Natural selection in rats
... chance of surviving and reproducing. H: The resistant rats breed and pass their features on. B: A mutation in a rat’s sex cells make its offspring resistant to warfarin. A: The mutated gene is passed on and is common in the rat population. C: The number of resistant rats ...
... chance of surviving and reproducing. H: The resistant rats breed and pass their features on. B: A mutation in a rat’s sex cells make its offspring resistant to warfarin. A: The mutated gene is passed on and is common in the rat population. C: The number of resistant rats ...
Genes, Protein Synthesis, and Mutations
... population and only the positive mutations and their “stonger” codes move forward into the next generation. 3. In this way, natural selection helps keep each type (or species) of organism strong. B. evolution = the process in which inherited characteristic within a population of one type of organism ...
... population and only the positive mutations and their “stonger” codes move forward into the next generation. 3. In this way, natural selection helps keep each type (or species) of organism strong. B. evolution = the process in which inherited characteristic within a population of one type of organism ...
Mutations PPT
... What is the name given for every set of three nitrogen bases on the DNA? What does one codon code for? When amino acids bond together, what do they form? ...
... What is the name given for every set of three nitrogen bases on the DNA? What does one codon code for? When amino acids bond together, what do they form? ...
Goal 3
... Mutations are changes in DNA coding and can be deletions, additions, or substitutions. Mutations can be random and spontaneous or caused by radiation and/or chemical exposure. Describe how mutations change amino acid sequence, protein function, phenotype. Only mutations in sex cells (egg and sperm) ...
... Mutations are changes in DNA coding and can be deletions, additions, or substitutions. Mutations can be random and spontaneous or caused by radiation and/or chemical exposure. Describe how mutations change amino acid sequence, protein function, phenotype. Only mutations in sex cells (egg and sperm) ...
CFC1, FOXH1, NODAL and ZIC3 Heterotaxy Syndrome Indication
... All coding exons as well as the exon/intron boundaries and a portion of untranslated regions of the gene(s) are amplified by PCR. Genomic DNA sequences from both forward and reverse directions are obtained by automatic fluorescent detection using an ABI PRISM® 3730 DNA Analyzer. Sequence variants di ...
... All coding exons as well as the exon/intron boundaries and a portion of untranslated regions of the gene(s) are amplified by PCR. Genomic DNA sequences from both forward and reverse directions are obtained by automatic fluorescent detection using an ABI PRISM® 3730 DNA Analyzer. Sequence variants di ...
organic compounds outline
... used in protein function of individual proteins _____________________ – copying the DNA gene to a strand of mRNA ____________________ – ribosomes assemble amino acids into the correct sequence Knows the sequence by the mRNA code Problems – __________________ Def: changes in the DNA seque ...
... used in protein function of individual proteins _____________________ – copying the DNA gene to a strand of mRNA ____________________ – ribosomes assemble amino acids into the correct sequence Knows the sequence by the mRNA code Problems – __________________ Def: changes in the DNA seque ...
ppt3 - NMSU Astronomy
... bases, which contain 30,000 to 120,000 genes. We don’t know today, but will in a few years (The Human Genome Project) “Different cell types, such as muscle cells or brain cells, differ only because they express, or actually use, different portions of their full set of genes. ...
... bases, which contain 30,000 to 120,000 genes. We don’t know today, but will in a few years (The Human Genome Project) “Different cell types, such as muscle cells or brain cells, differ only because they express, or actually use, different portions of their full set of genes. ...
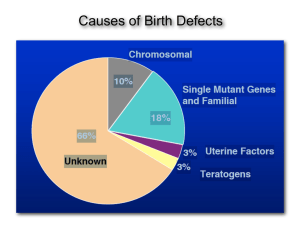
Causes of Birth Defects
... congenital defects: visible defects present at birth (due to any cause (genetic, developmental error…). syndrome: the symptoms that characterize any abnormal condition (due to genetics, development, chronic injury, etc.). pleiotropy: refers to the multiple structures effected by one gene or one muta ...
... congenital defects: visible defects present at birth (due to any cause (genetic, developmental error…). syndrome: the symptoms that characterize any abnormal condition (due to genetics, development, chronic injury, etc.). pleiotropy: refers to the multiple structures effected by one gene or one muta ...
Gene Mutations
... met thr try pro stop O THR still codes for THR O There is no example of a silent mutation because it does not affect the organisms phenotype. ...
... met thr try pro stop O THR still codes for THR O There is no example of a silent mutation because it does not affect the organisms phenotype. ...
