
Life Cycle of a Glioma* From a Molecular Genomic
... Jamshidi N, Diehn M, Bredel M, et al. Illuminating radiogenomic characteristics of glioblastoma multiforme through integration of MR imaging, messenger RNA expression, and DNA copy number variation. Radiology. 2014 Jan;270(1):12. doi: 10.1148/radiol.13130078. Epub 2013 Oct 28. ...
... Jamshidi N, Diehn M, Bredel M, et al. Illuminating radiogenomic characteristics of glioblastoma multiforme through integration of MR imaging, messenger RNA expression, and DNA copy number variation. Radiology. 2014 Jan;270(1):12. doi: 10.1148/radiol.13130078. Epub 2013 Oct 28. ...
Biotechnology toolkit part 2
... 4. The plasmids are transformed into bacteria. Plasmids are added to a suspension of bacteria. Transformation (the uptake of plasmids) is promoted by a chilling followed by a brief warming to 40ºC, a small proportion of the bacteria are transformed by taking up the DNA. 5. The bacteria and plasmid s ...
... 4. The plasmids are transformed into bacteria. Plasmids are added to a suspension of bacteria. Transformation (the uptake of plasmids) is promoted by a chilling followed by a brief warming to 40ºC, a small proportion of the bacteria are transformed by taking up the DNA. 5. The bacteria and plasmid s ...
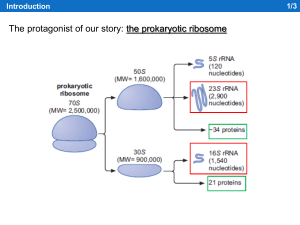
RiboT
... Okay, let’s stop for a moment…. RiboT is a fantastic molecule: a ribosome with tethered subunits, that is able to substain the expression of an entire genome! That’s incredible! So, what now? ...
... Okay, let’s stop for a moment…. RiboT is a fantastic molecule: a ribosome with tethered subunits, that is able to substain the expression of an entire genome! That’s incredible! So, what now? ...
Unit 8 Population Genetics Chp 23 Evolution of
... another occur because of chance events (sampling errors) that occur when populations are finite in size. ...
... another occur because of chance events (sampling errors) that occur when populations are finite in size. ...
Dominant Suppressors of Yeast Actin Mutations That Are Reciprocally Suppressed.
... Accepted for publication December 27, 1988 ...
... Accepted for publication December 27, 1988 ...
Molecular
... During last week’s lab you exposed his- mutant strains of S. typhimurium to suspected mutagens. Some of your his- bacteria reverted to a his+ phenotype, but how do you suppose this happened? As you remember, different mutagens affect DNA in different ways. However, even though a specific mutagen wil ...
... During last week’s lab you exposed his- mutant strains of S. typhimurium to suspected mutagens. Some of your his- bacteria reverted to a his+ phenotype, but how do you suppose this happened? As you remember, different mutagens affect DNA in different ways. However, even though a specific mutagen wil ...
Problem Sets Fall 1995
... recessive allele. In this scenerio both father and son would carry the recessive mutant allele on their X-chromosome but be unaffected by the trait. If new mutations occured this pedigree may be consistent with an X-linked recessive allele, however it would be highly unlikely. For an unaffected fath ...
... recessive allele. In this scenerio both father and son would carry the recessive mutant allele on their X-chromosome but be unaffected by the trait. If new mutations occured this pedigree may be consistent with an X-linked recessive allele, however it would be highly unlikely. For an unaffected fath ...
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
... collagen. In bone, collagen is derived from the protein products of two genes, proα1 (COL1A1) and proα2 (COL1A2). These gene products associate to form a trimeric protein consisting of two strands of proα1 and one strand of proα2; this association is initially electrostatic, but is later stabilized ...
... collagen. In bone, collagen is derived from the protein products of two genes, proα1 (COL1A1) and proα2 (COL1A2). These gene products associate to form a trimeric protein consisting of two strands of proα1 and one strand of proα2; this association is initially electrostatic, but is later stabilized ...
