Thyroid function and thyroid drugs
... . Panel D, in the absence of an antithyroid drug, the iodinating intermediate reacts with specific tyrosine residues in thyroglobulin (Tg) to form monoiodotyrosine and diiodotyrosine. Subsequent intramolecular coupling of MIT and DIT forms triiodothyronine, and the coupling of two DIT molecules for ...
... . Panel D, in the absence of an antithyroid drug, the iodinating intermediate reacts with specific tyrosine residues in thyroglobulin (Tg) to form monoiodotyrosine and diiodotyrosine. Subsequent intramolecular coupling of MIT and DIT forms triiodothyronine, and the coupling of two DIT molecules for ...
Local network regulation of orexin neurons in the lateral hypothalamus
... the LH/PFA. Orexin neurons not only send projections to remote brain areas but also contribute to the local network where they release multiple neurotransmitters to modulate its activity. These neurotransmitters have opposing actions, whose balance is determined by the amount released and postsynapt ...
... the LH/PFA. Orexin neurons not only send projections to remote brain areas but also contribute to the local network where they release multiple neurotransmitters to modulate its activity. These neurotransmitters have opposing actions, whose balance is determined by the amount released and postsynapt ...
Topic: Ecological Issues Aim : How do we take part in solving
... Stimulates the release of egg in females; stimulates secretion of sex hormones (testosterone, estrogen and progesterone) ...
... Stimulates the release of egg in females; stimulates secretion of sex hormones (testosterone, estrogen and progesterone) ...
Cushing's Disease
... Cortisol levels on Metyrapone 250mg nocte 0900 – 514nmol/l 1200 – 674nmol/l 1430 – 620nmol/l 1700 – 493nmol/l Mean -- 575nmol/l ...
... Cortisol levels on Metyrapone 250mg nocte 0900 – 514nmol/l 1200 – 674nmol/l 1430 – 620nmol/l 1700 – 493nmol/l Mean -- 575nmol/l ...
Essentials in the neuronal organization of the CNS
... Anatomy Department finds essential to appreciate the structure and function of the central nervous system. It is important to see clearly, however, that this handout does not substitute for the textbooks, but it can be used best in combination with the texts and the illustrations found in them. It w ...
... Anatomy Department finds essential to appreciate the structure and function of the central nervous system. It is important to see clearly, however, that this handout does not substitute for the textbooks, but it can be used best in combination with the texts and the illustrations found in them. It w ...
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone TSH Lecture NO. 2nd
... • Thyrotropin is synthesized by the RER of the thyrotropes of the ant. Pit. as Prohormone • It loses signal peptidase in RER and carbohydrate is added both in RER and Golgi • Both α and β chain are interlinked which is important for the bioactivity of the TSH • TSH undergoes post translational modif ...
... • Thyrotropin is synthesized by the RER of the thyrotropes of the ant. Pit. as Prohormone • It loses signal peptidase in RER and carbohydrate is added both in RER and Golgi • Both α and β chain are interlinked which is important for the bioactivity of the TSH • TSH undergoes post translational modif ...
smarter approach - Integrative Health Matters
... thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). The main function of these hormones is to increase metabolic activity throughout the body. ...
... thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). The main function of these hormones is to increase metabolic activity throughout the body. ...
The dorsal raphe nucleus—From silver stainings to a role in
... The dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) is a bilateral, heterogenous brainstem nucleus, located mainly in the ventral part of the periaqueductal gray matter of the midbrain. A majority of the nucleus' neurons utilize its major neurotransmitter, serotonin, but several other transmitters are also present. It c ...
... The dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) is a bilateral, heterogenous brainstem nucleus, located mainly in the ventral part of the periaqueductal gray matter of the midbrain. A majority of the nucleus' neurons utilize its major neurotransmitter, serotonin, but several other transmitters are also present. It c ...
Title: RECEPTORS of THYROID HORMONES Running title
... interacting with TRs and other nuclear receptors, but they also serve as platforms for the recruitment of secondary coactivators (York and O'Malley 2010). The p160 family of coactivators shows a conserved structure, with a nuclear receptor-interacting domain (RID) in their central region. The RID co ...
... interacting with TRs and other nuclear receptors, but they also serve as platforms for the recruitment of secondary coactivators (York and O'Malley 2010). The p160 family of coactivators shows a conserved structure, with a nuclear receptor-interacting domain (RID) in their central region. The RID co ...
