IDIOPATHIC HYPERTROPHIC SUBAORTIC STENOSIS (IHSS)
... • Don’t use nitroglycerin for angina pain. It dilates arteries, which may be harmful. ACTIVITY • Instructions will be provided about how much physical activity is ideal. Your ability to increase activity is dependent on your response to therapy. Don’t regard yourself as an invalid. • Strenuous activ ...
... • Don’t use nitroglycerin for angina pain. It dilates arteries, which may be harmful. ACTIVITY • Instructions will be provided about how much physical activity is ideal. Your ability to increase activity is dependent on your response to therapy. Don’t regard yourself as an invalid. • Strenuous activ ...
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
... a. Left ventricular hypertrophy b. Right ventricular hypertrophy c. An ejection click d. Systemic hypertension e. Pericardial effusion ...
... a. Left ventricular hypertrophy b. Right ventricular hypertrophy c. An ejection click d. Systemic hypertension e. Pericardial effusion ...
SORE THROAT or STREP THROAT??
... A sore throat is less likely to be strep throat if it is part of a typical cold, with runny nose, cough, sneezing, hoarseness, and similar symptoms. ...
... A sore throat is less likely to be strep throat if it is part of a typical cold, with runny nose, cough, sneezing, hoarseness, and similar symptoms. ...
CDVD Handout Stage C - Veterinary Cardiology Specialists
... arrow in the upper photo to the right, labeled “A”, represents the direction of normal blood flow from the left atrium into the left ventricular chamber. The arrow heading into the red structure (aorta), represents normal blood flow from the heart out to the body via the aorta. The last arrow pointe ...
... arrow in the upper photo to the right, labeled “A”, represents the direction of normal blood flow from the left atrium into the left ventricular chamber. The arrow heading into the red structure (aorta), represents normal blood flow from the heart out to the body via the aorta. The last arrow pointe ...
Communicable Diseases
... Bacteria/Viruses/Allergies/Substances which irritate the eye (Chlorine/Soaps) Pinkeye caused by Bacteria/Viruses are very ...
... Bacteria/Viruses/Allergies/Substances which irritate the eye (Chlorine/Soaps) Pinkeye caused by Bacteria/Viruses are very ...
Noninfectious disease
... Define the 5 different types of cancer? What is the difference between benign & ...
... Define the 5 different types of cancer? What is the difference between benign & ...
Information for Students and Physicians
... Shigellosis is an infectious disease caused by a group of bacteria called Shigella. Most who are infected with Shigella develop diarrhea, fever, and stomach cramps starting a day or two after they are exposed to the bacteria. The diarrhea is often bloody. Shigellosis usually resolves in 5 to 7 days. ...
... Shigellosis is an infectious disease caused by a group of bacteria called Shigella. Most who are infected with Shigella develop diarrhea, fever, and stomach cramps starting a day or two after they are exposed to the bacteria. The diarrhea is often bloody. Shigellosis usually resolves in 5 to 7 days. ...
Response of Immune System to Disease
... C. DISPOSAL: antibodies destroy pathogens D. IMMUNITY: some antibodies remain for future use (memory B cells) ...
... C. DISPOSAL: antibodies destroy pathogens D. IMMUNITY: some antibodies remain for future use (memory B cells) ...
Pathological Conditions: The Heart and Blood Vessels
... overcome increased resistance in arteries Vessels lose elasticity, become like solid pipes and place increased burden on heart to pump blood through body Mitral Valve Prolapse (MVP) – Improper closure of mitral valve when heart is pumping blood *Antibiotics are given at time of dental procedures t ...
... overcome increased resistance in arteries Vessels lose elasticity, become like solid pipes and place increased burden on heart to pump blood through body Mitral Valve Prolapse (MVP) – Improper closure of mitral valve when heart is pumping blood *Antibiotics are given at time of dental procedures t ...
rheumatic fever: an update - International Journal of Pharmacy and
... pharyngitis, and the clinical manifestation of the response and its severity in an individual is determined by host genetic susceptibility, the virulence of the infecting organism, and a conducive environment6, 7, 8. Although streptococci from serogroups B, C, G and F can cause pharyngitis and trigg ...
