Natural Hormone Replacement Therapy
... Levels must be >30ng/ml for significant benefit Optimal levels 55-70ng/ml, usually requires 4000IU Vit. D3 ...
... Levels must be >30ng/ml for significant benefit Optimal levels 55-70ng/ml, usually requires 4000IU Vit. D3 ...
8.1 endocrine gland note
... which only make up about 1 to 2 percent of the pancreas' mass. However, these Islets are very important and critical to the health of a human since they produce glucagon (alpha cells), insulin (beta cells), and somatostatin (delta cells). Glucagon and insulin are critical enzymes for maintaining a ...
... which only make up about 1 to 2 percent of the pancreas' mass. However, these Islets are very important and critical to the health of a human since they produce glucagon (alpha cells), insulin (beta cells), and somatostatin (delta cells). Glucagon and insulin are critical enzymes for maintaining a ...
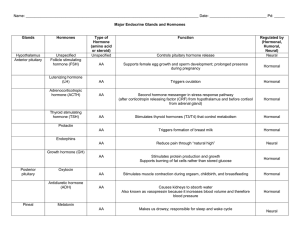
Endocrine Gland Matching
... Endocrine Gland Matching - KEY Match the hormones to the gland which secretes them. ...
... Endocrine Gland Matching - KEY Match the hormones to the gland which secretes them. ...
Hormones - Puro Health and Wellness
... another in their lives. Indirectly, it affects us all! It is reported that 60% of American women suffer from PMS. It is apparent that major interference with female hormone balance is occurring on a daily basis. A major cause of these changes is estrogen dominance. Estrogen dominance occurs when the ...
... another in their lives. Indirectly, it affects us all! It is reported that 60% of American women suffer from PMS. It is apparent that major interference with female hormone balance is occurring on a daily basis. A major cause of these changes is estrogen dominance. Estrogen dominance occurs when the ...
Digestive, Urinary and Endocrine Systems Test Review
... In the stomach, digestion of proteins begins with ____ and ____. A) Pepsin and Amylase B) Amylase and Lactase C) Hydrochloric Acid and Lipase D) Pepsin and Hydrochloric Acid ...
... In the stomach, digestion of proteins begins with ____ and ____. A) Pepsin and Amylase B) Amylase and Lactase C) Hydrochloric Acid and Lipase D) Pepsin and Hydrochloric Acid ...
File - Mr. Crabtree`s Science Class
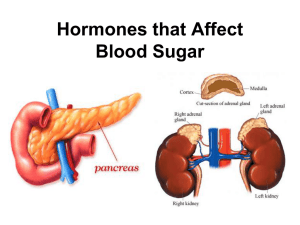
... maintenance of stable internal conditions in an organism”. Example: Blood sugar is too high, and the pancreas makes more insulin to reduce the level of insulin. Blood sugar goes down. When it is low enough, the production ceases. Insulin will be produced again when blood sugar again increases. ...
... maintenance of stable internal conditions in an organism”. Example: Blood sugar is too high, and the pancreas makes more insulin to reduce the level of insulin. Blood sugar goes down. When it is low enough, the production ceases. Insulin will be produced again when blood sugar again increases. ...
Endocrine System
... – stress = hypothalamus stimulus HRH release ACTH – adrenal gland releases corticosteroids (cortisol) • cortisol promotes synthesis of glucose (from muscle protein etc.) & suppresses immune system Homeostasis = extra fuel when not enough blood sugar or glycogen storage ...
... – stress = hypothalamus stimulus HRH release ACTH – adrenal gland releases corticosteroids (cortisol) • cortisol promotes synthesis of glucose (from muscle protein etc.) & suppresses immune system Homeostasis = extra fuel when not enough blood sugar or glycogen storage ...
Chapter 41 Endocrine System
... Pancreas The pancreas is a flattened organ located posterior to the stomach and can be classified as both an endocrine and an exocrine gland, or heterocrine gland. It is composed of two types of tissues: one of these produces and secretes digestive juices that go by way of the pancreatic duct to the ...
... Pancreas The pancreas is a flattened organ located posterior to the stomach and can be classified as both an endocrine and an exocrine gland, or heterocrine gland. It is composed of two types of tissues: one of these produces and secretes digestive juices that go by way of the pancreatic duct to the ...
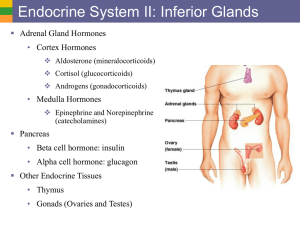
1c Endo Sys II - Inferior Glands
... Type: Steroid hormones, classified as gonadocorticoids; mostly androgens (male sex hormones, converted to testosterone in tissue) or estrogen in females, made in the zona reticularis of adreal cortex Regulation: Stimulated by ACTH from hypothalamus; inhibition mechanism unknown ...
... Type: Steroid hormones, classified as gonadocorticoids; mostly androgens (male sex hormones, converted to testosterone in tissue) or estrogen in females, made in the zona reticularis of adreal cortex Regulation: Stimulated by ACTH from hypothalamus; inhibition mechanism unknown ...