Integrative Statistical Methods for Mapping Disease Genes
... being sequenced; large amount of gene expression, protein-DNA interaction, and other types of genomic data are available. The key challenge is to extract "meaning" from data, to benefit our understanding of human diseases. In this talk, I will describe my recent work on identifying risk genes for co ...
... being sequenced; large amount of gene expression, protein-DNA interaction, and other types of genomic data are available. The key challenge is to extract "meaning" from data, to benefit our understanding of human diseases. In this talk, I will describe my recent work on identifying risk genes for co ...
Chpt. 5 Review Questions
... selecting organisms with desired traits to be parents of the next generation. ...
... selecting organisms with desired traits to be parents of the next generation. ...
Errors in the Code
... extra letter in or deleting a letter from the sequence will move all of the other letters over one, but the translation machinery is still going to read the sequence three letters at a time. All of the codons after the insertion will code for different amino acids, and the resulting polypeptide sequ ...
... extra letter in or deleting a letter from the sequence will move all of the other letters over one, but the translation machinery is still going to read the sequence three letters at a time. All of the codons after the insertion will code for different amino acids, and the resulting polypeptide sequ ...
11.3 Section Summary 6.3 – pages 296
... • Many mutations are caused by factors in the environment, such as radiation, chemicals, and even high temperatures. • Any external agent that can cause a change in DNA is called a mutagen. ...
... • Many mutations are caused by factors in the environment, such as radiation, chemicals, and even high temperatures. • Any external agent that can cause a change in DNA is called a mutagen. ...
ACTA2 - Cincinnati Children`s Hospital Medical Center
... defined as the presence of dilation and/or dissection of the ascending aorta in the absence of any connective tissue abnormalities and in the presence of a positive family history. It is estimated that 20% of thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections result from a genetic predisposition1. TAAD has b ...
... defined as the presence of dilation and/or dissection of the ascending aorta in the absence of any connective tissue abnormalities and in the presence of a positive family history. It is estimated that 20% of thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections result from a genetic predisposition1. TAAD has b ...
Genes & Chromosomes
... expression of traits are found on chromosomes. The chromosome theory of heredity states: That genes are located on the chromosome and each gene occupies a specific place on that chromosome. Each chromosome contains just one allele for each of its genes. ...
... expression of traits are found on chromosomes. The chromosome theory of heredity states: That genes are located on the chromosome and each gene occupies a specific place on that chromosome. Each chromosome contains just one allele for each of its genes. ...
chapter08
... Competent cells permit DNA to pass through their cell walls and membranes This process is termed transformation and can lead to the acquisition of new genes ...
... Competent cells permit DNA to pass through their cell walls and membranes This process is termed transformation and can lead to the acquisition of new genes ...
changes the natural gene flow
... dollars trying to force mutations? • The problem with selective breeding is that it is ALWAYS confined to genes that are already found within a population • Mutations, dangerous as they may be, offer endless possibility ...
... dollars trying to force mutations? • The problem with selective breeding is that it is ALWAYS confined to genes that are already found within a population • Mutations, dangerous as they may be, offer endless possibility ...
8 How Cellular Information is Altered
... under a set of specific set of environmental conditions Direct selection: an example of direct selection to find a mutant resistant to an antibiotic or toxic compound Indirect selection: isolate mutants that are deficient in their capacity to produce a necessary growth factor ...
... under a set of specific set of environmental conditions Direct selection: an example of direct selection to find a mutant resistant to an antibiotic or toxic compound Indirect selection: isolate mutants that are deficient in their capacity to produce a necessary growth factor ...
Genetics Open Ended Questions
... Genetically modified bacteria are producing human insulin and growth hormone for people who need them. Also, bacteria are being modified in order to produce the chemical needed to manufacture large amounts of medications. Other organisms, such as pigs and goats are being genetically modified to prod ...
... Genetically modified bacteria are producing human insulin and growth hormone for people who need them. Also, bacteria are being modified in order to produce the chemical needed to manufacture large amounts of medications. Other organisms, such as pigs and goats are being genetically modified to prod ...
Haploid (__)
... Entire human _______ (from all 46 chromosomes)if lined up would be about ________ long --- if just 1 place to start replication it would take _____ BUT each chromosome is replicated in about _____ sections about ______ nucleotides this entire process takes about __________ ...
... Entire human _______ (from all 46 chromosomes)if lined up would be about ________ long --- if just 1 place to start replication it would take _____ BUT each chromosome is replicated in about _____ sections about ______ nucleotides this entire process takes about __________ ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.