apbio ch 17 study guide
... In summary, genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nonoverlapping base triplets, or codons, each of which is translated into a specific amino acid during protein synthesis. ...
... In summary, genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nonoverlapping base triplets, or codons, each of which is translated into a specific amino acid during protein synthesis. ...
Presentation
... Restriction enzymes do not cut bacteria’s own DNA because the recognition sequences are modified. Methylases add methyl groups after replication; makes sequence unrecognizable by restriction enzyme. ...
... Restriction enzymes do not cut bacteria’s own DNA because the recognition sequences are modified. Methylases add methyl groups after replication; makes sequence unrecognizable by restriction enzyme. ...
Regulatory approaches to modern plant breeding
... resulting in a so-called mutation. It occurs spontaneously in nature and has been a driving force of evolution in general. It is also a main element of modern plant breeding as a result of exposure to mutagens such as certain chemicals or radiation since as early as the first half of the 20th centur ...
... resulting in a so-called mutation. It occurs spontaneously in nature and has been a driving force of evolution in general. It is also a main element of modern plant breeding as a result of exposure to mutagens such as certain chemicals or radiation since as early as the first half of the 20th centur ...
Identification of a novel streptococcal gene cassette mediating
... UV-induced mutagenesis. The appropriate UV dose for S. uberis cells was determined as follows. Overnight cultures were diluted 1:500 in THY broth and grown at 37°C until an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.2. Then, 2-ml aliquots were centrifuged (4,500 ⫻ g, 10 min, room temperature), and pelle ...
... UV-induced mutagenesis. The appropriate UV dose for S. uberis cells was determined as follows. Overnight cultures were diluted 1:500 in THY broth and grown at 37°C until an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.2. Then, 2-ml aliquots were centrifuged (4,500 ⫻ g, 10 min, room temperature), and pelle ...
Molecular clock: insights and pitfalls
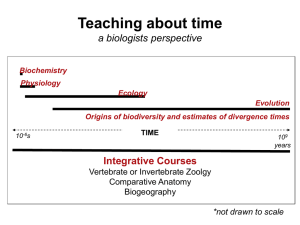
... Age estimates: how wrong can they be ? Probably not quite true but: -Increase in sequence length + marker number (genomic scale) - Increase of taxon sampling - Increase of the accuracy of fossil age estimates - Improvement of the methods modeling molecular evolution Its getting better… ...
... Age estimates: how wrong can they be ? Probably not quite true but: -Increase in sequence length + marker number (genomic scale) - Increase of taxon sampling - Increase of the accuracy of fossil age estimates - Improvement of the methods modeling molecular evolution Its getting better… ...
ch11dna - cpolumbo
... STR is another method of DNA typing. STR’s are locations (loci) on the chromosome that contain short sequences of 2 to 5 bases that repeat themselves in the DNA molecule. The advantages of this method are that it provides greater discrimination, requires less time, a smaller sample size, and the DNA ...
... STR is another method of DNA typing. STR’s are locations (loci) on the chromosome that contain short sequences of 2 to 5 bases that repeat themselves in the DNA molecule. The advantages of this method are that it provides greater discrimination, requires less time, a smaller sample size, and the DNA ...
Positive Selection Driving the Evolution of a Gene of Male
... we ask whether this selective pressure has been a constant force driving the evolution of Acp26Aa or whether it worked sporadically in the gene’s evolutionary past. By examining the divergence of Acp26Aa between the sibling species of Drosophila simulans and Drosophila melanogaster, as well as the p ...
... we ask whether this selective pressure has been a constant force driving the evolution of Acp26Aa or whether it worked sporadically in the gene’s evolutionary past. By examining the divergence of Acp26Aa between the sibling species of Drosophila simulans and Drosophila melanogaster, as well as the p ...
Gene Section IGK@ (Immunoglobulin Kappa) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... somatic mutations during the B cell differentiation in the lymph nodes, which will considerably increase their diversity. These somatic mutations can be analysed using IMGT/V-QUEST tool. ...
