Homogenization principle based multi
... Important requirements for homogenization using representative volume elements are imposed on the size of the RVE and on the applied boundary conditions. The size of the RVE has to be chosen large enough such that a sufficient number of inclusion particles or pores are present and the RVE really is ...
... Important requirements for homogenization using representative volume elements are imposed on the size of the RVE and on the applied boundary conditions. The size of the RVE has to be chosen large enough such that a sufficient number of inclusion particles or pores are present and the RVE really is ...
ppt
... May have several Deformational Phases May have an accompanying Metamorphic Cycles with one or more Reaction Events ...
... May have several Deformational Phases May have an accompanying Metamorphic Cycles with one or more Reaction Events ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 23, Metamorpic Textures
... May have several Deformational Phases May have an accompanying Metamorphic Cycles with one or more Reaction Events ...
... May have several Deformational Phases May have an accompanying Metamorphic Cycles with one or more Reaction Events ...
pnas1_lescar6
... almost helical diffraction pattern when diffracted along the long axis of the crystal.This behavior is also characteristic of strong tenedency of the protein to organize along two dimensions. The CTD was successfully phased from two wavelength anomalous data obtained for selenomethionine substituted ...
... almost helical diffraction pattern when diffracted along the long axis of the crystal.This behavior is also characteristic of strong tenedency of the protein to organize along two dimensions. The CTD was successfully phased from two wavelength anomalous data obtained for selenomethionine substituted ...
Lab #4: Minerals: Building Blocks of Rocks
... Composition and Structure of Minerals Isotopes and radioactive decay Mass number = sum of neutrons + protons in an atom Isotope = atom that exhibits variation in its mass number Unstable isotopes emit particles and energy in a process known as radioactive decay ...
... Composition and Structure of Minerals Isotopes and radioactive decay Mass number = sum of neutrons + protons in an atom Isotope = atom that exhibits variation in its mass number Unstable isotopes emit particles and energy in a process known as radioactive decay ...
Theoretical Modeling of Molar Volume and Thermal Expansion
... the end-member compound are of primary importance, since these properties concern the interactions between nearest-neighbor atoms. Proper values even for metastable or unstable end-members must be given in using the models. The common practice is to use as an approximation the formation energy or vo ...
... the end-member compound are of primary importance, since these properties concern the interactions between nearest-neighbor atoms. Proper values even for metastable or unstable end-members must be given in using the models. The common practice is to use as an approximation the formation energy or vo ...
mikrotehmoloogia aja..
... Because germanium had been used in the inventive work of Bardeen and Brattain, it was the object of early effort. Gordon Teal and J.B. Little10 adapted and improved a crystal-growth technique first used by J. Czochralski in 191711. (See Figures 4 and 5). The technique, which survives as today’s meth ...
... Because germanium had been used in the inventive work of Bardeen and Brattain, it was the object of early effort. Gordon Teal and J.B. Little10 adapted and improved a crystal-growth technique first used by J. Czochralski in 191711. (See Figures 4 and 5). The technique, which survives as today’s meth ...
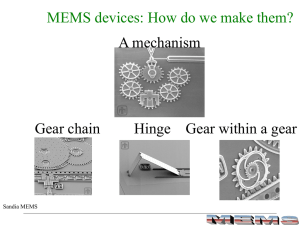
MEMS Processing
... - Amorphous/columnar grained structures: Compressive stress - Equiaxed grained structures: Tensile stress - Thick films have less stress than thinner films -ANNEALING CAN REDUCE STRESSES BY A FACTOR OF 10-100 ...
... - Amorphous/columnar grained structures: Compressive stress - Equiaxed grained structures: Tensile stress - Thick films have less stress than thinner films -ANNEALING CAN REDUCE STRESSES BY A FACTOR OF 10-100 ...
7.1 * minerals: building blocks of rocks
... Scientists who study, identify and classify rocks are called geologists. Some of the properties that geologists use to identify the minerals that make up rocks are: Colour Streak Lustre Hardness Crystal Structure Cleavage Magnetism Reaction with certain chemicals ...
... Scientists who study, identify and classify rocks are called geologists. Some of the properties that geologists use to identify the minerals that make up rocks are: Colour Streak Lustre Hardness Crystal Structure Cleavage Magnetism Reaction with certain chemicals ...
