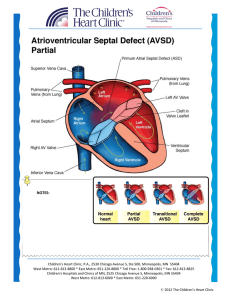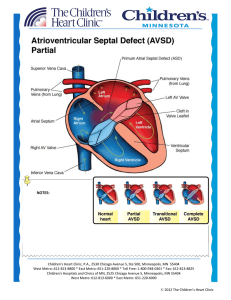
Atrioventricular Septal Defect AVSD
... Partial/Transitional: Often asymptomatic, unless mitral insufficiency is present. In the setting of mitral insufficiency, a murmur may be heard at left lower sternal border and the child may develop symptoms of congestive heart failure. Diagnostics: EKG: First degree heart block (prolonged PR in ...
... Partial/Transitional: Often asymptomatic, unless mitral insufficiency is present. In the setting of mitral insufficiency, a murmur may be heard at left lower sternal border and the child may develop symptoms of congestive heart failure. Diagnostics: EKG: First degree heart block (prolonged PR in ...
Atrioventricular Septal Defect AVSD
... Partial/Transitional: Often asymptomatic, unless mitral insufficiency is present. In the setting of mitral insufficiency, a murmur may be heard at left lower sternal border and the child may develop symptoms of congestive heart failure. Diagnostics: EKG: First degree heart block (prolonged PR in ...
... Partial/Transitional: Often asymptomatic, unless mitral insufficiency is present. In the setting of mitral insufficiency, a murmur may be heard at left lower sternal border and the child may develop symptoms of congestive heart failure. Diagnostics: EKG: First degree heart block (prolonged PR in ...
TF_Infectious Endocarditis_2015_cleaned
... One of the most difficult forms of IE to diagnose Must be suspected in the presence of frequently misleading symptoms, particularly in elderly patients Blood cultures are positive in 77% of cases Staphylococci are the most frequent pathogens The Duke criteria are difficult to apply in these patients ...
... One of the most difficult forms of IE to diagnose Must be suspected in the presence of frequently misleading symptoms, particularly in elderly patients Blood cultures are positive in 77% of cases Staphylococci are the most frequent pathogens The Duke criteria are difficult to apply in these patients ...
(3) Reporting criteria a) “Patients (confirmed cases)” In compliance
... (3) Reporting criteria a) “Patients (confirmed cases)” In compliance with Article 12 paragraph 1 of the Infectious Diseases Control Law, if a physician examines a patient with clinical characteristics as described in (2), suspects invasive pneumococcal infection from clinical findings, and makes a d ...
... (3) Reporting criteria a) “Patients (confirmed cases)” In compliance with Article 12 paragraph 1 of the Infectious Diseases Control Law, if a physician examines a patient with clinical characteristics as described in (2), suspects invasive pneumococcal infection from clinical findings, and makes a d ...
Chapter One and Two:
... Heredity: all the traits and properties that are passed along biologically from both parents to child. Resistance Skills: techniques that can help you refuse when you are urged to take part in an unsafe or unhealthful behavior. Goal: something you aim for that takes planning and work. Risk: actions ...
... Heredity: all the traits and properties that are passed along biologically from both parents to child. Resistance Skills: techniques that can help you refuse when you are urged to take part in an unsafe or unhealthful behavior. Goal: something you aim for that takes planning and work. Risk: actions ...
McCance: Pathophysiology, 6th Edition
... 4. Hemodynamic integrity of the cardiovascular system depends to a great extent on properly functioning cardiac valves. Congenital or acquired disorders that result in stenosis or incompetence or both can structurally alter the valves. 5. Characteristic heart sounds, cardiac murmurs, and systemic co ...
... 4. Hemodynamic integrity of the cardiovascular system depends to a great extent on properly functioning cardiac valves. Congenital or acquired disorders that result in stenosis or incompetence or both can structurally alter the valves. 5. Characteristic heart sounds, cardiac murmurs, and systemic co ...
Feline Heart Disease - Pride Veterinary Centre
... heart disease and not all cats with heart disease will have a murmur. Cats are also very good at hiding signs of their illness, and so their disease is often more severe by the time it is diagnosed. My Cat has been diagnosed with a cardiomyopathy – now what? There is no cure for cardiomyopathy, and ...
... heart disease and not all cats with heart disease will have a murmur. Cats are also very good at hiding signs of their illness, and so their disease is often more severe by the time it is diagnosed. My Cat has been diagnosed with a cardiomyopathy – now what? There is no cure for cardiomyopathy, and ...