Hormonal
... Type I Insulin-dependent (used to be called juvenile onset) Pancreas doesn’t produce insulin Genetic predisposition, due to autoimmune destruction of islet cells Type II Non-insulin dependent (formerly adult onset) Also has genetic risk factors but etiology is different Due to inability of insulin t ...
... Type I Insulin-dependent (used to be called juvenile onset) Pancreas doesn’t produce insulin Genetic predisposition, due to autoimmune destruction of islet cells Type II Non-insulin dependent (formerly adult onset) Also has genetic risk factors but etiology is different Due to inability of insulin t ...
Natural Hormone Replacement Therapy
... Doctors view steroids as drugs, not hormones Long-term , low-dose treatment is actually hormone replacement (prednisone ≤7.5mg, ...
... Doctors view steroids as drugs, not hormones Long-term , low-dose treatment is actually hormone replacement (prednisone ≤7.5mg, ...
PPT File
... Major endocrine glands (Male left, female on the right.) 1. Pineal gland 2. Pituitary gland 3. Thyroid gland 4. Thymus 5. Adrenal gland 6. Pancreas 7. Ovary 8.Testis ...
... Major endocrine glands (Male left, female on the right.) 1. Pineal gland 2. Pituitary gland 3. Thyroid gland 4. Thymus 5. Adrenal gland 6. Pancreas 7. Ovary 8.Testis ...
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
... includes ACTH, alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), beta-melanocytestimulating hormone (β-MSH) and gammamelanocyte-stimulating hormone (γ-MSH); these peptides are all cleavage products of a ...
... includes ACTH, alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), beta-melanocytestimulating hormone (β-MSH) and gammamelanocyte-stimulating hormone (γ-MSH); these peptides are all cleavage products of a ...
File
... The condition is usually caused by Graves' disease, an immune system problem that causes the thyroid gland to become very active. Hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood are very low. The deficiency slows body processes. Kids and teens with t ...
... The condition is usually caused by Graves' disease, an immune system problem that causes the thyroid gland to become very active. Hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood are very low. The deficiency slows body processes. Kids and teens with t ...
Endocrine Review
... 1. Which of the following controls the activity of all the others? a. thyroid gland b. pituitary gland c. adrenal cortex d. hypothalamus e. ovaries 2. The pancreas increases its output of insulin in response to a. an increase in body temperature b. changing cycles of light and dark c. a decrease in ...
... 1. Which of the following controls the activity of all the others? a. thyroid gland b. pituitary gland c. adrenal cortex d. hypothalamus e. ovaries 2. The pancreas increases its output of insulin in response to a. an increase in body temperature b. changing cycles of light and dark c. a decrease in ...
Endocrine System Notes
... WARM UP • List the 10 organs of the endocrine system, and one hormone produced by each. ...
... WARM UP • List the 10 organs of the endocrine system, and one hormone produced by each. ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... turn on activities of different organs in the body. ...
... turn on activities of different organs in the body. ...
File
... Adrenal Medulla • Emergency gland • Part of sympathetic nervous system • Produces 2 neurohormones – Epinephrine – Norepinephrine ...
... Adrenal Medulla • Emergency gland • Part of sympathetic nervous system • Produces 2 neurohormones – Epinephrine – Norepinephrine ...
8.2 Hormones that Affect Blood Sugar - Ms. Pasic
... – Both need iodine to be produced. – Used to oxidize sugar and other nutrients. – More T4 in the blood will “boost metabolism” ...
... – Both need iodine to be produced. – Used to oxidize sugar and other nutrients. – More T4 in the blood will “boost metabolism” ...
Chapter 25 The Endocrine Glands
... Panhypopituitarism: failure of secretion of all hormones. Secondary hypofunction of all target organs. Pituitary dwarfism: deficiency of growth hormone. Diabetes insipidus: lack of ADH causes excretion of large volume of extremely dilute urine. Pituitary tumors. Overproduction of growth hormone: cau ...
... Panhypopituitarism: failure of secretion of all hormones. Secondary hypofunction of all target organs. Pituitary dwarfism: deficiency of growth hormone. Diabetes insipidus: lack of ADH causes excretion of large volume of extremely dilute urine. Pituitary tumors. Overproduction of growth hormone: cau ...
Hirsutism-A Comprehensive Update of Embryology
... Hirsutism, defined as terminal hair on the body of a female, affects 5-10% of women. Of these the commonest cause is anovulation secondary to PCOS, which is a fairly common disorder affecting 6-10%of women of reproductive age group. Although ovary is the main source of androgen excess, evidence with ...
... Hirsutism, defined as terminal hair on the body of a female, affects 5-10% of women. Of these the commonest cause is anovulation secondary to PCOS, which is a fairly common disorder affecting 6-10%of women of reproductive age group. Although ovary is the main source of androgen excess, evidence with ...
Growth Hormone
... Increases milk production Maintains corpus luteum Inhibits ovary Dopamine controls rate of release ...
... Increases milk production Maintains corpus luteum Inhibits ovary Dopamine controls rate of release ...
endocrine1
... Adrenal medullary hormones (catecholamines) Peptide hormones (peptides & proteins) Steroid Hormones (derivatives of cholesterol) ...
... Adrenal medullary hormones (catecholamines) Peptide hormones (peptides & proteins) Steroid Hormones (derivatives of cholesterol) ...