ch_13_the_cardiovascular_systemx
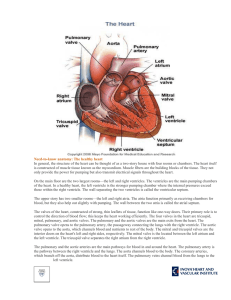
... is a double circuit: Pulmonary (lungs only) and systemic (rest of the body) Heart has 4 chambers: o 2 Atria – thin upper chambers that receive blood returning to the heart through veins.. Right and Left Atrium o 2 Ventricles – thick, muscular lower chambers. Receive blood from the atria above them. ...
... is a double circuit: Pulmonary (lungs only) and systemic (rest of the body) Heart has 4 chambers: o 2 Atria – thin upper chambers that receive blood returning to the heart through veins.. Right and Left Atrium o 2 Ventricles – thick, muscular lower chambers. Receive blood from the atria above them. ...
Heart and Vessels - Montgomery County Schools
... ●Your heart is a double pump. Circulation is a double circuit: Pulmonary (lungs only) and systemic (rest of the body) ●Heart has 4 chambers: o 2 Atria – thin upper chambers that receive blood returning to the heart through veins.. Right and Left Atrium o 2 Ventricles – thick, muscular lower chambers ...
... ●Your heart is a double pump. Circulation is a double circuit: Pulmonary (lungs only) and systemic (rest of the body) ●Heart has 4 chambers: o 2 Atria – thin upper chambers that receive blood returning to the heart through veins.. Right and Left Atrium o 2 Ventricles – thick, muscular lower chambers ...
The Inflammatory Response
... – This causes the receptor protein to change shape. Now the signal is changed into another form that the cell can recognize that will cause it to respond in a specific way. – This may occur in multiple steps called a CASCADE. ...
... – This causes the receptor protein to change shape. Now the signal is changed into another form that the cell can recognize that will cause it to respond in a specific way. – This may occur in multiple steps called a CASCADE. ...
The Human Heart
... The upper story has two smaller rooms—the left and right atria. The atria function primarily as receiving chambers for blood, but they also help out slightly with pumping. The wall between the two atria is called the atrial septum. The valves of the heart, constructed of strong, thin leaflets of tis ...
... The upper story has two smaller rooms—the left and right atria. The atria function primarily as receiving chambers for blood, but they also help out slightly with pumping. The wall between the two atria is called the atrial septum. The valves of the heart, constructed of strong, thin leaflets of tis ...
Nursing Care of the Adult with Rheumatic Disorders
... Immune system becomes hyper active and attacks normal tissue Increased production of autoantibodies Results in inflammation and brings about symptoms ...
... Immune system becomes hyper active and attacks normal tissue Increased production of autoantibodies Results in inflammation and brings about symptoms ...
Ontario introduces protocol for autopsies in unexplained sudden
... commonly overlooked disease that might also afflict family members. Dr. Michael Gollob, director of the Inherited Arrhythmia Clinic and Arrhythmia Research Laboratory at the Heart Institute, said many coroners and pathologists are not familiar with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, as ...
... commonly overlooked disease that might also afflict family members. Dr. Michael Gollob, director of the Inherited Arrhythmia Clinic and Arrhythmia Research Laboratory at the Heart Institute, said many coroners and pathologists are not familiar with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, as ...
11.1 The Heart - halkuffanatomy
... open and close heart valves. Arteries: Carries oxygenated blood away from the heart & lungs to the rest of the body. (red) Veins: Carries deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart & lungs. (blue) ...
... open and close heart valves. Arteries: Carries oxygenated blood away from the heart & lungs to the rest of the body. (red) Veins: Carries deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart & lungs. (blue) ...
Childhood Illnesses and Prevention
... Protecting children from germs and illness is not always possible, but it is our responsibility to help children avoid these illnesses as much as possible. Keeping ill children away from other children is part of that responsibility. A child should remain at home for 24 hours after having a fever, v ...
... Protecting children from germs and illness is not always possible, but it is our responsibility to help children avoid these illnesses as much as possible. Keeping ill children away from other children is part of that responsibility. A child should remain at home for 24 hours after having a fever, v ...