... somatic mutations during the B cell differentiation in the lymph nodes, which will considerably increase their diversity. These somatic mutations can be analysed using IMGT/V-QUEST tool. ...
PCR lab - fog.ccsf.edu
... The parent molecule has two complementary strands of DNA. Each base is paired by hydrogen bonding with its specific partner, A with T and G with C. ...
... The parent molecule has two complementary strands of DNA. Each base is paired by hydrogen bonding with its specific partner, A with T and G with C. ...
Brooker Chapter 14
... two operator sites (red) located 93 bp apart in the DNA causing a loop to form in the DNA. As a result expression of the lac operon is turned off. This model also shows the CAP protein (dark blue) binding to the CAP site in the promoter (dark blue DNA). The -10 & -35 sequences of the promoter are in ...
... two operator sites (red) located 93 bp apart in the DNA causing a loop to form in the DNA. As a result expression of the lac operon is turned off. This model also shows the CAP protein (dark blue) binding to the CAP site in the promoter (dark blue DNA). The -10 & -35 sequences of the promoter are in ...
Teaching deep time through macroevolution and
... 2. Students create character matrix and extract DNA/ sequence the 28s rRNA gene. [scaled up repetition, base pair differences are empirically determined] 3. Students align sequences, calculate the number of differences among taxa and use a computer program to generate a phylogenetic tree [more compl ...
... 2. Students create character matrix and extract DNA/ sequence the 28s rRNA gene. [scaled up repetition, base pair differences are empirically determined] 3. Students align sequences, calculate the number of differences among taxa and use a computer program to generate a phylogenetic tree [more compl ...
References - UTH e
... mutation screening. Partial DNA sequences, at the genomic or the cDNA level, from a gene associated with disease, or some other interesting phenotype, immediately enable gene-specific PCR reactions to be designed. Amplification of the appropriate gene segment then enables rapid testing for the prese ...
... mutation screening. Partial DNA sequences, at the genomic or the cDNA level, from a gene associated with disease, or some other interesting phenotype, immediately enable gene-specific PCR reactions to be designed. Amplification of the appropriate gene segment then enables rapid testing for the prese ...
CFTR: The Gene Associated with Cystic Fibrosis Official Gene
... just because two people might have the same two copies of the mutated CFTR gene, each may experience very different symptoms. This is because the development of a disorder such as CF is greatly influenced by environmental factors and genetic factors other than CFTR . According to the Cystic Fibrosis ...
... just because two people might have the same two copies of the mutated CFTR gene, each may experience very different symptoms. This is because the development of a disorder such as CF is greatly influenced by environmental factors and genetic factors other than CFTR . According to the Cystic Fibrosis ...
$doc.title
... using parental strains that differed at a large number of marker loci that could be readily counter-selected, and then perform a linkage analysis to find markers associated with fitness effects (in essence QTL mapping applied to bacteria). However, fitness as a trait may be influenced by so many gen ...
... using parental strains that differed at a large number of marker loci that could be readily counter-selected, and then perform a linkage analysis to find markers associated with fitness effects (in essence QTL mapping applied to bacteria). However, fitness as a trait may be influenced by so many gen ...
Fatty Acids - Mayo Clinic
... HIV-1 RNA quantitation is performed by PCR using the Roche Amplicor System. Plasma is chemically extracted and the viral RNA is precipitated with isopropanol. A known amount of a standard synthetic RNA molecule is added to each specimen to permit quantitation of HIV RNA by a comparison of resulting ...
... HIV-1 RNA quantitation is performed by PCR using the Roche Amplicor System. Plasma is chemically extracted and the viral RNA is precipitated with isopropanol. A known amount of a standard synthetic RNA molecule is added to each specimen to permit quantitation of HIV RNA by a comparison of resulting ...
International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents Prevalence of
... although the reason for this finding remains unclear. Nevertheless, the overall frequency of resistance to nalidixic acid amounted to 2.2% and thus appears to be relatively low in Serbia compared with other countries in East and West Europe. On the other hand, none of the isolates tested appeared to ...
