a-amino acid
... • Nitric oxide (.N=O) is a gas which can diffuse rapidly into cells, and is a messenger that ...
... • Nitric oxide (.N=O) is a gas which can diffuse rapidly into cells, and is a messenger that ...
Re-identification of the N-terminal amino acid residue and its
... Key words: bacterial antenna complex, MALDI-TOF/MS, NMR, N-terminal methylation Recently, we have reported an oxidative modification of α-polypeptide of core light-harvesting complex (LH 1) from purple nonsulfur photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum (R.) rubrum and its consequence for the stabilit ...
... Key words: bacterial antenna complex, MALDI-TOF/MS, NMR, N-terminal methylation Recently, we have reported an oxidative modification of α-polypeptide of core light-harvesting complex (LH 1) from purple nonsulfur photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum (R.) rubrum and its consequence for the stabilit ...
Biochemistry I, Spring Term 2003 - Second Exam:
... 5. Which of the statements regarding enzymes is false? a) Enzymes are usually proteins that function as catalysts. b) Enzymes are usually specific. c) Enzymes may be used many times for a specific reaction. d) The active site of an enzyme remains rigid and does not change shape. 6. The nucleophile t ...
... 5. Which of the statements regarding enzymes is false? a) Enzymes are usually proteins that function as catalysts. b) Enzymes are usually specific. c) Enzymes may be used many times for a specific reaction. d) The active site of an enzyme remains rigid and does not change shape. 6. The nucleophile t ...
Practice Exam 3
... Which enzyme catalyzes a reaction in which NADH is produced? _____________________ Which enzyme converts G3P into 1,3 BPG? __________________________ Name two enzyme reactions from glycolysis that operate at G ≈ 0 _______________________ 8. Three reactions in glycolysis operate far from equilibrium ...
... Which enzyme catalyzes a reaction in which NADH is produced? _____________________ Which enzyme converts G3P into 1,3 BPG? __________________________ Name two enzyme reactions from glycolysis that operate at G ≈ 0 _______________________ 8. Three reactions in glycolysis operate far from equilibrium ...
Practice Exam 3 Answers
... Which enzyme converts G3P into 1,3 BPG? __________________________ Name two enzyme reactions from glycolysis that operate at G ≈ 0 _______________________ 8. Three reactions in glycolysis operate far from equilibrium and are potential sites for major flux control. List the three enzymes and discuss ...
... Which enzyme converts G3P into 1,3 BPG? __________________________ Name two enzyme reactions from glycolysis that operate at G ≈ 0 _______________________ 8. Three reactions in glycolysis operate far from equilibrium and are potential sites for major flux control. List the three enzymes and discuss ...
Barbara Soldo
... PPi Release Activity in the Presence of Amino-acyl Acceptor. In order to monitor the complete A-domain catalyzed reaction, we attempted to measure acceleration of PPi release as a result of interdomain transfer of aminoacyl to TycA holo-PCP domain added in trans. TycA PCP domain was coexpressed toge ...
... PPi Release Activity in the Presence of Amino-acyl Acceptor. In order to monitor the complete A-domain catalyzed reaction, we attempted to measure acceleration of PPi release as a result of interdomain transfer of aminoacyl to TycA holo-PCP domain added in trans. TycA PCP domain was coexpressed toge ...
Molecular Modeling of Substrate Binding in Wild
... genetically modified bacteria expressing the gene for 2,5 diketo-D-gluconic acid reductase.1,2 These genetic manipulations have resulted in bacteria that can directly produce 2-KLG from D-glucose. In principle, this method may have considerable advantage over the currently used Reichstein and Grussn ...
... genetically modified bacteria expressing the gene for 2,5 diketo-D-gluconic acid reductase.1,2 These genetic manipulations have resulted in bacteria that can directly produce 2-KLG from D-glucose. In principle, this method may have considerable advantage over the currently used Reichstein and Grussn ...
Pivotal Role of Water in the Mechanism of
... level expression of the holoenzyme and its functional domains make this protein a very attractive model for studying flavoprotein-reductase-utilizing class II P450s. The greatest insights into the structure/function relationship of P450 enzymes have been gained from studies on P450cam. The availabil ...
... level expression of the holoenzyme and its functional domains make this protein a very attractive model for studying flavoprotein-reductase-utilizing class II P450s. The greatest insights into the structure/function relationship of P450 enzymes have been gained from studies on P450cam. The availabil ...
Lecture 6
... Because these side chains have basic groups, they accept protons at pH values lower than the pKa of the side chain ...
... Because these side chains have basic groups, they accept protons at pH values lower than the pKa of the side chain ...
Review - Columbus Labs
... 2. Initiator tRNA. In eukaryotes, the initiating amino acid is methionine rather than N-formylmethionine. However, as in prokaryotes, a special tRNA participates in initiation. 3. Initiation. The initiating codon in eukaryotes is always AUG. Eukaryotes, in contrast with prokaryotes, do not use a spe ...
... 2. Initiator tRNA. In eukaryotes, the initiating amino acid is methionine rather than N-formylmethionine. However, as in prokaryotes, a special tRNA participates in initiation. 3. Initiation. The initiating codon in eukaryotes is always AUG. Eukaryotes, in contrast with prokaryotes, do not use a spe ...
Amino acids, introduction
... Ser, Thr, (Tyr) Met, Cys Phe, Tyr, Trp, (His) Arg, Lys, Asp, Glu, (His) Gly (no R), Pro (cyclic) ...
... Ser, Thr, (Tyr) Met, Cys Phe, Tyr, Trp, (His) Arg, Lys, Asp, Glu, (His) Gly (no R), Pro (cyclic) ...
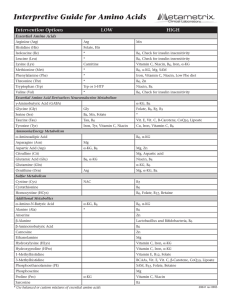
Interpretive Guide for Amino Acids
... Phosphoserine High - functional magnesium deficiency causing incomplete conversion to serine. ...
... Phosphoserine High - functional magnesium deficiency causing incomplete conversion to serine. ...
Metabolism & Enzymes
... facilitate chemical reactions increase rate of reaction without being consumed reduce activation energy don’t change free energy (G) released or required ...
... facilitate chemical reactions increase rate of reaction without being consumed reduce activation energy don’t change free energy (G) released or required ...
Amino Acid Oxidation and the Urea Cycle
... Phenylalanine Hydroxylase; then the pathway proceeds with the breakdown of tyrosine to fumarate plus acetoacetate. Homogentisate is an intermediate in this pathway. ...
... Phenylalanine Hydroxylase; then the pathway proceeds with the breakdown of tyrosine to fumarate plus acetoacetate. Homogentisate is an intermediate in this pathway. ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.