THE PEDUNCULOPONTINE NUCLEUS: Towards a Functional
... varies according to the frequency of stimulation (from no response to a prolonged response), even when the duration of the stimulus remained constant (Garcia-Rill et al., 2001). These variable responses may relate to variations in the co-release of neurotransmitters from PPN terminals. In addition t ...
... varies according to the frequency of stimulation (from no response to a prolonged response), even when the duration of the stimulus remained constant (Garcia-Rill et al., 2001). These variable responses may relate to variations in the co-release of neurotransmitters from PPN terminals. In addition t ...
Plasma thyrotropin concentration in the male pig: profile from
... male pig. An increase in plasma TSH could also conceivably contribute to Sertoli cell development since TSH can stimulate cellular activity in the immature animal (Hutson and Stocco, 1981). In adult male pigs the TSH response to TRH was reduced in May and particularly high in August. Seasonal variat ...
... male pig. An increase in plasma TSH could also conceivably contribute to Sertoli cell development since TSH can stimulate cellular activity in the immature animal (Hutson and Stocco, 1981). In adult male pigs the TSH response to TRH was reduced in May and particularly high in August. Seasonal variat ...
Course of spinocerebellar axons in the ventral and lateral funiculi of
... both sides, although less extensively in the rostral part in one of them (C254), and not completely on the right side in either of them. The termination site in sublobules VIIB and VIIIA was covered by the injection in one of them (C257). In this case there was also a very minor involvement of the p ...
... both sides, although less extensively in the rostral part in one of them (C254), and not completely on the right side in either of them. The termination site in sublobules VIIB and VIIIA was covered by the injection in one of them (C257). In this case there was also a very minor involvement of the p ...
Cortical and subcortical afferents to the nucleus reticularis tegmenti
... Labeled tracer was injected into several cortical areas. In two cases (M-1R and M-2R, not shown), injections were limited to area 17 located dorsomedial to the external calcarine fissure, and caudal to the lunate sulcus, that is, within area 17 representing central vision (Talbot & Marshall, 1941, t ...
... Labeled tracer was injected into several cortical areas. In two cases (M-1R and M-2R, not shown), injections were limited to area 17 located dorsomedial to the external calcarine fissure, and caudal to the lunate sulcus, that is, within area 17 representing central vision (Talbot & Marshall, 1941, t ...
06-pons + midbrain
... -it is involved in motor control. -It receives afferents from motor cortex of frontal lobe (cortico-rubral Fs.). -it sends efferents to spinal cord as rubrospinal tract, which cross in ventral tegmental decussation. and to inferior olivary nucleus of medulla, via central tegmental tract as rubrooliv ...
... -it is involved in motor control. -It receives afferents from motor cortex of frontal lobe (cortico-rubral Fs.). -it sends efferents to spinal cord as rubrospinal tract, which cross in ventral tegmental decussation. and to inferior olivary nucleus of medulla, via central tegmental tract as rubrooliv ...
Secretsto Exceptional Health
... Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that regulate many physical and emotional processes including movement, stress response, cognition, emotions, energy, cravings, pain and more. Functioning primarily in the central nervous system (CNS), neurotransmitters facilitate communication between the b ...
... Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that regulate many physical and emotional processes including movement, stress response, cognition, emotions, energy, cravings, pain and more. Functioning primarily in the central nervous system (CNS), neurotransmitters facilitate communication between the b ...
Neuropeptides in the Drosophila central complex in modulation of
... expressing 121y-GAL4-driven GFP. 121y-GAL4 drives GFP expression in the upper and lower part of the fb (A) and in tangential neurons ventral to the calyxes (ca) of the mushroom bodies in the median posterior protocerebrum (MPP) (D). Immunolabeling is detected in the fb (B) and in neurons in the MPP ...
... expressing 121y-GAL4-driven GFP. 121y-GAL4 drives GFP expression in the upper and lower part of the fb (A) and in tangential neurons ventral to the calyxes (ca) of the mushroom bodies in the median posterior protocerebrum (MPP) (D). Immunolabeling is detected in the fb (B) and in neurons in the MPP ...
CIGNA Specialty Pharmacy Services Growth Hormone Fax Order Form
... Has the diagnosis of Turner’s Syndrome been established by genetic testing? Yes No Please note that documentation of genetic testing is required for review of this request. ...