... although the reason for this finding remains unclear. Nevertheless, the overall frequency of resistance to nalidixic acid amounted to 2.2% and thus appears to be relatively low in Serbia compared with other countries in East and West Europe. On the other hand, none of the isolates tested appeared to ...
Radiation-Sensitivity and Transcription Profiles in
... individualization of radiation treatment. Radiation-induced transcriptional responses have been studied using DNA microarray (Kis et al. 2006; Jen and Cheung, 2006). Some previous studies have also examined cells harboring mutant p53 using DNA microarray (Amandson et al. 2003; Scian et al. 2004), bu ...
... individualization of radiation treatment. Radiation-induced transcriptional responses have been studied using DNA microarray (Kis et al. 2006; Jen and Cheung, 2006). Some previous studies have also examined cells harboring mutant p53 using DNA microarray (Amandson et al. 2003; Scian et al. 2004), bu ...
DNA Structure & Function
... extracted from cells, they are often used as rDNA vectors Foreign DNA fragments (genes) can be cut and pasted into the plasmids, and then introduced to a new host organism ...
... extracted from cells, they are often used as rDNA vectors Foreign DNA fragments (genes) can be cut and pasted into the plasmids, and then introduced to a new host organism ...
Worksheet
... shown to Crick and Watson without her permission and they subsequently published their model before she had an opportunity to publish her work. Her work is now is widely recognised as being as important to the discovery of DNA as Crick and Watson, but unfortunately she has never shared in the Nobel ...
... shown to Crick and Watson without her permission and they subsequently published their model before she had an opportunity to publish her work. Her work is now is widely recognised as being as important to the discovery of DNA as Crick and Watson, but unfortunately she has never shared in the Nobel ...
Genetic Engineering Test - NHCS
... ____ 1. The evolution from a common ancestor to a variety of species is an example of _____. a) divergent evolution b) cross-pollination c) vegetative propagation ____ 2. Mutations such as polyploidy and crossing over provide the genetic basis for _____. a) evolution b) spontaneous generation c) bio ...
... ____ 1. The evolution from a common ancestor to a variety of species is an example of _____. a) divergent evolution b) cross-pollination c) vegetative propagation ____ 2. Mutations such as polyploidy and crossing over provide the genetic basis for _____. a) evolution b) spontaneous generation c) bio ...
method, a successful experiment must be verified by Southern blots
... purified DNA has provided simple, rapid methods for the molecular cloning of mutant forms of genes ("eviction" of mutant genes) and for the introduction into yeast of mutant genes constructed in vitro ("transplacement" of mutant genes). This chapter will place these techniques in a conceptual framew ...
... purified DNA has provided simple, rapid methods for the molecular cloning of mutant forms of genes ("eviction" of mutant genes) and for the introduction into yeast of mutant genes constructed in vitro ("transplacement" of mutant genes). This chapter will place these techniques in a conceptual framew ...
Test 2
... DNA binding protein comes in to prevent the unwound DNA from winding back up The DnaB then serves as the start of the DNA polymerase complex that will include DNA gyrase and primase a well as DNA polymerase, but that is considered part of the elongation step This process only occurs once in the cell ...
... DNA binding protein comes in to prevent the unwound DNA from winding back up The DnaB then serves as the start of the DNA polymerase complex that will include DNA gyrase and primase a well as DNA polymerase, but that is considered part of the elongation step This process only occurs once in the cell ...
Biology 321 Spring 2013 Assignment Set #4 Problems sorted by type
... ❖ Problem 16 As discussed in lecture, the hormone gibberellin (GA) is an important determinant of plant height. A friend of yours has two dwarf strains of rice: strain A and strain B. Each strain is true breeding and carries mutations in just one gene. Strain A has a recessive mutation in a gene req ...
... ❖ Problem 16 As discussed in lecture, the hormone gibberellin (GA) is an important determinant of plant height. A friend of yours has two dwarf strains of rice: strain A and strain B. Each strain is true breeding and carries mutations in just one gene. Strain A has a recessive mutation in a gene req ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.