Introduction - GEOCITIES.ws
... The bottleneck effect occurs when the numbers of individuals in a larger population are drastically reduced by a disaster. By chance, some alleles may be overrepresented and others underrepresented among the survivors. Some alleles may be eliminated altogether. Genetic drift will continue to ...
... The bottleneck effect occurs when the numbers of individuals in a larger population are drastically reduced by a disaster. By chance, some alleles may be overrepresented and others underrepresented among the survivors. Some alleles may be eliminated altogether. Genetic drift will continue to ...
Lecture 35: Basics of DNA Cloning-I
... cohesive ends are generated. These single stranded sticky ends can form hydrogen bond with the complementary DNA sequence from different source. For example, two DNA sequences of different origin both containing EcoR1 restriction site can be ligated if they are digested with the EcoR1 restriction en ...
... cohesive ends are generated. These single stranded sticky ends can form hydrogen bond with the complementary DNA sequence from different source. For example, two DNA sequences of different origin both containing EcoR1 restriction site can be ligated if they are digested with the EcoR1 restriction en ...
[15] Recombineering: In Vivo Genetic Engineering in E. coli, S
... small enough that they can be provided by synthetic oligonucleotides. Red Proteins and Properties Homologous recombination is the process whereby segments of DNA are exchanged between two DNA molecules through regions of identical DNA sequence, the end result being new combinations of genetic materi ...
... small enough that they can be provided by synthetic oligonucleotides. Red Proteins and Properties Homologous recombination is the process whereby segments of DNA are exchanged between two DNA molecules through regions of identical DNA sequence, the end result being new combinations of genetic materi ...
Specific BRCA1 gene variations amongst young
... a mutation generated by a nucleotide exchange was detected in 8% of patients, most of whom were young women (≤40). This mutation leads to substitution of the amino acid glutamine by an arginine at position 356 of the polypeptide sequence (Q356R). Although this mutation was previously characterised a ...
... a mutation generated by a nucleotide exchange was detected in 8% of patients, most of whom were young women (≤40). This mutation leads to substitution of the amino acid glutamine by an arginine at position 356 of the polypeptide sequence (Q356R). Although this mutation was previously characterised a ...
Evolution
... For the vast majority of human genes, the pressure of natural selection is usually far more gentle. As a consequence, the resulting evolution is so slow as to be difficult to detect in only a few generations. In the case of recessive traits such as albinism, homozygous recessive individuals are only ...
... For the vast majority of human genes, the pressure of natural selection is usually far more gentle. As a consequence, the resulting evolution is so slow as to be difficult to detect in only a few generations. In the case of recessive traits such as albinism, homozygous recessive individuals are only ...
SyntheticTheoryofEvo..
... For the vast majority of human genes, the pressure of natural selection is usually far more gentle. As a consequence, the resulting evolution is so slow as to be difficult to detect in only a few generations. In the case of recessive traits such as albinism, homozygous recessive individuals are only ...
... For the vast majority of human genes, the pressure of natural selection is usually far more gentle. As a consequence, the resulting evolution is so slow as to be difficult to detect in only a few generations. In the case of recessive traits such as albinism, homozygous recessive individuals are only ...
Practice test 2
... DNA would be classified as a _____. a. clone c. plasmid b. DNA fingerprint d. transgenic organism 8. In 1974, Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer inserted a gene from an African clawed frog into a bacterium. The bacterium produced the protein coded for by the inserted frog gene. This insertion of a smal ...
... DNA would be classified as a _____. a. clone c. plasmid b. DNA fingerprint d. transgenic organism 8. In 1974, Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer inserted a gene from an African clawed frog into a bacterium. The bacterium produced the protein coded for by the inserted frog gene. This insertion of a smal ...