Schramm and P. Scott Hefty L. Yuan, Scott Lovell, Kevin P. Battaile
... Chlamydia are obligate intracellular bacteria and include pathogenic species for which the requisite electron transport quinone is undetermined. The metabolically active form of Chlamydia replicates within a microaerophilic environment inside a modified intracellular vacuole (9). Early speculation s ...
... Chlamydia are obligate intracellular bacteria and include pathogenic species for which the requisite electron transport quinone is undetermined. The metabolically active form of Chlamydia replicates within a microaerophilic environment inside a modified intracellular vacuole (9). Early speculation s ...
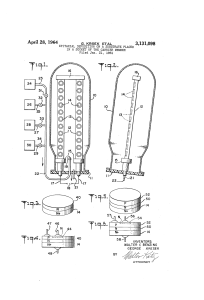
D.C. electrical conductivity measurements on ADP single crystals
... used for the growth of single crystals by slow (free) evaporation method. ADP was added with urea and thiourea separately each in six different ADP: impurity molecular ratios, viz. 1 : 0⋅000 (pure ADP), 1 : 0⋅002, 1 : 0⋅004, 1 : 0⋅006, 1 : 0⋅008 and 1 : 0⋅010. The impurity was dissolved in 3⋅5 M sol ...
... used for the growth of single crystals by slow (free) evaporation method. ADP was added with urea and thiourea separately each in six different ADP: impurity molecular ratios, viz. 1 : 0⋅000 (pure ADP), 1 : 0⋅002, 1 : 0⋅004, 1 : 0⋅006, 1 : 0⋅008 and 1 : 0⋅010. The impurity was dissolved in 3⋅5 M sol ...
Minerals - SchoolRack
... Minerals are naturally occurring from the Earth and rocks are made up from minerals ...
... Minerals are naturally occurring from the Earth and rocks are made up from minerals ...
Application of grain boundary engineering concepts
... has approximately 500 triple junctions across the coating (see Fig. l(b)). As a result, the probability of crack arrest is increased considerably, leading to a higher resistance to cracking. Several techniques are now available for producing nanocrystalline materials such as sputtering, gas condensa ...
... has approximately 500 triple junctions across the coating (see Fig. l(b)). As a result, the probability of crack arrest is increased considerably, leading to a higher resistance to cracking. Several techniques are now available for producing nanocrystalline materials such as sputtering, gas condensa ...
Mineral-Exam-parent - Windsor C
... ALL SAMPLES MUST MEET THE FOLLOWING REQUIREMENTS TO BE CLASSIFIED AS MINERAL All minerals must occur naturally ...
... ALL SAMPLES MUST MEET THE FOLLOWING REQUIREMENTS TO BE CLASSIFIED AS MINERAL All minerals must occur naturally ...
Ch 2.2 Notes - North Mac Schools
... Streak – color of mineral in powdered form Rub mineral against an unglazed tile ...
... Streak – color of mineral in powdered form Rub mineral against an unglazed tile ...
AN EFFICIENT METHOD FOR BAND STRUCTURE CALCULATIONS IN 2D PHOTONIC CRYSTALS
... Discrete versions of the variational problems (8), (9) are then obtained in the standard way by introducing for a given “discretization level” N, an approximating subspace SN ⊂ H 1 (Ω). Problem (8) is then replaced by the discrete problem: find nonzero uN ∈ SN and ω 2 such that ...
... Discrete versions of the variational problems (8), (9) are then obtained in the standard way by introducing for a given “discretization level” N, an approximating subspace SN ⊂ H 1 (Ω). Problem (8) is then replaced by the discrete problem: find nonzero uN ∈ SN and ω 2 such that ...
Crystal structure

In mineralogy and crystallography, a crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. It describes a highly ordered structure, occurring due to the intrinsic nature of its constituents to form symmetric patterns.The crystal lattice can be thought of as an array of 'small boxes' infinitely repeating in all three spatial directions. Such a unit cell is the smallest unit of volume that contains all of the structural and symmetry information to build-up the macroscopic structure of the lattice by translation.Patterns are located upon the points of a lattice, which is an array of points repeating periodically in three dimensions. The lengths of the edges of a unit cell and the angles between them are called the lattice parameters. The symmetry properties of the crystal are embodied in its space group.A crystal's structure and symmetry play a role in determining many of its physical properties, such as cleavage, electronic band structure, and optical transparency.