Amino Acid Catabolism - Chemistry Courses: About
... the same as the first step of fatty acid oxidation. The fourth step involves an ATPdependent carboxylation, the fifth step is a hydration, and the last step is a cleavage reaction to give products. Draw the intermediates of leucine degradation. ...
... the same as the first step of fatty acid oxidation. The fourth step involves an ATPdependent carboxylation, the fifth step is a hydration, and the last step is a cleavage reaction to give products. Draw the intermediates of leucine degradation. ...
Amino Acid Catabolism - Chemistry Courses: About
... the same as the first step of fatty acid oxidation. The fourth step involves an ATPdependent carboxylation, the fifth step is a hydration, and the last step is a cleavage reaction to give products. Draw the intermediates of leucine degradation. ...
... the same as the first step of fatty acid oxidation. The fourth step involves an ATPdependent carboxylation, the fifth step is a hydration, and the last step is a cleavage reaction to give products. Draw the intermediates of leucine degradation. ...
Brookfield Academy Upper School SMART Team
... regulatory region, binding SAM. Upon binding with SAM, the C-terminal domain is removed, and the enzyme functions as a homodimer. The PLP is covalently attached to CBS by lysine 119, while the heme is reversibly bound to CBS by coordination with cystine 52 and histidine 65. Over 150 mutations have b ...
... regulatory region, binding SAM. Upon binding with SAM, the C-terminal domain is removed, and the enzyme functions as a homodimer. The PLP is covalently attached to CBS by lysine 119, while the heme is reversibly bound to CBS by coordination with cystine 52 and histidine 65. Over 150 mutations have b ...
Enzymes - Coleg y Cymoedd Moodle
... E.g. - Hydrolases. These are found in lysosomes and hydrolyse (break down) substances cell has taken in by phagocytosis. - ATPases found inside mitochondria. Involved in synthesis of ATP in aerobic respiration. Enzymes that act outside cells = extracellular enzymes. E.g. Digestive enzymes in the ali ...
... E.g. - Hydrolases. These are found in lysosomes and hydrolyse (break down) substances cell has taken in by phagocytosis. - ATPases found inside mitochondria. Involved in synthesis of ATP in aerobic respiration. Enzymes that act outside cells = extracellular enzymes. E.g. Digestive enzymes in the ali ...
Engineering carbonic anhydrase for highly selective ester hydrolysis Gunnar Höst
... tuning of protein parameters, without being critical for the structural integrity. By introducing variation in such positions the catalytic performance of an enzyme can be changed without destroying its ability to fold. Prior to the advent of recombinant technology and protein engineering, the only ...
... tuning of protein parameters, without being critical for the structural integrity. By introducing variation in such positions the catalytic performance of an enzyme can be changed without destroying its ability to fold. Prior to the advent of recombinant technology and protein engineering, the only ...
Identification of two amino acid residues which - Wiley-VCH
... The position of the α424Arg residue within the three dimensional structure of the α subunit was examined in order to determine whether the location of the arginine side chain was compatible with a role in neutralizing the charge on the electronegative substrate. A model structure for the Hex A α-sub ...
... The position of the α424Arg residue within the three dimensional structure of the α subunit was examined in order to determine whether the location of the arginine side chain was compatible with a role in neutralizing the charge on the electronegative substrate. A model structure for the Hex A α-sub ...
REGULATORY ENZYMES
... frequently form organized, multi-component macromolecular complexes that perform a particular cellular process. Similarly, it follows that the substrates associated with a given pathway can also be localized to the same organelle or cytosolic location. This segregation ...
... frequently form organized, multi-component macromolecular complexes that perform a particular cellular process. Similarly, it follows that the substrates associated with a given pathway can also be localized to the same organelle or cytosolic location. This segregation ...
Chapter 16 Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... H3N—CH2—COOH Positive ion at a pH lower than pI Total charge = 1+ ...
... H3N—CH2—COOH Positive ion at a pH lower than pI Total charge = 1+ ...
Lecture 12 Enzymes: Inhibition
... wall synthesis (eukaryotic cells don't have this enzyme) – Normal transpeptidase catalytic mechanism: nucleophilic attack of enzyme Ser–OH on substrate, making a covalent acyl-enzyme intermediate – Covalent intermediate continues in enzyme-catalyzed reaction to form peptide cross-link in peptidoglyc ...
... wall synthesis (eukaryotic cells don't have this enzyme) – Normal transpeptidase catalytic mechanism: nucleophilic attack of enzyme Ser–OH on substrate, making a covalent acyl-enzyme intermediate – Covalent intermediate continues in enzyme-catalyzed reaction to form peptide cross-link in peptidoglyc ...
Lecture 13
... for reduction >10-12 use the pro-R hydrogen while those reactions with a Keq <10-10 use the pro-S hydrogen. The reasons for this are still unclear ...
... for reduction >10-12 use the pro-R hydrogen while those reactions with a Keq <10-10 use the pro-S hydrogen. The reasons for this are still unclear ...
