Biochemical and genetic characterization of the
... DNA ligase, was initially identified in a screen for conditional lethal cell division cycle mutants (15). Subsequently, it was demonstrated that cdc9 mutants exhibit hypersensitivity to a wide range of DNA damaging agents and hyper-recombination (16–19). Based on amino acid sequence homology, the po ...
... DNA ligase, was initially identified in a screen for conditional lethal cell division cycle mutants (15). Subsequently, it was demonstrated that cdc9 mutants exhibit hypersensitivity to a wide range of DNA damaging agents and hyper-recombination (16–19). Based on amino acid sequence homology, the po ...
The Topology of the Possible
... In the following it is useful to think of all possible sequences of a given length as related to one another by a notion of distance. The distance between two sequences is the smallest number of mutations required to convert one sequence into the other. The direct neighbors of a sequence are all se ...
... In the following it is useful to think of all possible sequences of a given length as related to one another by a notion of distance. The distance between two sequences is the smallest number of mutations required to convert one sequence into the other. The direct neighbors of a sequence are all se ...
Mitochondria tutorial
... Scroll down the page to get to the tiny thin white text-entry box, located just above the three buttons labeled create map, clear DNA, and get demo DNA. Now, paste the sequence that you retrieved into the white box. Don't worry about changing the spaces and returns; the program deals with them just ...
... Scroll down the page to get to the tiny thin white text-entry box, located just above the three buttons labeled create map, clear DNA, and get demo DNA. Now, paste the sequence that you retrieved into the white box. Don't worry about changing the spaces and returns; the program deals with them just ...
Ch. 13 Bioengineering
... England in the mid1980’s. • DNA evidence exonerated one man, and convicted another. • Described in The Blooding, by Joseph Wambaugh ...
... England in the mid1980’s. • DNA evidence exonerated one man, and convicted another. • Described in The Blooding, by Joseph Wambaugh ...
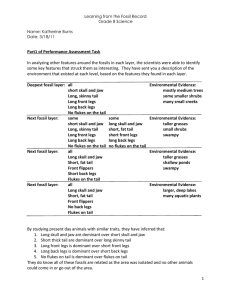
Learning from the Fossil Record Grade 8 Science Name: Katherine
... stayed as an advantage. The organisms feature, Long front legs, changed from one layer to the next. This organism changed, by instead of just all long front legs there were some short front legged organisms in the next layer. The long front legs is dominant which means it could be either Ll or LL . ...
... stayed as an advantage. The organisms feature, Long front legs, changed from one layer to the next. This organism changed, by instead of just all long front legs there were some short front legged organisms in the next layer. The long front legs is dominant which means it could be either Ll or LL . ...
Supplementary METHODS
... hour at 37ºC. Samples were irradiated with UVA light (365 nm, 1.8 J/cm2) to induce psoralen ICLs at the target site in the plasmid DNA. A 188 bp plasmid fragment surrounding the site-specific ICL was released by digestion with EcoRI and SacI enzymes, radiolabeled at the 5’ ends using T4 polynucleoti ...
... hour at 37ºC. Samples were irradiated with UVA light (365 nm, 1.8 J/cm2) to induce psoralen ICLs at the target site in the plasmid DNA. A 188 bp plasmid fragment surrounding the site-specific ICL was released by digestion with EcoRI and SacI enzymes, radiolabeled at the 5’ ends using T4 polynucleoti ...
Supplementary Table S1: Published information about
... Somatic muscle attachment during Drosophila embryogenesis. Mutations in masquerade affect axonal guidance and taste behavior in Drosophila The gastrulation defective (gd) locus encodes a novel serine protease that is involved in specifying the dorsal-ventral axis during embryonic development. At lea ...
... Somatic muscle attachment during Drosophila embryogenesis. Mutations in masquerade affect axonal guidance and taste behavior in Drosophila The gastrulation defective (gd) locus encodes a novel serine protease that is involved in specifying the dorsal-ventral axis during embryonic development. At lea ...
3.3 How Do You Identify and Clone a Gene of Interest?
... • DNA microarray analysis • Single-stranded DNA molecules are attached onto a slide using a robotic arrayer fitted with tiny pins • Can have over 10,000 spots of DNA • Extract mRNA from tissue of interest, tag it with fluorescent dye, and incubate overnight with the slide • mRNA will hybridize to sp ...
... • DNA microarray analysis • Single-stranded DNA molecules are attached onto a slide using a robotic arrayer fitted with tiny pins • Can have over 10,000 spots of DNA • Extract mRNA from tissue of interest, tag it with fluorescent dye, and incubate overnight with the slide • mRNA will hybridize to sp ...
between genotype and phenotype: protein
... phenotypic variation during periods of environmental change. As the rate of evolution is limited by heritable variation in fitness, this chaperone-mediated mechanism might allow populations and lineages to better adapt to severe environmental change. The expression of random genetic variation is exp ...
... phenotypic variation during periods of environmental change. As the rate of evolution is limited by heritable variation in fitness, this chaperone-mediated mechanism might allow populations and lineages to better adapt to severe environmental change. The expression of random genetic variation is exp ...
440age2 - eweb.furman.edu
... be selected for even if it also led to negative consequences later in life. - In C. elegans, the age-1 gene has two effects. - 1) It increases reproductive output at a young age, and - 2) it causes senescence. Mutations in the gene increase lifespan by 80%. Again, early reproduction really has a dis ...
... be selected for even if it also led to negative consequences later in life. - In C. elegans, the age-1 gene has two effects. - 1) It increases reproductive output at a young age, and - 2) it causes senescence. Mutations in the gene increase lifespan by 80%. Again, early reproduction really has a dis ...