File
... Drained from the lungs ______ pulmonary veins left ___________ ________________ valve left ___________________ ___________ semilunar valve ___________ body tissues dumps off ________________ and picks up carbon dioxide. Cardiac Circulation Although the heart ____________________ are ...
... Drained from the lungs ______ pulmonary veins left ___________ ________________ valve left ___________________ ___________ semilunar valve ___________ body tissues dumps off ________________ and picks up carbon dioxide. Cardiac Circulation Although the heart ____________________ are ...
Heart Notes
... • Angina – heart pain due to ischemia. Usually not present when patient is resting. • Myocardial Infarction (MI) – Interruption in blood supply to a part of the heart leading to necrosis of the area. ...
... • Angina – heart pain due to ischemia. Usually not present when patient is resting. • Myocardial Infarction (MI) – Interruption in blood supply to a part of the heart leading to necrosis of the area. ...
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart can no longer pump
... heart's pumping action is lost, blood may back up in other areas of the body. Fluid builds up in the lungs, liver, gastrointestinal tract, and the arms and legs. This is called congestive heart failure. Symptoms of heart failure may include: ...
... heart's pumping action is lost, blood may back up in other areas of the body. Fluid builds up in the lungs, liver, gastrointestinal tract, and the arms and legs. This is called congestive heart failure. Symptoms of heart failure may include: ...
Heart Lab Questions
... 2. What is the muscular layer of the heart is called? 3. What is the name of the sac surrounding the heart? 4. What is the function of the heart? 5. What is the function of an artery? 6. What is the function of a vein? 7. What is the specific space in the thoracic cavity where the heart is located? ...
... 2. What is the muscular layer of the heart is called? 3. What is the name of the sac surrounding the heart? 4. What is the function of the heart? 5. What is the function of an artery? 6. What is the function of a vein? 7. What is the specific space in the thoracic cavity where the heart is located? ...
Mitral Valve Vegetation
... filling the chambers of the heart. This is necessary because neither the heart valves nor the vegetations adherent to them are supplied by blood vessels. Antibiotics are continued for a long time, typically two to six weeks. Specific drug regimens differ depending on the classification of the endoca ...
... filling the chambers of the heart. This is necessary because neither the heart valves nor the vegetations adherent to them are supplied by blood vessels. Antibiotics are continued for a long time, typically two to six weeks. Specific drug regimens differ depending on the classification of the endoca ...
Anatomy and Physiology for Emergency Care
... Physiology for Emergency Care Chapter 13 The Heart ...
... Physiology for Emergency Care Chapter 13 The Heart ...
The Heart - Northern Highlands
... The Heart Overview of Heart Anatomy: Use the following website to complete the following questions about the anatomy of the heart: http://www.worldinvisible.com/apologet/humbody/heart.htm ...
... The Heart Overview of Heart Anatomy: Use the following website to complete the following questions about the anatomy of the heart: http://www.worldinvisible.com/apologet/humbody/heart.htm ...
Title: The Cardiac Conduction System
... system generates an electric current. This current can be detected by electrodes placed on the outside of the body. This recording is called an electrocardiogram or EKG 1-The EKG is a series of up and down waves produced by the cardiac muscle fibers during each beat 2- We are used to seeing what is ...
... system generates an electric current. This current can be detected by electrodes placed on the outside of the body. This recording is called an electrocardiogram or EKG 1-The EKG is a series of up and down waves produced by the cardiac muscle fibers during each beat 2- We are used to seeing what is ...
Management
... 2 major OR 1 major and 3 minor OR all 5 minor criteria Major • +ve blood culture typical organism in 2 separate cultures or persistently +ve blood cultures • Endocardium involved • Positive echo or new valvular regurgitation ...
... 2 major OR 1 major and 3 minor OR all 5 minor criteria Major • +ve blood culture typical organism in 2 separate cultures or persistently +ve blood cultures • Endocardium involved • Positive echo or new valvular regurgitation ...
Cardiac Infections
... Clinical Presentation Spectrum of disease process Mild-to-severe Can cause sudden death Patients may also present in the subclinical phase, with minimal symptoms Can also have pericarditis (myopericarditis) ...
... Clinical Presentation Spectrum of disease process Mild-to-severe Can cause sudden death Patients may also present in the subclinical phase, with minimal symptoms Can also have pericarditis (myopericarditis) ...
