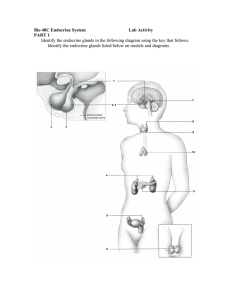
Review for endocrine system
... 15. What is the master endocrine gland? 16. What are the 2 parts of the pituitary? 17. Which part of the gland is most active? 18. What is..TSH< ACTH< LH< and FSH and what does each do? 19. What part of the pituitary just stores hormones? 20. T3 and T4 are hormones for regulating your metabolism…the ...
... 15. What is the master endocrine gland? 16. What are the 2 parts of the pituitary? 17. Which part of the gland is most active? 18. What is..TSH< ACTH< LH< and FSH and what does each do? 19. What part of the pituitary just stores hormones? 20. T3 and T4 are hormones for regulating your metabolism…the ...
3/14/13 The Endocrine System: Session 24
... The pancreas produces what two hormone that help regulate blood glucose levels? a. Insulin and GH b. GH and PRL c. Insulin and glucagon d. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) ...
... The pancreas produces what two hormone that help regulate blood glucose levels? a. Insulin and GH b. GH and PRL c. Insulin and glucagon d. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) ...
Hormones in Animals
... their own receptors thus reducing the sensitivity of the target cell to the hormone • The components of the signal transduction mechanism may also become sensitized or desensitized to the signal ...
... their own receptors thus reducing the sensitivity of the target cell to the hormone • The components of the signal transduction mechanism may also become sensitized or desensitized to the signal ...
Chapter 9 - Endocrine System Overview coordinate and directs the
... acts on just about all body cells increases ability to transport glucose across their plasma membranes glucose oxidized for energy or converted to glycogen or fat for storage as blood glucose levels fall, the stimulus for insulin release ends (negative feedback) absolutely necessary for the use of g ...
... acts on just about all body cells increases ability to transport glucose across their plasma membranes glucose oxidized for energy or converted to glycogen or fat for storage as blood glucose levels fall, the stimulus for insulin release ends (negative feedback) absolutely necessary for the use of g ...
Estimation of LH,FSH, Prolactin And TSH Levels In Polycystic
... Background &Objectives:-PCOS is the most common endocrine disorders among women between the ages of 18 and 44. It affects approximately 5% to 10% of this age group. It is one of the leading causes of poor fertility. PCOS patients usually develop thyroid disorders which have an adverse effect on fert ...
... Background &Objectives:-PCOS is the most common endocrine disorders among women between the ages of 18 and 44. It affects approximately 5% to 10% of this age group. It is one of the leading causes of poor fertility. PCOS patients usually develop thyroid disorders which have an adverse effect on fert ...
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System
... • Non-Tropic Hormones: – Prolactin stimulates mammary gland growth and milk synthesis in mammals. ...
... • Non-Tropic Hormones: – Prolactin stimulates mammary gland growth and milk synthesis in mammals. ...
Alex
... calcium levels. The hormone regulates the calcium levels in the blood by increasing the reabsorption of calcium in the kidneys and also by directing the uptake of calcium from the digestive system This gland is important for bring about healthy nerve and muscle function and bone structure ...
... calcium levels. The hormone regulates the calcium levels in the blood by increasing the reabsorption of calcium in the kidneys and also by directing the uptake of calcium from the digestive system This gland is important for bring about healthy nerve and muscle function and bone structure ...
Chapter 11 Review
... Which gland fails to produce enough of its hormone in the disease diabetes mellitus? a. Adrenal b. Hypothalamus c. Pancreas d. Parathyroid ...
... Which gland fails to produce enough of its hormone in the disease diabetes mellitus? a. Adrenal b. Hypothalamus c. Pancreas d. Parathyroid ...
File - Endocrine System
... _____ pituitary gland (pi-TOO-i-tar-ē) (also called the hypophysis) (Located on the inferior side of the brain in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone. The pituitary stalk attaches the gland to the hypothalamus portion of the brain. The pituitary gland is divided into an anterior lobe (the adenohy ...
