Chem 2A Final Review
... 55. According to Le Chatelier’s principle what effects will take place on the equilibrium of the following reaction: CO2 + H2 H2O + CO a) Increase [H2] b) Increase [H2O] c) remove H2O and CO 56. Calculate the equilibrium constant for: N2O4 2NO2 [N2O4] = 0.12 M [2NO2] = 0.55 M 57. The answer tha ...
... 55. According to Le Chatelier’s principle what effects will take place on the equilibrium of the following reaction: CO2 + H2 H2O + CO a) Increase [H2] b) Increase [H2O] c) remove H2O and CO 56. Calculate the equilibrium constant for: N2O4 2NO2 [N2O4] = 0.12 M [2NO2] = 0.55 M 57. The answer tha ...
Fundamentals Diagnostic Quiz
... b) Most of the space of an atom is empty space. *c) The nuclear model in which the positive charge is held densely in the center of the atom is no longer ...
... b) Most of the space of an atom is empty space. *c) The nuclear model in which the positive charge is held densely in the center of the atom is no longer ...
visual problems - Western Oregon University
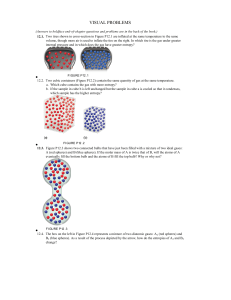
... C2H4(g) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) 12.79. Lightbulb Filaments Tungsten (W) is the favored metal for lightbulb filaments, in part because of its high melting point of 3422°C. The enthalpy of fusion of tungsten is 35.4 kJ/mol. What is its entropy of fusion? 12.80. Making Methanol The element hydr ...
... C2H4(g) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) 12.79. Lightbulb Filaments Tungsten (W) is the favored metal for lightbulb filaments, in part because of its high melting point of 3422°C. The enthalpy of fusion of tungsten is 35.4 kJ/mol. What is its entropy of fusion? 12.80. Making Methanol The element hydr ...
Combining the Benefits of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous
... use tunable phase behavior to achieve homogeneous catalysis with ease of separation. Tunable solvents are homogeneous mixtures of water or polyethylene glycol with organics such as acetonitrile, dioxane, and THF that can be used for homogeneously catalyzed reactions. Modest pressures of a soluble ga ...
... use tunable phase behavior to achieve homogeneous catalysis with ease of separation. Tunable solvents are homogeneous mixtures of water or polyethylene glycol with organics such as acetonitrile, dioxane, and THF that can be used for homogeneously catalyzed reactions. Modest pressures of a soluble ga ...
Chapter 9 Stoichiometry
... 5. Calculate the mass of a reactant or product from the mass of a different reactant or product. 6. Describe a method for determining which of two reactants is a limiting reactant. 7. Calculate the amount in moles of a product produced, given the amounts in moles of two reactants, one of which is in ...
... 5. Calculate the mass of a reactant or product from the mass of a different reactant or product. 6. Describe a method for determining which of two reactants is a limiting reactant. 7. Calculate the amount in moles of a product produced, given the amounts in moles of two reactants, one of which is in ...
Sample Exercise 3.1 Interpreting and Balancing Chemical Equations
... Write the balanced equation for the reaction that occurs when methanol, CH3OH(l), is burned in air. Solution When any compound containing C, H, and O is combusted, it reacts with the O2(g) in air to produce CO2(g) and H2O(g). Thus, the unbalanced equation is CH3OH(l) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g) In thi ...
... Write the balanced equation for the reaction that occurs when methanol, CH3OH(l), is burned in air. Solution When any compound containing C, H, and O is combusted, it reacts with the O2(g) in air to produce CO2(g) and H2O(g). Thus, the unbalanced equation is CH3OH(l) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g) In thi ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... An experiment is set up to determine the molecular mass of a water-soluble, nonvolatile, non-electrolyte. The equipment listed above is availeable to use. No other equipment is available. (a) Briefly list the steps needed to carry out this experiment. (b) What experimental data needs to be collected ...
... An experiment is set up to determine the molecular mass of a water-soluble, nonvolatile, non-electrolyte. The equipment listed above is availeable to use. No other equipment is available. (a) Briefly list the steps needed to carry out this experiment. (b) What experimental data needs to be collected ...
Appendix N CONCENTRATION UNITS
... concentration units because molar solutions are easy to prepare. In general, a molar solution is prepared by placing a known quantity of solute in a volumetric flask and adding solvent until the flask is filled to the calibration mark. Molar concentration is used in many common laboratory applicatio ...
... concentration units because molar solutions are easy to prepare. In general, a molar solution is prepared by placing a known quantity of solute in a volumetric flask and adding solvent until the flask is filled to the calibration mark. Molar concentration is used in many common laboratory applicatio ...
Chemical Reactions of Copper and Percent Recovery
... their smells) commonly formed in chemical reactions are H2S (rotten egg), SO2 (burnt match), CO2 (odorless, doesn’t support combustion), O2 (odorless, supports combustion), H2 (odorless, explosive), and NH3 (ammonia). Equation 8 shows a general reaction of carbonates and acids. ...
... their smells) commonly formed in chemical reactions are H2S (rotten egg), SO2 (burnt match), CO2 (odorless, doesn’t support combustion), O2 (odorless, supports combustion), H2 (odorless, explosive), and NH3 (ammonia). Equation 8 shows a general reaction of carbonates and acids. ...
Slide 1
... Write the balanced equation for the reaction that occurs when methanol, CH 3OH(l), is burned in air. Solution When any compound containing C, H, and O is combusted, it reacts with the O 2(g) in air to produce CO2(g) and H2O(g). Thus, the unbalanced equation is CH3OH(l) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g) In t ...
... Write the balanced equation for the reaction that occurs when methanol, CH 3OH(l), is burned in air. Solution When any compound containing C, H, and O is combusted, it reacts with the O 2(g) in air to produce CO2(g) and H2O(g). Thus, the unbalanced equation is CH3OH(l) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g) In t ...
10-Stoichiometry
... Stoichiometry with Multiple Reagents •Perform same steps for all reactants •Choose least amount of product ...
... Stoichiometry with Multiple Reagents •Perform same steps for all reactants •Choose least amount of product ...