File
... Describe and compare action potentials in cardiac pacemaker and contractile (ie. Muscle) cells. Name the components of the conduction system of the heart, and trace the conduction pathway. Draw a diagram of a normal electrocardiogram tracing. Name the individual waves and intervals, and indicate wha ...
... Describe and compare action potentials in cardiac pacemaker and contractile (ie. Muscle) cells. Name the components of the conduction system of the heart, and trace the conduction pathway. Draw a diagram of a normal electrocardiogram tracing. Name the individual waves and intervals, and indicate wha ...
Canine Chronic Mitral Valvular Disease Nick Schroeder DVM
... Basically, age-related degeneration develops on one of the valves on the left side of the heart, which is known as the mitral valve. This disease may also affect other valves within the heart, and the tricuspid valve (on the right side of the heart) is the next most commonly affected. Normal valve t ...
... Basically, age-related degeneration develops on one of the valves on the left side of the heart, which is known as the mitral valve. This disease may also affect other valves within the heart, and the tricuspid valve (on the right side of the heart) is the next most commonly affected. Normal valve t ...
Rheumatic fever
... ~ accompanying pericarditis with acute myocardial infarction (so-called pericarditis epistenocardiaca) ~ viral pericarditides – Coxsackie A, B; HSV; Influenza (symptomatically leading sign is thoracal pain, so it is a diagnostic problem to differentiate from an acute ...
... ~ accompanying pericarditis with acute myocardial infarction (so-called pericarditis epistenocardiaca) ~ viral pericarditides – Coxsackie A, B; HSV; Influenza (symptomatically leading sign is thoracal pain, so it is a diagnostic problem to differentiate from an acute ...
he heart - TECC Science
... Further (Flightpath C&B ): To be able to describe the function of the main structures of the human heart, describe the problems that can develop in blood vessels in the human heart, and their treatments. Suggest advantages and disadvantages of using stents and statins. Challenge Flightpath A): Expla ...
... Further (Flightpath C&B ): To be able to describe the function of the main structures of the human heart, describe the problems that can develop in blood vessels in the human heart, and their treatments. Suggest advantages and disadvantages of using stents and statins. Challenge Flightpath A): Expla ...
Rheumatic fever

Rheumatic fever, also known as acute rheumatic fever (ARF), is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a throat infection. Signs and symptoms include fever, multiple painful joints, involuntary muscle movements, and a characteristic but uncommon non itchy rash known as erythema marginatum. The heart is involved in about half of cases. Permanent damage to the heart valves, known as rheumatic heart disease (RHD), usually only occurs after multiple attacks but may occasionally occur after a single case of ARF. The damaged valves may result in heart failure. The abnormal valves also increase the risk of the person developing atrial fibrillation and infection of the valves.Acute rheumatic fever may occur following an infection of the throat by the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes. If it is untreated ARF occurs in up to three percent of people. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve the production of antibodies against a person's own tissues. Some people due to their genetics are more likely to get the disease when exposed to the bacteria than others. Other risk factors include malnutrition and poverty. Diagnosis of ARF is often based on the presence of signs and symptoms in combination with evidence of a recent streptococcal infection.Treating people who have strep throat with antibiotics, such as penicillin, decreases their risk of getting ARF. This often involves testing people with sore throats for the infection, which may not be available in the developing world. Other preventative measures include improved sanitation. In those with ARF and RHD prolonged periods of antibiotics are sometimes recommended. Gradual return to normal activities may occur following an attack. Once RHD develops, treatment is more difficult. Occasionally valve replacement surgery or repair is required. Otherwise complications are treated as per normal.Acute rheumatic fever occurs in about 325,000 children each year and about 18 million people currently have rheumatic heart disease. Those who get ARF are most often between the ages of 5 and 14, with 20% of first-time attacks occurring in adults. The disease is most common in the developing world and among indigenous peoples in the developed world. In 2013 it resulted in 275,000 deaths down from 374,000 deaths in 1990. Most deaths occur in the developing world where as many as 12.5% of people affected may die each year. Descriptions of the condition are believed to date back to at least the 5th century BCE in the writings of Hippocrates. The disease is so named because its symptoms are similar to those of some rheumatic disorders.