Cockatiel Genetics
... For conception to take place, one of the male's sex chromosomes must pair with one of the hen's. A single chromosome referred to as "X" is a male chromosome; a single chromosome referred to as "Y" is a female chromosome. Female birds are conceived when an X (male) and Y (female) chromosome are paire ...
... For conception to take place, one of the male's sex chromosomes must pair with one of the hen's. A single chromosome referred to as "X" is a male chromosome; a single chromosome referred to as "Y" is a female chromosome. Female birds are conceived when an X (male) and Y (female) chromosome are paire ...
Homologous and Nonhomologous Rearrangements: Interactions
... as a circular double-strand binary string containing a variable number of genes separated by non-coding sequences (figure 1). Genes are identified and decoded thanks to an explicit transcription-translation process based upon predefined signaling sequences. Then, an abstract “folding” process gives ...
... as a circular double-strand binary string containing a variable number of genes separated by non-coding sequences (figure 1). Genes are identified and decoded thanks to an explicit transcription-translation process based upon predefined signaling sequences. Then, an abstract “folding” process gives ...
Amino Acids and Their Properties
... A point mutation is a substitution of 1 amino acid for another An accepted mutation is one that is passed down through the generations Will a mutation be accepted if it is helpful? Harmful? Neutral? Helpful in some circumstances, harmful in others? ...
... A point mutation is a substitution of 1 amino acid for another An accepted mutation is one that is passed down through the generations Will a mutation be accepted if it is helpful? Harmful? Neutral? Helpful in some circumstances, harmful in others? ...
Down Syndrome Research and Practice Volume 5 Issue 3 Pages
... disturbance of the oxidant-antioxidant system could be the direct cause of this chromosomal nondisjunction. These data as well as the predominant maternal origin of the extra chromosome and the age-dependent incidence was the basis for the mtDNA sequencing in a donor of extra chromosome 21. Three ne ...
... disturbance of the oxidant-antioxidant system could be the direct cause of this chromosomal nondisjunction. These data as well as the predominant maternal origin of the extra chromosome and the age-dependent incidence was the basis for the mtDNA sequencing in a donor of extra chromosome 21. Three ne ...
Chapter 6 Genetic analysis of two loci
... lost in an existing mutant (aa), either through mutation of a different site within the same gene (i.e. an intragenic suppressor), or by mutation of a different gene (i.e. an intergenic suppressor). There are many mechanisms by which intergenic suppressor mutations may restore wild-type function. On ...
... lost in an existing mutant (aa), either through mutation of a different site within the same gene (i.e. an intragenic suppressor), or by mutation of a different gene (i.e. an intergenic suppressor). There are many mechanisms by which intergenic suppressor mutations may restore wild-type function. On ...
12_Lecture_Presentation - Cornerstone Charter Academy
... – Another source is a gene carrier, called a vector ...
... – Another source is a gene carrier, called a vector ...
Press Release: The 1995 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
... success were very uncertain. For one, the number of genes involved might be very great. But they got started. Their experimental strategy was unique and well planned. They treated flies with mutagenic substances so as to damage (mutate) approximately half of the Drosophila genes at random (saturatio ...
... success were very uncertain. For one, the number of genes involved might be very great. But they got started. Their experimental strategy was unique and well planned. They treated flies with mutagenic substances so as to damage (mutate) approximately half of the Drosophila genes at random (saturatio ...
A new drug inactivates the helicase enzyme by binding to its active
... This answer suggests the student may understand that the two strands in a double helix must have complementary base pairs, but does not understand that the pairing of old and new DNA strands should not pose any incompatibility in this pairing as long as DNA replication takes place successfully. The ...
... This answer suggests the student may understand that the two strands in a double helix must have complementary base pairs, but does not understand that the pairing of old and new DNA strands should not pose any incompatibility in this pairing as long as DNA replication takes place successfully. The ...
Genetic counseling in Angelman syndrome: The challenges of
... increased risk of recurrence. Connerton-Moyer et al. [1997] report on 2 families in which there is recurrence of Angelman syndrome (1 in second cousins, and 1 in first cousins once-removed). However, further molecular and cytogenetic evaluation in these families showed that the children did not have ...
... increased risk of recurrence. Connerton-Moyer et al. [1997] report on 2 families in which there is recurrence of Angelman syndrome (1 in second cousins, and 1 in first cousins once-removed). However, further molecular and cytogenetic evaluation in these families showed that the children did not have ...
1. Nucleic Acids and Chromosomes
... The high fidelity of DNA replication requires a proof-reading mechanism to ensure no mistakes are made. Mutations (changes in DNA sequence) are very dangerous to the organism. Any errors in replication cannot be repaired. DNA replication has an error frequency of about 1 change per 109 base pair ...
... The high fidelity of DNA replication requires a proof-reading mechanism to ensure no mistakes are made. Mutations (changes in DNA sequence) are very dangerous to the organism. Any errors in replication cannot be repaired. DNA replication has an error frequency of about 1 change per 109 base pair ...
induction of instability at selected loci in maize
... Ds‐induced chromosome breakage and loss of acentric fragment with downstream loci in 2 synapsed chromosomes. ...
... Ds‐induced chromosome breakage and loss of acentric fragment with downstream loci in 2 synapsed chromosomes. ...
Simple Sequence Repeats as Advantageous Mutators
... regulatory region of this gene, much of which is absent in the two asocial species. (Interestingly, bonobos (Pan paniscus) and humans, two primate species characterized by high empathic and sexual bonding, also share a highly homologous SSR-rich tract upstream of the avpr1a gene, while the correspon ...
... regulatory region of this gene, much of which is absent in the two asocial species. (Interestingly, bonobos (Pan paniscus) and humans, two primate species characterized by high empathic and sexual bonding, also share a highly homologous SSR-rich tract upstream of the avpr1a gene, while the correspon ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.