... pharyngitis, and the clinical manifestation of the response and its severity in an individual is determined by host genetic susceptibility, the virulence of the infecting organism, and a conducive environment6, 7, 8. Although streptococci from serogroups B, C, G and F can cause pharyngitis and trigg ...
Anatomy of the Cardiovascular System
... Covered by a sac called the pericardium Fibrous Pericardium – tough, loose-fitting, and inelastic Serous Pericardium – has two layers 1. Parietal layer – lines fibrous pericardium 2. Visceral layer (epicardium) – adheres to the outside of the heart. ...
... Covered by a sac called the pericardium Fibrous Pericardium – tough, loose-fitting, and inelastic Serous Pericardium – has two layers 1. Parietal layer – lines fibrous pericardium 2. Visceral layer (epicardium) – adheres to the outside of the heart. ...
Heart Anatomy Notes for students
... Blood supply that oxygenates and nourishes the heart is provided by the right and left _________________________________ that branch from the base of the ________________ and encircle the heart in the coronary sulcus (atrioventricular groove) and the junction of the atria and ventricles ...
... Blood supply that oxygenates and nourishes the heart is provided by the right and left _________________________________ that branch from the base of the ________________ and encircle the heart in the coronary sulcus (atrioventricular groove) and the junction of the atria and ventricles ...
Drugs to Treat Autoimmune Diseases
... • Genetic predisposition and environmental factors relevant • Immunoglobulins, T cell receptors, major histocompatibilty complex • T Cell Bypass- The requirement of T cells to activate B cells in order to produce large amounts of antibodies is bypassed • Molecular Mimicry- An exogenous antigen share ...
... • Genetic predisposition and environmental factors relevant • Immunoglobulins, T cell receptors, major histocompatibilty complex • T Cell Bypass- The requirement of T cells to activate B cells in order to produce large amounts of antibodies is bypassed • Molecular Mimicry- An exogenous antigen share ...
March 24 (PP)
... Negative selection eliminates self reactive lymphocytes Autoimmune diseases caused by body responding to self antigens MHC genes involved; genetically based ...
... Negative selection eliminates self reactive lymphocytes Autoimmune diseases caused by body responding to self antigens MHC genes involved; genetically based ...
Chapter 18
... flaps upward – but the flaps can only go so far up because of the chords attached. ...
... flaps upward – but the flaps can only go so far up because of the chords attached. ...
Valvular Heart Disease
... • Loud Opening S1 snap: heard at the apex when leaflets are still mobile – Due to the abrupt halt in leaflet motion in early diastole, after rapid initial rapid opening, due to fusion at the leaflet tips. – A shorter S2 to opening snap interval indicates more severe disease. ...
... • Loud Opening S1 snap: heard at the apex when leaflets are still mobile – Due to the abrupt halt in leaflet motion in early diastole, after rapid initial rapid opening, due to fusion at the leaflet tips. – A shorter S2 to opening snap interval indicates more severe disease. ...
Name Birthdate - Downriver ENT
... Name ______________________________________ Birthdate __________ Date ___________________________ Do you: ...
... Name ______________________________________ Birthdate __________ Date ___________________________ Do you: ...
Cardiovascular 22 – Heart Valve Disease
... Know the main ways in which heart valves dysfunction. Know the disease processes Understand the effects of valve dysfunction on the heart Understand the different clinical consequences of dysfunctioning heart valves. Understand the principals of treatment. ...
... Know the main ways in which heart valves dysfunction. Know the disease processes Understand the effects of valve dysfunction on the heart Understand the different clinical consequences of dysfunctioning heart valves. Understand the principals of treatment. ...
Chronic valve disease
... Dogs are commonly affected, but cats are rarely affected to a clinically significant degree. Heart valves function as check valves, ensuring efficient one-way blood flow as the heart pumps. There are four heart valves, located between the upper and lower chambers of the heart and between the lower c ...
... Dogs are commonly affected, but cats are rarely affected to a clinically significant degree. Heart valves function as check valves, ensuring efficient one-way blood flow as the heart pumps. There are four heart valves, located between the upper and lower chambers of the heart and between the lower c ...
Heart failure
... pulmonary oedema causes pleural effusion, which will usually start at the right base but be bilateral as it progresses. Look for anaemia which can exacerbate symptoms. It is important to look for the Jugular venous pulse in all patients with suspected heart failure. When the patient is at 30-45o the ...
