Angelina Jolie
... gene, seizes in helping cells grow and divide. Due to this uncontrollable division, cells are likely to form tumors. CHEK2, a tumor suppressor gene, which when appearing in the mutated form causes Li-Fraumeni along with increasing the risk of other cancers such as breast cancer. ...
... gene, seizes in helping cells grow and divide. Due to this uncontrollable division, cells are likely to form tumors. CHEK2, a tumor suppressor gene, which when appearing in the mutated form causes Li-Fraumeni along with increasing the risk of other cancers such as breast cancer. ...
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
... • DNA controls the structure and function of the cell. • So what happens when the sequence of DNA nucleotides in a gene is changed? – A substituted base in the DNA molecule changes the structure of a protein – Sometimes it may have little or no harmful effect. – Other times, however, the change can ...
... • DNA controls the structure and function of the cell. • So what happens when the sequence of DNA nucleotides in a gene is changed? – A substituted base in the DNA molecule changes the structure of a protein – Sometimes it may have little or no harmful effect. – Other times, however, the change can ...
CANCER OCCURS when cell division gets out of control
... - point mutations – ras - loss of protein domains – v-erbB - gene fusions - bcr1 and abl fusion; enhancer-bcl2 fusion ...
... - point mutations – ras - loss of protein domains – v-erbB - gene fusions - bcr1 and abl fusion; enhancer-bcl2 fusion ...
GENETICS EOCT STUDY GUIDE 1. DNA Bases: Guanine RNA
... size of a given amino acid can vary chemical composition of a given amino acid can vary. sequence and number of amino acids is different. the same amino acid can have many different properties. ...
... size of a given amino acid can vary chemical composition of a given amino acid can vary. sequence and number of amino acids is different. the same amino acid can have many different properties. ...
DNA Jeopardy Review
... transcription hits a terminator sequence, but in eukaryotes the pre-mRNA is cleaved from the growing RNA chain ...
... transcription hits a terminator sequence, but in eukaryotes the pre-mRNA is cleaved from the growing RNA chain ...
PowerPoint
... • Stable, heritable changes in sequence of bases in DNA – point mutations most common • from alteration of single pairs of nucleotide • from the addition or deletion of nucleotide pairs ...
... • Stable, heritable changes in sequence of bases in DNA – point mutations most common • from alteration of single pairs of nucleotide • from the addition or deletion of nucleotide pairs ...
Mutations
... • Stable, heritable changes in sequence of bases in DNA – point mutations most common • from alteration of single pairs of nucleotide • from the addition or deletion of nucleotide pairs ...
... • Stable, heritable changes in sequence of bases in DNA – point mutations most common • from alteration of single pairs of nucleotide • from the addition or deletion of nucleotide pairs ...
sickle-shaped
... Down’s syndrome (also known as Trisomy 21) is a genetic deviation that results in short size, a round face & varying degrees of mental retardation. Why do ...
... Down’s syndrome (also known as Trisomy 21) is a genetic deviation that results in short size, a round face & varying degrees of mental retardation. Why do ...
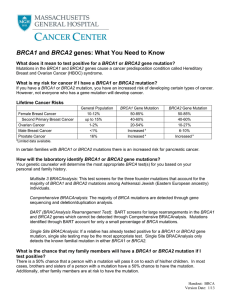
BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes: What You Need to Know
... sequencing and deletion/duplication analysis. BART (BRACAnalysis Rearrangement Test): BART screens for large rearrangements in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes which cannot be detected through Comprehensive BRACAnalysis. Mutations identified through BART account for only a small percentage of BRCA mutation ...
... sequencing and deletion/duplication analysis. BART (BRACAnalysis Rearrangement Test): BART screens for large rearrangements in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes which cannot be detected through Comprehensive BRACAnalysis. Mutations identified through BART account for only a small percentage of BRCA mutation ...
Dr. Shivani_extranuclear inheritance
... – Paramecin produced by kappa particles (100200 per cell) that replicate in cytoplasm – Kappa particles contain DNA and protein and require a nuclear gene (K, ―little k‖ strains are sensitive) for maintenance – Kappa particles are bacterialike and may contain temperate phage ...
... – Paramecin produced by kappa particles (100200 per cell) that replicate in cytoplasm – Kappa particles contain DNA and protein and require a nuclear gene (K, ―little k‖ strains are sensitive) for maintenance – Kappa particles are bacterialike and may contain temperate phage ...
extranuclear inheritance
... – Paramecin produced by kappa particles (100200 per cell) that replicate in cytoplasm – Kappa particles contain DNA and protein and require a nuclear gene (K, “little k” strains are sensitive) for maintenance – Kappa particles are bacterialike and may contain temperate phage ...
... – Paramecin produced by kappa particles (100200 per cell) that replicate in cytoplasm – Kappa particles contain DNA and protein and require a nuclear gene (K, “little k” strains are sensitive) for maintenance – Kappa particles are bacterialike and may contain temperate phage ...
How DNA Controls the Workings of the Cell
... Below are two partial sequences of DNA bases (shown for only one strand of DNA) Sequence 1 is from a human and sequence 2 is from a cow. In both humans and cows, this sequence is part of a set of instructions for controlling a bodily function. In this case, the sequence contains the gene to make the ...
... Below are two partial sequences of DNA bases (shown for only one strand of DNA) Sequence 1 is from a human and sequence 2 is from a cow. In both humans and cows, this sequence is part of a set of instructions for controlling a bodily function. In this case, the sequence contains the gene to make the ...