Nitrogen Balance
... Pyruvate • The carbon skeletons of six amino acids are converted in whole or in part to pyruvate. • These are alanine, tryptophan, cysteine, serine, glycine, and threonine. • All carbon atoms of gly, ala, cys, and ser are converted to pyruvate. • Only two carbon atoms of thr and three of trp form py ...
... Pyruvate • The carbon skeletons of six amino acids are converted in whole or in part to pyruvate. • These are alanine, tryptophan, cysteine, serine, glycine, and threonine. • All carbon atoms of gly, ala, cys, and ser are converted to pyruvate. • Only two carbon atoms of thr and three of trp form py ...
ppt-file
... to E. coli, the malic enzyme and the carboxylating and decarboxylating enzymes linking Pyr with OAA are included. External metabolites: lysine, acetate, glucose, NAD/NADH, O2, CO2 and NH3. By contrast, the cofactors ATP/ADP, and NADP/NADPH are here internal. This scheme gives rise to 36 elem. modes ...
... to E. coli, the malic enzyme and the carboxylating and decarboxylating enzymes linking Pyr with OAA are included. External metabolites: lysine, acetate, glucose, NAD/NADH, O2, CO2 and NH3. By contrast, the cofactors ATP/ADP, and NADP/NADPH are here internal. This scheme gives rise to 36 elem. modes ...
Quiz - Columbus Labs
... The structure of a glycogen phosphorylase monomer, showing the locations of the catalytic site, the PLP cofactor site, the allosteric effector site, the glycogen storage site, the tower helix (residues 262 through 278), and the subunit ...
... The structure of a glycogen phosphorylase monomer, showing the locations of the catalytic site, the PLP cofactor site, the allosteric effector site, the glycogen storage site, the tower helix (residues 262 through 278), and the subunit ...
metabolism of amino acids
... • Due to the defective branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex• Lead to accumulation of leucine in blood- and excreted to urine – smell like maple syrup • Untreated lead to abnormal development of the brain, mental retardation, and death in early ...
... • Due to the defective branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex• Lead to accumulation of leucine in blood- and excreted to urine – smell like maple syrup • Untreated lead to abnormal development of the brain, mental retardation, and death in early ...
Identification of Two Antiparallel-sheet Structure of Cobrotoxin in
... afraj.This protein, which blocks the neuromuscular transmission at post-synaptic membrane by the specific binding to acetylcholine receptors, contains 62 aminoacid residues (Mr 6949) with four disulfide bridges (1,2). The concept of a structurally and functionally invariant residue of cobrotoxin has ...
... afraj.This protein, which blocks the neuromuscular transmission at post-synaptic membrane by the specific binding to acetylcholine receptors, contains 62 aminoacid residues (Mr 6949) with four disulfide bridges (1,2). The concept of a structurally and functionally invariant residue of cobrotoxin has ...
- Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... plasmid replicated proteins, which may not have the same carbohydrates attached as the human form. Glycosylation usually occurs at asparagine residues in Asn-X-Ser/Thr sequons where X does not equal proline Approximately 30% of all 1663 PDB entries (Sep 2003) containing carbohydrates contain err ...
... plasmid replicated proteins, which may not have the same carbohydrates attached as the human form. Glycosylation usually occurs at asparagine residues in Asn-X-Ser/Thr sequons where X does not equal proline Approximately 30% of all 1663 PDB entries (Sep 2003) containing carbohydrates contain err ...
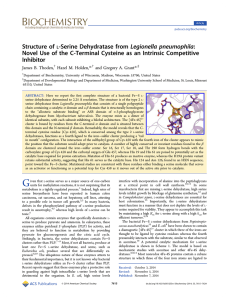
Structure of L‑Serine Dehydratase from Legionella
... domain, which harbors the active site cluster, is composed of 11 α helices. Given that the α carbons for the two subunits of the dimer superimpose with a root-mean-square deviation of 0.25 Å, the following discussion will refer only to subunit B. The electron density corresponding to the iron−sulfur ...
... domain, which harbors the active site cluster, is composed of 11 α helices. Given that the α carbons for the two subunits of the dimer superimpose with a root-mean-square deviation of 0.25 Å, the following discussion will refer only to subunit B. The electron density corresponding to the iron−sulfur ...
chapter 19 addendum
... off, rearranging to form a phenylthiohydantoin. This can be compared to a standard, and the amino acid identified. Each amino acid is removed from the N terminus and identified this way… and the process is automated on a machine. ...
... off, rearranging to form a phenylthiohydantoin. This can be compared to a standard, and the amino acid identified. Each amino acid is removed from the N terminus and identified this way… and the process is automated on a machine. ...
Tutorial Kit (Biochemistry-300 L)
... non-consumable substances that reduce the activation energy necessary for a chemical reaction to occur. Enzymes are highly specific to the reactions they catalyze. They are of vital importance for life because most chemical reactions of the cells and tissues are catalyzed by enzymes. Without enzymat ...
... non-consumable substances that reduce the activation energy necessary for a chemical reaction to occur. Enzymes are highly specific to the reactions they catalyze. They are of vital importance for life because most chemical reactions of the cells and tissues are catalyzed by enzymes. Without enzymat ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.