... _____ pituitary gland (pi-TOO-i-tar-ē) (also called the hypophysis) (Located on the inferior side of the brain in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone. The pituitary stalk attaches the gland to the hypothalamus portion of the brain. The pituitary gland is divided into an anterior lobe (the adenohy ...
Hormones
... sexual characteristics Consists of endocrine glands which secretes hormones Hormones – chemical substances that regulates the activities of organs and tissues ...
... sexual characteristics Consists of endocrine glands which secretes hormones Hormones – chemical substances that regulates the activities of organs and tissues ...
endocrinology - GEOCITIES.ws
... 24 urine free cortisol (i.e.: is there cortisol in urine even at night), 2) dexamethasone test (i.e.: administer dexamethasone see if cortisol still high after some time if high confirm dx). Confirmed diagnosis: 1) Plasma ACTH detectable (i.e.: ACTH cause) / undetectable (i.e.: adrenal/stero ...
... 24 urine free cortisol (i.e.: is there cortisol in urine even at night), 2) dexamethasone test (i.e.: administer dexamethasone see if cortisol still high after some time if high confirm dx). Confirmed diagnosis: 1) Plasma ACTH detectable (i.e.: ACTH cause) / undetectable (i.e.: adrenal/stero ...
Endocrine Notes
... People with this disease consume large quantities of food but lose body fat and weight Most pronounced symptoms are enlargement of gland (GOITER) and bulging of eyeballs (EXOPHTHALMOS) Rx – total or partial removal of thyroid gland, drugs to reduce thyroxine, radiation HYPOTHYROIDISM Not eno ...
... People with this disease consume large quantities of food but lose body fat and weight Most pronounced symptoms are enlargement of gland (GOITER) and bulging of eyeballs (EXOPHTHALMOS) Rx – total or partial removal of thyroid gland, drugs to reduce thyroxine, radiation HYPOTHYROIDISM Not eno ...
Hormone testing - Theosteocenter
... (HDL), prevents bone loss, helps form collagen which benefits the appearance of the skin, improves cognitive function and increases the immune response. However, estradiol also exerts a strong proliferative effect on hormone sensitive tissues like the breast, uterus and ovary so it must be properly ...
... (HDL), prevents bone loss, helps form collagen which benefits the appearance of the skin, improves cognitive function and increases the immune response. However, estradiol also exerts a strong proliferative effect on hormone sensitive tissues like the breast, uterus and ovary so it must be properly ...
Endocrine System
... People with this disease consume large quantities of food but lose body fat and weight Most pronounced symptoms are enlargement of gland (GOITER) and bulging of eyeballs (EXOPHTHALMOS) Rx – total or partial removal of thyroid gland, drugs to reduce thyroxine, radiation HYPOTHYROIDISM Not eno ...
... People with this disease consume large quantities of food but lose body fat and weight Most pronounced symptoms are enlargement of gland (GOITER) and bulging of eyeballs (EXOPHTHALMOS) Rx – total or partial removal of thyroid gland, drugs to reduce thyroxine, radiation HYPOTHYROIDISM Not eno ...
******* 1
... newborn period or in early childhood. The milder form, called Non-classical CAH (NCAH), may cause symptoms at anytime from infancy through adulthood. NCAH is a much more common disorder than Classical CAH. When the pituitary gland senses that there is not enough cortisol present in the bloodst ...
... newborn period or in early childhood. The milder form, called Non-classical CAH (NCAH), may cause symptoms at anytime from infancy through adulthood. NCAH is a much more common disorder than Classical CAH. When the pituitary gland senses that there is not enough cortisol present in the bloodst ...
PowerPoint
... Weight loss Ravenous appetite Irritability, anxiety Fatigue Hyperactivity Graves’ disease ...
... Weight loss Ravenous appetite Irritability, anxiety Fatigue Hyperactivity Graves’ disease ...
Outline28 Reproduction
... - occurs in seminiferous tubules of testes spermatogonia → primary spermatocyte → secondary spermatocytes → spermatids → sperm meiosis I meiosis II maturation Sertoli cells - support developing spermatocytes + endocrine function blood testis barrier - tight junctions between Sertoli cells form barri ...
... - occurs in seminiferous tubules of testes spermatogonia → primary spermatocyte → secondary spermatocytes → spermatids → sperm meiosis I meiosis II maturation Sertoli cells - support developing spermatocytes + endocrine function blood testis barrier - tight junctions between Sertoli cells form barri ...
