Chapter 16: Reaction Rates
... expressed as mol/(L · s). Brackets around the formula for a substance denote its molar concentration. For example, [NO 2] represents the molar concentration of NO 2. Reaction rates are determined experimentally by measuring the concentrations of reactants and/or products as an actual chemical reacti ...
... expressed as mol/(L · s). Brackets around the formula for a substance denote its molar concentration. For example, [NO 2] represents the molar concentration of NO 2. Reaction rates are determined experimentally by measuring the concentrations of reactants and/or products as an actual chemical reacti ...
SAMPLE EXERCISE 4.5 Comparing Acid Strengths
... Solve: (a) When bonded to a nonmetal, hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1 (rule 3b). Because the H 2S molecule is neutral, the sum of the oxidation numbers must equal zero (rule 4). Letting x equal the oxidation number of S, we have 2(+1) + x = 0. Thus, S has an oxidation number of –2. (b) Becaus ...
... Solve: (a) When bonded to a nonmetal, hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1 (rule 3b). Because the H 2S molecule is neutral, the sum of the oxidation numbers must equal zero (rule 4). Letting x equal the oxidation number of S, we have 2(+1) + x = 0. Thus, S has an oxidation number of –2. (b) Becaus ...
Document
... Solve: (a) When bonded to a nonmetal, hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1 (rule 3b). Because the H 2S molecule is neutral, the sum of the oxidation numbers must equal zero (rule 4). Letting x equal the oxidation number of S, we have 2(+1) + x = 0. Thus, S has an oxidation number of –2. (b) Becaus ...
... Solve: (a) When bonded to a nonmetal, hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1 (rule 3b). Because the H 2S molecule is neutral, the sum of the oxidation numbers must equal zero (rule 4). Letting x equal the oxidation number of S, we have 2(+1) + x = 0. Thus, S has an oxidation number of –2. (b) Becaus ...
Document
... CHECK The units of the answer are correct. The magnitude of the answer (25.8 g) is less than the initial mass of CO2 (37.8 g). This is reasonable because each carbon in CO2 has two oxygen atoms associated with it, while in C6H12O6 each carbon has only one oxygen atom associated with it and two hydro ...
... CHECK The units of the answer are correct. The magnitude of the answer (25.8 g) is less than the initial mass of CO2 (37.8 g). This is reasonable because each carbon in CO2 has two oxygen atoms associated with it, while in C6H12O6 each carbon has only one oxygen atom associated with it and two hydro ...
Document
... what would happen to the equilibrium constant? A) It would double its value. B) It would become half its current value. C) It would quadruple its value. D) It would not change its value. E) It would depend on the initial conditions of the product. ...
... what would happen to the equilibrium constant? A) It would double its value. B) It would become half its current value. C) It would quadruple its value. D) It would not change its value. E) It would depend on the initial conditions of the product. ...
2010
... iii) Using oxidation number, explain why the conversion of ammonia to nitric(V) acid is called catalytic oxidation of ammonia (2 marks) iv) Ammonia and nitric(V) acid are used in the manufacture of ammonium nitrate fertilizer. Calculate the amount of nitric (V) acid required to manufacture 1000kg am ...
... iii) Using oxidation number, explain why the conversion of ammonia to nitric(V) acid is called catalytic oxidation of ammonia (2 marks) iv) Ammonia and nitric(V) acid are used in the manufacture of ammonium nitrate fertilizer. Calculate the amount of nitric (V) acid required to manufacture 1000kg am ...
Document
... If you drop a small ball into a bowl, the ball will bounce around and then come to rest in the center of the bowl. The ball has reached static equilibrium. Static equilibrium is a state in which nothing changes. Chemical equilibrium is different from static equilibrium because it is dynamic. In a dy ...
... If you drop a small ball into a bowl, the ball will bounce around and then come to rest in the center of the bowl. The ball has reached static equilibrium. Static equilibrium is a state in which nothing changes. Chemical equilibrium is different from static equilibrium because it is dynamic. In a dy ...
File
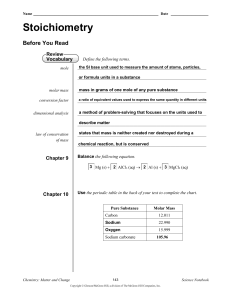
... the study of quantitative relationships between amounts of ______________________________________________________________ reactants used and products formed by a chemical reaction ______________________________________________________________ ...
... the study of quantitative relationships between amounts of ______________________________________________________________ reactants used and products formed by a chemical reaction ______________________________________________________________ ...