... Has the diagnosis of Turner’s Syndrome been established by genetic testing? Yes No Please note that documentation of genetic testing is required for review of this request. ...
Pineal Gland - Meridian Kinesiology
... Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN) of the Hypothalamus. The Pineal Gland is intricately connected to the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN) of the Hypothalamus (this accounts for its involvement in Circadian Rhythm). The Pineal Gland translates input signals such as Light and Temperature into Nerve Impulses f ...
... Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN) of the Hypothalamus. The Pineal Gland is intricately connected to the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN) of the Hypothalamus (this accounts for its involvement in Circadian Rhythm). The Pineal Gland translates input signals such as Light and Temperature into Nerve Impulses f ...
Editor-in-Chief: Olufemi E. Idowu. Neurological surgery
... • Tumours of the pituitary gland that are characterized by the absence of clinical and biochemical evidence of pituitary hormonal overproduction • Constitute 25 – 30 % of pituitary tumours • Usually histologically benign • Symptoms are usually due to size and pressure effects on the surrounding stru ...
... • Tumours of the pituitary gland that are characterized by the absence of clinical and biochemical evidence of pituitary hormonal overproduction • Constitute 25 – 30 % of pituitary tumours • Usually histologically benign • Symptoms are usually due to size and pressure effects on the surrounding stru ...
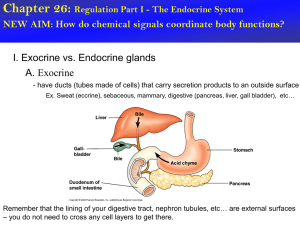
NEW AIM: How do chemical signals coordinate body functions? I
... - ductless, hormones secreted into blood - IMPORTANT: hormones circulate and influence ONLY cells with receptors for them (target cells) - >50 known hormones in vertebrates There are two main types of hormone secreting cells 1. Endocrine cells, which typically secrete their hormone in response to a ...
... - ductless, hormones secreted into blood - IMPORTANT: hormones circulate and influence ONLY cells with receptors for them (target cells) - >50 known hormones in vertebrates There are two main types of hormone secreting cells 1. Endocrine cells, which typically secrete their hormone in response to a ...
Chapter 26
... cells with receptors for them (target cells) - >50 known hormones in vertebrates There are two main types of hormone secreting cells 1. Endocrine cells, which typically secrete their hormone in response to a chemical stimulus like a ...
... cells with receptors for them (target cells) - >50 known hormones in vertebrates There are two main types of hormone secreting cells 1. Endocrine cells, which typically secrete their hormone in response to a chemical stimulus like a ...
Effect of Seasonal Temperature Changes on Thyroid Structure and
... Abstract: The thyroid is the largest and one of the phylogenetically oldest endocrine glands in vertebrate species. It is the first endocrine structure to become recognizable during an animal’s development. Although the thyroid gland is structurally conserved in all vertebrate species, exhibiting a ...
... Abstract: The thyroid is the largest and one of the phylogenetically oldest endocrine glands in vertebrate species. It is the first endocrine structure to become recognizable during an animal’s development. Although the thyroid gland is structurally conserved in all vertebrate species, exhibiting a ...
Thyrotropin releasing hormone interactions with growth hormone
... groups were tested within each time period by the LSDtest (Steel and Torrie, 1980). For Exp. 3, the maximum GH concentration achieved within the first 30 min after exercise was selected from the overall data set, and the natural log of these data were analyzed in a 6 × 6 Latin square ANOVA due to he ...
... groups were tested within each time period by the LSDtest (Steel and Torrie, 1980). For Exp. 3, the maximum GH concentration achieved within the first 30 min after exercise was selected from the overall data set, and the natural log of these data were analyzed in a 6 × 6 Latin square ANOVA due to he ...
identification of central cholinergic neurons containing both choline
... was localized immunohistochemically and AChE was localized histochemically in normal, colchicinetreated, or diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP)-treated rats, either in neighboring sections by standard procedures or simultaneously in the same sections by immunofluorescence for ChAT, followed by photogra ...
... was localized immunohistochemically and AChE was localized histochemically in normal, colchicinetreated, or diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP)-treated rats, either in neighboring sections by standard procedures or simultaneously in the same sections by immunofluorescence for ChAT, followed by photogra ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.