Name Chapter 18: Alterations of Hormonal Regulation I
... Some insulin production continues in type 2 diabetes mellitus, but the size and number of beta cells decrease. Initially insulin secretion may be high, but it declines with time. Low insulin and high glucagon causes hyperglycemia, but usually not ketoacidosis. Increased lipid metabolism result ...
... Some insulin production continues in type 2 diabetes mellitus, but the size and number of beta cells decrease. Initially insulin secretion may be high, but it declines with time. Low insulin and high glucagon causes hyperglycemia, but usually not ketoacidosis. Increased lipid metabolism result ...
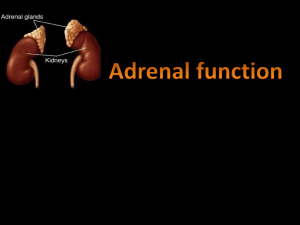
Approach to common endocrine disorders
... Cortisol functions: • help the body respond to stress • helps maintain blood pressure and cardiovascular function • helps slow the immune system's inflammatory response • helps balance the effects of insulin in breaking down sugar for energy • helps regulate the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates ...
... Cortisol functions: • help the body respond to stress • helps maintain blood pressure and cardiovascular function • helps slow the immune system's inflammatory response • helps balance the effects of insulin in breaking down sugar for energy • helps regulate the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates ...
Podcast summary chapter 15
... exopthalmos and other signs of Grave’s disease may develop. Four small parathyroid glands lie buried, behind the thyroid gland. These glands are responsible for maintaining blood calcium levels. There are other endocrine organs in the body as well. The heart, kidneys and stomach produce hormones, as ...
... exopthalmos and other signs of Grave’s disease may develop. Four small parathyroid glands lie buried, behind the thyroid gland. These glands are responsible for maintaining blood calcium levels. There are other endocrine organs in the body as well. The heart, kidneys and stomach produce hormones, as ...
Follicle-stimulating Hormone (FSH) FSH is a hormone made by the
... A blood sample is drawn from a vein. No test preparation is required, but a woman’s sample should be collected on certain days of her menstrual cycle. What Do the Abnormal Results Mean? In women, higher-than-normal FSH levels are often caused by primary ovarian failure and may be due to: Ovarian a ...
... A blood sample is drawn from a vein. No test preparation is required, but a woman’s sample should be collected on certain days of her menstrual cycle. What Do the Abnormal Results Mean? In women, higher-than-normal FSH levels are often caused by primary ovarian failure and may be due to: Ovarian a ...
Evaluation and Treatment of Women with Hirsutism
... When evaluating hirsutism, it is important to remember that it is only one sign of hyperandrogenism. Other abnormalities associated with excessive levels of androgen are listed in Table 2.6,8 Increased androgen effect that results in hirsutism can be familial, idiopathic, or caused by excess androge ...
... When evaluating hirsutism, it is important to remember that it is only one sign of hyperandrogenism. Other abnormalities associated with excessive levels of androgen are listed in Table 2.6,8 Increased androgen effect that results in hirsutism can be familial, idiopathic, or caused by excess androge ...
NOTES- Endocrine System (feedback)
... site: the target cells have receptors on them for this purpose ...
... site: the target cells have receptors on them for this purpose ...
5331 MT1 2017 review
... B. The hypothalamus secretes gonadotrophin releasing hormone to inhibit the anterior pituitary gland production of luteinizing hormone C. High levels of estradiol stimulate the anterior pituitary to release follicle stimulating hormone D. Estrogen causes a rise in temperature after ovulation E. None ...
... B. The hypothalamus secretes gonadotrophin releasing hormone to inhibit the anterior pituitary gland production of luteinizing hormone C. High levels of estradiol stimulate the anterior pituitary to release follicle stimulating hormone D. Estrogen causes a rise in temperature after ovulation E. None ...
The Endocrine System
... About 100 different hormones have been identified. The pituitary, pancreas, thyroid, adrenals, and gonads are a few of the endocrine glands. ...
... About 100 different hormones have been identified. The pituitary, pancreas, thyroid, adrenals, and gonads are a few of the endocrine glands. ...