Chapter 1
... – provides a guide tube for the sprouting end of a severed neuron to grow through – extending axon guided to its destination as it during development – But: typically only in peripheral nervous system. ...
... – provides a guide tube for the sprouting end of a severed neuron to grow through – extending axon guided to its destination as it during development – But: typically only in peripheral nervous system. ...
Endocrine System - HCC Learning Web
... thyroid hormones, epinephrine, norepinephrine and melatonin. – Peptide hormones: are chains of amino acids, e.g. TSH, LH, FSH, ADH, Oxytocin, GH and PRL. – Lipid derivatives: are divided into two classes ‐ ...
... thyroid hormones, epinephrine, norepinephrine and melatonin. – Peptide hormones: are chains of amino acids, e.g. TSH, LH, FSH, ADH, Oxytocin, GH and PRL. – Lipid derivatives: are divided into two classes ‐ ...
Participation of γ-Aminobutyric Acid Mechanism in the Nucleus
... Mentors: Stephanie Tjen-a-looi, John Longhurst In recent years, electroacupuncture (EA) has gained recognition as a safe and effective technique for treating several cardiovascular complications, and studies have validated its ability in manipulating blood pressure and heart rate. EA application at ...
... Mentors: Stephanie Tjen-a-looi, John Longhurst In recent years, electroacupuncture (EA) has gained recognition as a safe and effective technique for treating several cardiovascular complications, and studies have validated its ability in manipulating blood pressure and heart rate. EA application at ...
HORMONE REPLACEMENT - American Hormones, Inc.
... •Different types of Natural Estrogens •Difference between “Natural” and other commonly used Estrogens •Benefits of estrogen replacement •Do estrogens increase cancer risks? •Estrogens & risk of stroke and heart attack •Estrogens and risk of Alzheimer’s •Bi-est and Tri-est •How to switch patients ove ...
... •Different types of Natural Estrogens •Difference between “Natural” and other commonly used Estrogens •Benefits of estrogen replacement •Do estrogens increase cancer risks? •Estrogens & risk of stroke and heart attack •Estrogens and risk of Alzheimer’s •Bi-est and Tri-est •How to switch patients ove ...
Thyrotropin-releasing Hormone (TRH)
... Clinical Background Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a tripeptide produced in the hypothalamus, other central nervous system sites, and the gastrointestinal tract, especially the pancreas. TRH stimulates TSH synthesis and release. Most circulating TRH, which is rapidly degraded, is probably de ...
... Clinical Background Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a tripeptide produced in the hypothalamus, other central nervous system sites, and the gastrointestinal tract, especially the pancreas. TRH stimulates TSH synthesis and release. Most circulating TRH, which is rapidly degraded, is probably de ...
Name: Period: ______ Ch 9: The Endocrine System Objectives
... Although blood-borne hormones circulates all the organs of the body, I given hormone affects only certain _____________ or _____________ (target cells or organs). In order for target cells to respond to the hormone, it must have specific ____________ ________________ on its plasma membrane, or in it ...
... Although blood-borne hormones circulates all the organs of the body, I given hormone affects only certain _____________ or _____________ (target cells or organs). In order for target cells to respond to the hormone, it must have specific ____________ ________________ on its plasma membrane, or in it ...
Chapter 16 Notes
... 3 major systems in the body work together and send messages to all cells – nervous system, immune system, and endocrine system Endocrine system is especially important during teen years – regulate growth and development Endocrine glands – ductless, tubeless organs or groups of cells that secre ...
... 3 major systems in the body work together and send messages to all cells – nervous system, immune system, and endocrine system Endocrine system is especially important during teen years – regulate growth and development Endocrine glands – ductless, tubeless organs or groups of cells that secre ...
The Endocrine System
... secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates nerve endings in the nipples which stimulates the hypothalamus to release p ...
... secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates nerve endings in the nipples which stimulates the hypothalamus to release p ...
HSa_Cocaine_high_same_as_cigerettes_new_sex
... dopamine to communicate. Normally, dopamine is released by a neuron in response to a pleasurable signal (e.g., the smell of good food), and then recycled back into the cell that released it, shutting off the signal between neurons. Cocaine acts by preventing the dopamine from being recycled, causing ...
... dopamine to communicate. Normally, dopamine is released by a neuron in response to a pleasurable signal (e.g., the smell of good food), and then recycled back into the cell that released it, shutting off the signal between neurons. Cocaine acts by preventing the dopamine from being recycled, causing ...
LESSON 14 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM INTRODUCTION The
... The endocrine system is composed of glandular tissue located in most areas of the body. They are referred to as endocrine glands because they release their specific chemicals directly into the bloodstream. These chemicals are called hormones because they can regulate many different body functions. H ...
... The endocrine system is composed of glandular tissue located in most areas of the body. They are referred to as endocrine glands because they release their specific chemicals directly into the bloodstream. These chemicals are called hormones because they can regulate many different body functions. H ...
Lect 08 Endocrine 1 - intro (KKD)
... controls reproduction regulates red blood cell production controls circulation, digestion, absorption of food ...
... controls reproduction regulates red blood cell production controls circulation, digestion, absorption of food ...