Name that Gene Project The National Center for Biotechnology
... B) In the world of molecular biology, what is a vector? Answer on the data sheet. C) If a sequence does not correspond to a natural organism but instead represents a man-made construct, the SOURCE ORGANISM entry will be identified as an artificial sequence. How many of the top ten matches are artifi ...
... B) In the world of molecular biology, what is a vector? Answer on the data sheet. C) If a sequence does not correspond to a natural organism but instead represents a man-made construct, the SOURCE ORGANISM entry will be identified as an artificial sequence. How many of the top ten matches are artifi ...
Lesson Overview
... Insertions and deletions are point mutations in which one base is inserted or removed from the DNA sequence. Insertions and deletions are also called frameshift mutations because they shift the “reading frame” of the genetic message. ...
... Insertions and deletions are point mutations in which one base is inserted or removed from the DNA sequence. Insertions and deletions are also called frameshift mutations because they shift the “reading frame” of the genetic message. ...
I have a VUS - Mayo Clinic
... your other family members to see if the genetic change went along with the medical conditions in your family. Your health care provider can help you figure out if this would be useful in your particular situation. Researchers can also try to find other people not related to you who have this VUS and ...
... your other family members to see if the genetic change went along with the medical conditions in your family. Your health care provider can help you figure out if this would be useful in your particular situation. Researchers can also try to find other people not related to you who have this VUS and ...
Elucidation of the Genetic Code
... proflavin inserts between two base pairs Has dimensions of a purine‐pyrymidine basepair ...
... proflavin inserts between two base pairs Has dimensions of a purine‐pyrymidine basepair ...
DNA SEQUENCING AND GENE STRUCTURE
... further along the DNA, under the first gene of the operon. This binding site has no physiological function. We could locate this binding site on a restriction fragment by repeating the methylation-protection experiment and identifying bases protected by the lac repressor. I used the methylation patt ...
... further along the DNA, under the first gene of the operon. This binding site has no physiological function. We could locate this binding site on a restriction fragment by repeating the methylation-protection experiment and identifying bases protected by the lac repressor. I used the methylation patt ...
Highly conserved features of DNA binding between two divergent
... protein from S.cerevisiae (9). Proteins from this subfamily are involved in pre-mRNA splicing and there is no clear evidence yet that they can act as transcription factors (10). Single mutations of the tryptophan residues in the first or second repeat of Cef1p did not affect function of the protein ...
... protein from S.cerevisiae (9). Proteins from this subfamily are involved in pre-mRNA splicing and there is no clear evidence yet that they can act as transcription factors (10). Single mutations of the tryptophan residues in the first or second repeat of Cef1p did not affect function of the protein ...
Join us for 2013
... 2. Denisovan Genome: Bring ancient girl to life Svante Pääbo and his colleagues sequenced DNA that they isolated from a finger bone fragment discovered in the Denisova Cave in southern Siberia. They found that it belonged to a young girl who lived in Siberia's Denisova Cave more than 50,000 years ago ...
... 2. Denisovan Genome: Bring ancient girl to life Svante Pääbo and his colleagues sequenced DNA that they isolated from a finger bone fragment discovered in the Denisova Cave in southern Siberia. They found that it belonged to a young girl who lived in Siberia's Denisova Cave more than 50,000 years ago ...
The Difference Makers
... 4. Would evolution still happen if there were no transposons, retrotransposons or retroviruses messing with the genome? [Yes, but it would probably be slower, relying on ordinary mutations that arise during DNA replication when cells divide or genetic recombination of chromosomes in a new generati ...
... 4. Would evolution still happen if there were no transposons, retrotransposons or retroviruses messing with the genome? [Yes, but it would probably be slower, relying on ordinary mutations that arise during DNA replication when cells divide or genetic recombination of chromosomes in a new generati ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.









![[15] Recombineering: In Vivo Genetic Engineering in E. coli, S](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004714893_1-0f26f8c0250e6700b822c560c415d9ab-300x300.png)