... pulmonary oedema causes pleural effusion, which will usually start at the right base but be bilateral as it progresses. Look for anaemia which can exacerbate symptoms. It is important to look for the Jugular venous pulse in all patients with suspected heart failure. When the patient is at 30-45o the ...
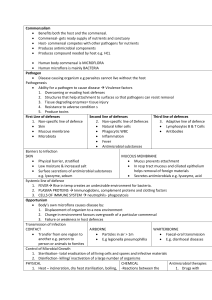
Commensalism • Benefits both the host and the commensal
... Commensal- gets ready supply of nutrients and sanctuary Host- commensal competes with other pathogens for nutrients Produces antimicrobial components Produces compound needed by host e.g. HCL Human body commensal is MICROFLORA Human microflora is mainly BACTERIA Pathogen Disease causin ...
... Commensal- gets ready supply of nutrients and sanctuary Host- commensal competes with other pathogens for nutrients Produces antimicrobial components Produces compound needed by host e.g. HCL Human body commensal is MICROFLORA Human microflora is mainly BACTERIA Pathogen Disease causin ...
Severe combined immune deficiency syndrome
... 8. Infections that do not resolve with antibiotic treatment for two or more months 9. Failure to gain weight or grow normally 10. Infections that require intravenous antibiotic treatment 11. Deep-seated infections, such as pneumonia that affects an entire lung or an abscess in the liver 12. Persiste ...
... 8. Infections that do not resolve with antibiotic treatment for two or more months 9. Failure to gain weight or grow normally 10. Infections that require intravenous antibiotic treatment 11. Deep-seated infections, such as pneumonia that affects an entire lung or an abscess in the liver 12. Persiste ...
Respiratory and Circulatory Systems
... Sponge, hydra, planaria – diffusion Earthworm – aortic arches Insect – dorsal heart Fish – 2-chambered heart Amphibian – 3 chambered heart Reptile and bird – 3+ chambered heart ...
... Sponge, hydra, planaria – diffusion Earthworm – aortic arches Insect – dorsal heart Fish – 2-chambered heart Amphibian – 3 chambered heart Reptile and bird – 3+ chambered heart ...
Rheumatic fever

Rheumatic fever, also known as acute rheumatic fever (ARF), is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a throat infection. Signs and symptoms include fever, multiple painful joints, involuntary muscle movements, and a characteristic but uncommon non itchy rash known as erythema marginatum. The heart is involved in about half of cases. Permanent damage to the heart valves, known as rheumatic heart disease (RHD), usually only occurs after multiple attacks but may occasionally occur after a single case of ARF. The damaged valves may result in heart failure. The abnormal valves also increase the risk of the person developing atrial fibrillation and infection of the valves.Acute rheumatic fever may occur following an infection of the throat by the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes. If it is untreated ARF occurs in up to three percent of people. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve the production of antibodies against a person's own tissues. Some people due to their genetics are more likely to get the disease when exposed to the bacteria than others. Other risk factors include malnutrition and poverty. Diagnosis of ARF is often based on the presence of signs and symptoms in combination with evidence of a recent streptococcal infection.Treating people who have strep throat with antibiotics, such as penicillin, decreases their risk of getting ARF. This often involves testing people with sore throats for the infection, which may not be available in the developing world. Other preventative measures include improved sanitation. In those with ARF and RHD prolonged periods of antibiotics are sometimes recommended. Gradual return to normal activities may occur following an attack. Once RHD develops, treatment is more difficult. Occasionally valve replacement surgery or repair is required. Otherwise complications are treated as per normal.Acute rheumatic fever occurs in about 325,000 children each year and about 18 million people currently have rheumatic heart disease. Those who get ARF are most often between the ages of 5 and 14, with 20% of first-time attacks occurring in adults. The disease is most common in the developing world and among indigenous peoples in the developed world. In 2013 it resulted in 275,000 deaths down from 374,000 deaths in 1990. Most deaths occur in the developing world where as many as 12.5% of people affected may die each year. Descriptions of the condition are believed to date back to at least the 5th century BCE in the writings of Hippocrates. The disease is so named because its symptoms are similar to those of some rheumatic disorders.