Revised (12 Sept 2009) Topic: Chemical Equilibrium
... and NCS−(aq) ions (making the denominator bigger). Thus, although both forward and reverse reactions occur simultaneously, the reverse reaction will predominate to decrease the Fe(NCS)2+(aq) concentration until equilibrium is established. When the reverse reaction occurs to a greater extent than the ...
... and NCS−(aq) ions (making the denominator bigger). Thus, although both forward and reverse reactions occur simultaneously, the reverse reaction will predominate to decrease the Fe(NCS)2+(aq) concentration until equilibrium is established. When the reverse reaction occurs to a greater extent than the ...
Section 6.3 Balancing Chemical Equations
... • whether one metal will displace another metal from a compound can be determined by the relative reactivities of the 2 metals. The activity series of metals lists metals in order of decreasing reactivity. A reactive metal will replace any metal listed below it in the activity series. • the product ...
... • whether one metal will displace another metal from a compound can be determined by the relative reactivities of the 2 metals. The activity series of metals lists metals in order of decreasing reactivity. A reactive metal will replace any metal listed below it in the activity series. • the product ...
unit iii kinetics and mechanism of reactions in metal complexes
... Pt(II) complexes are widely used for studying the mechanism and kinetics since the substitutions are comparatively slow and hence easier to study. From kinetic studies scientists have arrived at an associative SN2 mechanism for substitution reactions in square planar complexes. Consider a nucleophil ...
... Pt(II) complexes are widely used for studying the mechanism and kinetics since the substitutions are comparatively slow and hence easier to study. From kinetic studies scientists have arrived at an associative SN2 mechanism for substitution reactions in square planar complexes. Consider a nucleophil ...
NOTES + W.I.S.K. + Glossary
... extremes. . Electronegativity values are a useful guide but properties will still need to be studied to provide confirmation. A simple summary of bonding covered in Higher Chemistry is shown below, where EN = difference in electronegativity values between the two atoms forming the bond. ...
... extremes. . Electronegativity values are a useful guide but properties will still need to be studied to provide confirmation. A simple summary of bonding covered in Higher Chemistry is shown below, where EN = difference in electronegativity values between the two atoms forming the bond. ...
7.1 Describing Reactions
... most likely count them by the pair rather than individually. The counting units you use depend on what you are counting. For example, you might count eggs by the dozen or paper by the ream. Chemists also need practical units for counting things. Although you can describe a reaction in terms of atoms ...
... most likely count them by the pair rather than individually. The counting units you use depend on what you are counting. For example, you might count eggs by the dozen or paper by the ream. Chemists also need practical units for counting things. Although you can describe a reaction in terms of atoms ...
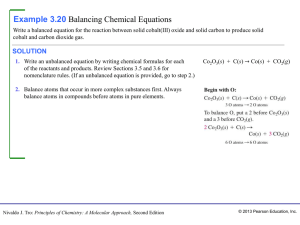
Chapter 3
... moles of that substance. 3. Use the balanced equation to set up the appropriate mole ratios. 4. Use the appropriate mole ratios to calculate the number of moles of the desired reactant or product. 5. Convert from moles back to grams if required by the ...
... moles of that substance. 3. Use the balanced equation to set up the appropriate mole ratios. 4. Use the appropriate mole ratios to calculate the number of moles of the desired reactant or product. 5. Convert from moles back to grams if required by the ...
The Concept of Limiting Reactant
... moles of that substance. 3. Use the balanced equation to set up the appropriate mole ratios. 4. Use the appropriate mole ratios to calculate the number of moles of the desired reactant or product. 5. Convert from moles back to grams if required by the ...
... moles of that substance. 3. Use the balanced equation to set up the appropriate mole ratios. 4. Use the appropriate mole ratios to calculate the number of moles of the desired reactant or product. 5. Convert from moles back to grams if required by the ...
Topic 4 - Lloyd Crosby
... a. Acid-base reactions The reaction of an acid and a base to produce a salt, possibly water, and – in a few cases – a gas b. Acid A substance that is able to donate an H+ ion (proton) and therefore increase the concentration of H+ (aq) when it dissolves in water (1) Strong acid (a) An acid that comp ...
... a. Acid-base reactions The reaction of an acid and a base to produce a salt, possibly water, and – in a few cases – a gas b. Acid A substance that is able to donate an H+ ion (proton) and therefore increase the concentration of H+ (aq) when it dissolves in water (1) Strong acid (a) An acid that comp ...