Dear Parents and Guardians
... How is it treated? Strep infections are usually treated with an oral antibiotic, starting either with characteristic symptoms or after a strep test is positive. Sometimes an injection of antibiotic may also be used to treat strep. Why is it important that your child receive treatment? There are two ...
... How is it treated? Strep infections are usually treated with an oral antibiotic, starting either with characteristic symptoms or after a strep test is positive. Sometimes an injection of antibiotic may also be used to treat strep. Why is it important that your child receive treatment? There are two ...
Immune Response
... Cells recognize invaders and release chemicals called histamines These cause increased blood flow (which causes swelling) to get more white blood cells WBCs attack pathogens Lymph nodes may also swell with fluid when they fight infection ...
... Cells recognize invaders and release chemicals called histamines These cause increased blood flow (which causes swelling) to get more white blood cells WBCs attack pathogens Lymph nodes may also swell with fluid when they fight infection ...
Dilated cardiomyopathy
... There are varying stages of dilated cardiomyopathy. Dogs may be considered predisposed to the disease but not have any signs of it yet. An example of this would be a high risk breed such as a Doberman Pinscher or a Great Dane or a dog who has a family history of the disease. In these cases, routine ...
... There are varying stages of dilated cardiomyopathy. Dogs may be considered predisposed to the disease but not have any signs of it yet. An example of this would be a high risk breed such as a Doberman Pinscher or a Great Dane or a dog who has a family history of the disease. In these cases, routine ...
before movements ceased. The (Swedo SE et al. Sydenham`s dance
... a 6-year period showed that 61% had Bannwarth's syndrome with paresis, a painful lymphocytic meningoradiculitis, during the second stage of the disease. CNS involvement in the early stages was rare; 4% had myelitis and 1 patient had acute encephalitis. The final morbidity after a 3 year median follo ...
... a 6-year period showed that 61% had Bannwarth's syndrome with paresis, a painful lymphocytic meningoradiculitis, during the second stage of the disease. CNS involvement in the early stages was rare; 4% had myelitis and 1 patient had acute encephalitis. The final morbidity after a 3 year median follo ...
Valvular Heart Disease - Home
... Blood regurgitates from LV into LA. LV volume increases progressively as severity of MR increases. – Increased blood return to LA: pulmonary veins + regurgitant volume from previous beat. ...
... Blood regurgitates from LV into LA. LV volume increases progressively as severity of MR increases. – Increased blood return to LA: pulmonary veins + regurgitant volume from previous beat. ...
Comparison of two patients with mitral stenosis and importance of
... end result of carditis, which affects 30% to 45% of patients with acute rheumatic fever (3). Injury to the cardiac valves, which is the hallmark of rheumatic heart disease, may be chronic and progressive and, in conjunction with left ventricular dysfunction, can lead to congestive heart failure and ...
... end result of carditis, which affects 30% to 45% of patients with acute rheumatic fever (3). Injury to the cardiac valves, which is the hallmark of rheumatic heart disease, may be chronic and progressive and, in conjunction with left ventricular dysfunction, can lead to congestive heart failure and ...
Autoimmunity - the IID and GHTP
... • The MHC accomplishes its major role in immune recognition by satisfying two distinct molecular functions: – Binding of peptides (or in some cases non-peptidic molecules) – Interaction with T cells, usually via the αβ T-cell receptor (TCR). MHC PEPTIDE ...
... • The MHC accomplishes its major role in immune recognition by satisfying two distinct molecular functions: – Binding of peptides (or in some cases non-peptidic molecules) – Interaction with T cells, usually via the αβ T-cell receptor (TCR). MHC PEPTIDE ...
Chapter 12 Checkpoint Questions 2012
... 20. If the cardioinhibitory center of the medulla oblongata were damaged, which part of the autonomic nervous system would be affected, and how would the heart be influenced? Explain your answer. ...
... 20. If the cardioinhibitory center of the medulla oblongata were damaged, which part of the autonomic nervous system would be affected, and how would the heart be influenced? Explain your answer. ...
Name: Date Completed
... 2. Go around the room and exchange liquids from your test tube with three other people. 3. Record the names of the persons with whom you interchange liquid in the order in which you made the exchanges. 4. After you are finished with the exchanges, go to the instructor who will add glucose indicator ...
... 2. Go around the room and exchange liquids from your test tube with three other people. 3. Record the names of the persons with whom you interchange liquid in the order in which you made the exchanges. 4. After you are finished with the exchanges, go to the instructor who will add glucose indicator ...
