Homomorphisms and Topological Semigroups.
... tive topological semigroups and an extension of the theorem from groups which states that continuous homomorphisms are open mappings under suitable topological conditions. The second section is on the character semigroup (continuous complex valued homomorphisms) of compact topo logical semigroups. ...
... tive topological semigroups and an extension of the theorem from groups which states that continuous homomorphisms are open mappings under suitable topological conditions. The second section is on the character semigroup (continuous complex valued homomorphisms) of compact topo logical semigroups. ...
Holt McDougal Algebra 1 2-3 Solving Inequalities by
... 2-3 Multiplying or Dividing Remember, solving inequalities is similar to solving equations. To solve an inequality that contains multiplication or division, undo the operation by dividing or multiplying both sides of the inequality by the same number. The following rules show the properties of inequ ...
... 2-3 Multiplying or Dividing Remember, solving inequalities is similar to solving equations. To solve an inequality that contains multiplication or division, undo the operation by dividing or multiplying both sides of the inequality by the same number. The following rules show the properties of inequ ...
MATHEMATICAL STATEMENTS AND PROOFS In this note we
... We will assume that the reader is familiar with the basic notation connected with sets. Thus if A, B are sets then “a ∈ A” means that a is an element in A; “A ∪ B” is the union of A and B; “A ∩ B” is the intersection of A and B; and “A − B” is the difference set A minus B (i.e. the set containing al ...
... We will assume that the reader is familiar with the basic notation connected with sets. Thus if A, B are sets then “a ∈ A” means that a is an element in A; “A ∪ B” is the union of A and B; “A ∩ B” is the intersection of A and B; and “A − B” is the difference set A minus B (i.e. the set containing al ...
Document
... conjunction operator ∧ (binary) and the disjunction operator ∨ (binary), each of them being used to connect formulae (the variables themselves are atomic formulae). Insofar as a propositional formula is built in an inductive way (since the connectives apply on formulae), it can be seen as a rooted, ...
... conjunction operator ∧ (binary) and the disjunction operator ∨ (binary), each of them being used to connect formulae (the variables themselves are atomic formulae). Insofar as a propositional formula is built in an inductive way (since the connectives apply on formulae), it can be seen as a rooted, ...
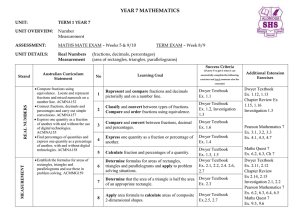
Year 7 Unit Plan 2016
... Express one quantity as a fraction of another with and without the use of digital technologies. ACMNA155 Find percentages of quantities and express one quantity as a percentage of another, with and without digital technologies. ACMNA158 Establish the formulas for areas of rectangles, triangles ...
... Express one quantity as a fraction of another with and without the use of digital technologies. ACMNA155 Find percentages of quantities and express one quantity as a percentage of another, with and without digital technologies. ACMNA158 Establish the formulas for areas of rectangles, triangles ...
Eigentheory of Cayley-Dickson algebras
... Lemma 2.13 (DDD, Lem. 4.4). Standard basis elements are alternative. 2.14. Subalgebras. A subalgebra of An is an R-linear subspace containing 1 that is closed under both multiplication and conjugation. Definition 2.15. For any elements a1 , a2 , . . . , ak in An , let !!a1 , a2 , . . . , ak "" denot ...
... Lemma 2.13 (DDD, Lem. 4.4). Standard basis elements are alternative. 2.14. Subalgebras. A subalgebra of An is an R-linear subspace containing 1 that is closed under both multiplication and conjugation. Definition 2.15. For any elements a1 , a2 , . . . , ak in An , let !!a1 , a2 , . . . , ak "" denot ...
MATHLINKS: GRADE 6 STUDENT PACKET 9 EXPRESSIONS AND
... Find a menu item with a cost that makes the following equations true. Within the same problem, the refers to the same item. In different problems, the need not represent the same menu item. ...
... Find a menu item with a cost that makes the following equations true. Within the same problem, the refers to the same item. In different problems, the need not represent the same menu item. ...
On Dummett`s Pragmatist Justification Procedure
... the definitions are stated irrespective of the particular constants or rules provided. Dummett’s approach is thus more general and can, in principle, be applied to any logic. For our particular case, the self-justifying rules are the standard elimination rules of propositional intuitionistic logic: ...
... the definitions are stated irrespective of the particular constants or rules provided. Dummett’s approach is thus more general and can, in principle, be applied to any logic. For our particular case, the self-justifying rules are the standard elimination rules of propositional intuitionistic logic: ...