Mutations and Genetic Disease Most genetic diseases are caused
... This image and caption from The Book of Man by Walter Bodmer and Robin McKie. The type of mutation exemplified in sickle cell anemia is called a substitution, because one nucleotide base is substituted for another. Other types of mutations include insertions and deletions, both of which can have dis ...
... This image and caption from The Book of Man by Walter Bodmer and Robin McKie. The type of mutation exemplified in sickle cell anemia is called a substitution, because one nucleotide base is substituted for another. Other types of mutations include insertions and deletions, both of which can have dis ...
Mutations Worksheet
... If a substitution changes the amino acid, it’s called a MISSENSE point mutation. If a substitution does not change the amino acid, it’s called a SILENT point mutation. If a substitution changes the amino acid to a “stop,” it’s called a NONSENSE point mutation. Complete the boxes below. Classify each ...
... If a substitution changes the amino acid, it’s called a MISSENSE point mutation. If a substitution does not change the amino acid, it’s called a SILENT point mutation. If a substitution changes the amino acid to a “stop,” it’s called a NONSENSE point mutation. Complete the boxes below. Classify each ...
The Cell Cycle and Cancer
... replicated correctly. (If DNA does not copy itself correctly, a gene mutation occurs. DNA replication animation:click on DNA picture ...
... replicated correctly. (If DNA does not copy itself correctly, a gene mutation occurs. DNA replication animation:click on DNA picture ...
GENETICS 603 EXAM 1 Part 1: Closed book October 3, 2014 NAME
... sequence his•cys•met•asp•gly. No activity was found in an acridine (ICR-‐170) induced mutation, but in a revertant found after a second treatment with ICR-‐170, the equivalent sequence of amino acids was ...
... sequence his•cys•met•asp•gly. No activity was found in an acridine (ICR-‐170) induced mutation, but in a revertant found after a second treatment with ICR-‐170, the equivalent sequence of amino acids was ...
Chapter 12 DNA and RNA ANSWER KEY
... acids used in the construction of proteins. 8. Answers may vary. Having a sequence of DNA that could be edited into several different mRNA molecules makes it possible for a single gene to produce several different proteins specifically used in different tissues. This allows a cell to carry less gene ...
... acids used in the construction of proteins. 8. Answers may vary. Having a sequence of DNA that could be edited into several different mRNA molecules makes it possible for a single gene to produce several different proteins specifically used in different tissues. This allows a cell to carry less gene ...
RNA - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... promoter. Will stop transcribing when a termination signal is ...
... promoter. Will stop transcribing when a termination signal is ...
Insertional mutagenesis in zebrafish rapidly identifies genes
... Genes required for early vertebrate development • Two classes of mutants, broad and specific • They suggest that genes required for protein synthesis, RNA processing, DNA replication and chromatin assembly give rise to non-specific mutations • Genes required for transcription factors, receptors and ...
... Genes required for early vertebrate development • Two classes of mutants, broad and specific • They suggest that genes required for protein synthesis, RNA processing, DNA replication and chromatin assembly give rise to non-specific mutations • Genes required for transcription factors, receptors and ...
Cell and Molecular Biology
... Neoplasia is an abnormal accumulation of cells that occurs because of an imbalance between cellular proliferation and cellular attrition. Cells proliferate as they pass through the cell cycle and undergo mitosis. Attrition, due to programmed cell death, removes cells from a tissue. ...
... Neoplasia is an abnormal accumulation of cells that occurs because of an imbalance between cellular proliferation and cellular attrition. Cells proliferate as they pass through the cell cycle and undergo mitosis. Attrition, due to programmed cell death, removes cells from a tissue. ...
About Genetic Diseases
... deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). There are over 20,000 genes distributed over the 23 pairs of chromosomes. Each gene defines different function, controlling the various activities of the human body. The relationship between the cell nucleus, chromosomes, genes and DNA, can be illustrated by an analogy t ...
... deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). There are over 20,000 genes distributed over the 23 pairs of chromosomes. Each gene defines different function, controlling the various activities of the human body. The relationship between the cell nucleus, chromosomes, genes and DNA, can be illustrated by an analogy t ...
Biology 6 Study Guide – Exam #2
... regulation of the lac operon in response to lactose and glucose ...
... regulation of the lac operon in response to lactose and glucose ...
Module_2_Key_Facts
... A mutation produces a change in the DNA codons and is likely to result in a polypeptide with a different amino acid sequence. Change in polypeptide structure may alter the way the protein functions. As a result of mutation, enzymes may function less efficiently or not at all, causing a metabolic blo ...
... A mutation produces a change in the DNA codons and is likely to result in a polypeptide with a different amino acid sequence. Change in polypeptide structure may alter the way the protein functions. As a result of mutation, enzymes may function less efficiently or not at all, causing a metabolic blo ...
Mutation and DNA Repair
... base and is removed by repair enzymes. However, in many places, a C followed by a G (CpG: the “p” is the connecting phosphate) gets methylated: a CH3 group is attached to the 5 position on the ring. When 5-methyl cytosine is spontaneously deaminated, it is converted to thymine, a standard DNA base. ...
... base and is removed by repair enzymes. However, in many places, a C followed by a G (CpG: the “p” is the connecting phosphate) gets methylated: a CH3 group is attached to the 5 position on the ring. When 5-methyl cytosine is spontaneously deaminated, it is converted to thymine, a standard DNA base. ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.