Heart Physiology Cardiac Conduction System Electrical System
... sympathetic nervous system speeds up heart rate and force (cardioacceleratory center) parasympathetic nervous system slow down heart rate and force (cardioinhibitory center) ...
... sympathetic nervous system speeds up heart rate and force (cardioacceleratory center) parasympathetic nervous system slow down heart rate and force (cardioinhibitory center) ...
Slide 1
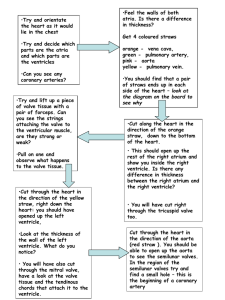
... •Try and lift up a piece of valve tissue with a pair of forceps. Can you see the strings attaching the valve to the ventricular muscle, are they strong or weak? •Pull on one and observe what happens to the valve tissue. ...
... •Try and lift up a piece of valve tissue with a pair of forceps. Can you see the strings attaching the valve to the ventricular muscle, are they strong or weak? •Pull on one and observe what happens to the valve tissue. ...
Arrhythmias
... pacemakers)· In certain condition, non conducting cells have a slow, rising phase 4, which allows them to fire without a signal from the pacemaker. It is due to an increase in intracellular Ca2+ which · An increased intracellular Ca2+ occur in : A. Use of cardiac glycosides B. Increased sympathe ...
... pacemakers)· In certain condition, non conducting cells have a slow, rising phase 4, which allows them to fire without a signal from the pacemaker. It is due to an increase in intracellular Ca2+ which · An increased intracellular Ca2+ occur in : A. Use of cardiac glycosides B. Increased sympathe ...
So Your Pet Has a Heart Murmur…
... the heartbeat which is caused by the rhythmic closure of the heart valves. Blood flow within the heart is normally smooth and silent. Therefore, the presence of a murmur alerts your veterinarian to the presence of abnormal or turbulent blood flow. Although some murmurs may be “innocent”, most murmur ...
... the heartbeat which is caused by the rhythmic closure of the heart valves. Blood flow within the heart is normally smooth and silent. Therefore, the presence of a murmur alerts your veterinarian to the presence of abnormal or turbulent blood flow. Although some murmurs may be “innocent”, most murmur ...
Worm therapy: Multiple Sclerosis
... Known to express CD4 glycoprotein in their surface. Th cells secrete cytokines that attract fresh macrophages, lymphocytes and other cytokines ...
... Known to express CD4 glycoprotein in their surface. Th cells secrete cytokines that attract fresh macrophages, lymphocytes and other cytokines ...
Rheumatic fever

Rheumatic fever, also known as acute rheumatic fever (ARF), is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a throat infection. Signs and symptoms include fever, multiple painful joints, involuntary muscle movements, and a characteristic but uncommon non itchy rash known as erythema marginatum. The heart is involved in about half of cases. Permanent damage to the heart valves, known as rheumatic heart disease (RHD), usually only occurs after multiple attacks but may occasionally occur after a single case of ARF. The damaged valves may result in heart failure. The abnormal valves also increase the risk of the person developing atrial fibrillation and infection of the valves.Acute rheumatic fever may occur following an infection of the throat by the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes. If it is untreated ARF occurs in up to three percent of people. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve the production of antibodies against a person's own tissues. Some people due to their genetics are more likely to get the disease when exposed to the bacteria than others. Other risk factors include malnutrition and poverty. Diagnosis of ARF is often based on the presence of signs and symptoms in combination with evidence of a recent streptococcal infection.Treating people who have strep throat with antibiotics, such as penicillin, decreases their risk of getting ARF. This often involves testing people with sore throats for the infection, which may not be available in the developing world. Other preventative measures include improved sanitation. In those with ARF and RHD prolonged periods of antibiotics are sometimes recommended. Gradual return to normal activities may occur following an attack. Once RHD develops, treatment is more difficult. Occasionally valve replacement surgery or repair is required. Otherwise complications are treated as per normal.Acute rheumatic fever occurs in about 325,000 children each year and about 18 million people currently have rheumatic heart disease. Those who get ARF are most often between the ages of 5 and 14, with 20% of first-time attacks occurring in adults. The disease is most common in the developing world and among indigenous peoples in the developed world. In 2013 it resulted in 275,000 deaths down from 374,000 deaths in 1990. Most deaths occur in the developing world where as many as 12.5% of people affected may die each year. Descriptions of the condition are believed to date back to at least the 5th century BCE in the writings of Hippocrates. The disease is so named because its symptoms are similar to those of some rheumatic disorders.