adeno- 5 gland; -hypo 5 below (adenohypophysis: also called the anterior pituitary, a gland positioned at the base of the hypothalamus) andro- 5 male; -gen 5 produce (androgens: the principal male steroid hormones, ...
... adeno- 5 gland; -hypo 5 below (adenohypophysis: also called the anterior pituitary, a gland positioned at the base of the hypothalamus) andro- 5 male; -gen 5 produce (androgens: the principal male steroid hormones, ...
hypothalamic-pituitary axis
... • Regulation of gametogenesis • Males: – Sertoli cells – development of spermatozoa – Inhibited by inhibin ...
... • Regulation of gametogenesis • Males: – Sertoli cells – development of spermatozoa – Inhibited by inhibin ...
L7 - Endocrine system - Moodle
... https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:1808_The_Anterior_Pituitary_Complex.jpg https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:1807_The_Posterior_Pituitary_Complex.jpg ...
... https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:1808_The_Anterior_Pituitary_Complex.jpg https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:1807_The_Posterior_Pituitary_Complex.jpg ...
Hypothalamus - pituitary
... the sympathetic nervous system made up of modified neuron somas. It secretes catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine) in response to sympathetic stimulation. Their effects mimic those of the sympathetic nervous system but last longer because they are secreted into the blood. They a ...
... the sympathetic nervous system made up of modified neuron somas. It secretes catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine) in response to sympathetic stimulation. Their effects mimic those of the sympathetic nervous system but last longer because they are secreted into the blood. They a ...
Clues
... 38. Glands embedded in the posterior portion of the thyroid gland. 41. Hormone produced by the thymus gland. 43. Anterior pituitary hormone that stimulates the growth of bones and muscles. (abbr.) 45. Disorder that occurs due to hypersecretion of GH in adults. 46. Hormone produced by the posterior p ...
... 38. Glands embedded in the posterior portion of the thyroid gland. 41. Hormone produced by the thymus gland. 43. Anterior pituitary hormone that stimulates the growth of bones and muscles. (abbr.) 45. Disorder that occurs due to hypersecretion of GH in adults. 46. Hormone produced by the posterior p ...