Lesion of Central Part of the Dorsomedial Nucleus Alters
... PVN functions as revealed by changes m CRH and AVP mRNA levels under basal and stress conditions It is well recognized that the basal as well as stress-induced activity of CRH neurons is under the control of brainstem ascending projections and that the mam extrahypothalamic inputs to the PVN have no ...
... PVN functions as revealed by changes m CRH and AVP mRNA levels under basal and stress conditions It is well recognized that the basal as well as stress-induced activity of CRH neurons is under the control of brainstem ascending projections and that the mam extrahypothalamic inputs to the PVN have no ...
Brain stem - Wikispaces
... cranial nerves (from 3rd to 12th). 3. Site of emergence of cranial nerves (from 3rd to 12th). 4. Contains groups of nuclei & related fibers known as reticular formation responsible for: control of level of consciousness, perception of pain, regulation of cardiovascular & respiratory systems. ...
... cranial nerves (from 3rd to 12th). 3. Site of emergence of cranial nerves (from 3rd to 12th). 4. Contains groups of nuclei & related fibers known as reticular formation responsible for: control of level of consciousness, perception of pain, regulation of cardiovascular & respiratory systems. ...
The Endocrine System
... secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates nerve endings in the nipples which stimulates the hypothalamus to release p ...
... secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates nerve endings in the nipples which stimulates the hypothalamus to release p ...
Unit-III-The-Nervous-and-Endocrine-Systems
... and decreasing potassium. Posterior pituitary gland secretes vasopressin (in addition to oxytocin), constricting blood vessels and raising blood pressure. Oxytocin in women sparks labor during pregnancy. Pancreas secretes insulin, regulating the level of sugar in the bloodstream. Ovaries secrete est ...
... and decreasing potassium. Posterior pituitary gland secretes vasopressin (in addition to oxytocin), constricting blood vessels and raising blood pressure. Oxytocin in women sparks labor during pregnancy. Pancreas secretes insulin, regulating the level of sugar in the bloodstream. Ovaries secrete est ...
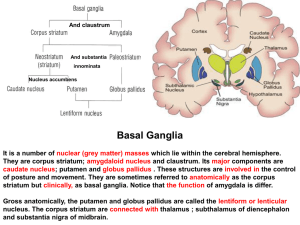
21. Basal ganglion
... The basal ganglia are referred as extrapyramidal motor system. Their function is to facilitate purposeful behaviour and movements and to inhibit unwanted or inappropriate (not suitable ) movements. When a movement is initiated from the cerebral cortex, impulses discharge not only through corticospin ...
... The basal ganglia are referred as extrapyramidal motor system. Their function is to facilitate purposeful behaviour and movements and to inhibit unwanted or inappropriate (not suitable ) movements. When a movement is initiated from the cerebral cortex, impulses discharge not only through corticospin ...
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Nicolas
... Nicolas Fenton March 3rd, 2014 Dave Champlin ...
... Nicolas Fenton March 3rd, 2014 Dave Champlin ...
Pathophysiology and basic science in hyponatraemia
... release arginine-vasopressin (AVP), the antidiuretic hormone • Volume regulation including Angiotensin II osmoregulatory gain • Unregulated AVP release by tumors or infections • Concentration and dilution of the urine ...
... release arginine-vasopressin (AVP), the antidiuretic hormone • Volume regulation including Angiotensin II osmoregulatory gain • Unregulated AVP release by tumors or infections • Concentration and dilution of the urine ...
Follicle Stimulating Hormone, FSH, clone 1038
... The antibody is specific for FSH. The specificity was ascertained by ELISA and immunohistochemistry. Follicle stimulating hormone is produced in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. Immunoglobulin type Murine IgG1 Use Staining of FSH producing cells. Instructions for use The antibody can be use ...
... The antibody is specific for FSH. The specificity was ascertained by ELISA and immunohistochemistry. Follicle stimulating hormone is produced in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. Immunoglobulin type Murine IgG1 Use Staining of FSH producing cells. Instructions for use The antibody can be use ...
Thyroid Emergencies Show Notes (Word Format)
... ©2017 EM Basic LLC, Steve Carroll DO. May freely distribute with proper attribution ...
... ©2017 EM Basic LLC, Steve Carroll DO. May freely distribute with proper attribution ...
Hormone Action Cloze
... Use your Cornell Notes, Figure 13.5 (p. 488) and Figure 13.7 (p. 490) to complete the sentences. There are two types of Hormone Action. They are classified as either ______________________or _________________________. Steroid Hormone Action Once secreted by the endocrine gland, a steroid hormone cro ...
... Use your Cornell Notes, Figure 13.5 (p. 488) and Figure 13.7 (p. 490) to complete the sentences. There are two types of Hormone Action. They are classified as either ______________________or _________________________. Steroid Hormone Action Once secreted by the endocrine gland, a steroid hormone cro ...
hormones 4
... thiroglobulin (TGB, contain tyrosine amino acid) within follicular cells & packed in secretary vesicles & release to lumen through exocytosis (material accumulated in lumen is the colloid) ...
... thiroglobulin (TGB, contain tyrosine amino acid) within follicular cells & packed in secretary vesicles & release to lumen through exocytosis (material accumulated in lumen is the colloid) ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.