Lecture-13-Environments - Computation Structures Group
... • We want to separate the implementation of perceptual tasks from the uses to which perception is put • Some modules advertise the class of “behavioral events” they are capable of recognizing and signaling – These events are organized into a taxonomy – The same event can be signaled by quite differe ...
... • We want to separate the implementation of perceptual tasks from the uses to which perception is put • Some modules advertise the class of “behavioral events” they are capable of recognizing and signaling – These events are organized into a taxonomy – The same event can be signaled by quite differe ...
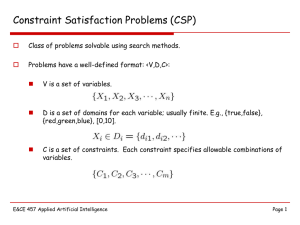
276 - 313
... • In the worst case we expand all but the last node at level • Every node that is generated must remain in memory, because it may belong to the solution path • Let be the branching factor of the search • Thus the worst-case time and space complexities are ...
... • In the worst case we expand all but the last node at level • Every node that is generated must remain in memory, because it may belong to the solution path • Let be the branching factor of the search • Thus the worst-case time and space complexities are ...
Economic reasoning and artificial intelligence The Harvard
... and economics. We start this review by describing progress on the question of how to operationalize rationality, and how to construct AI agents that are able to reason about other AIs. Supposing that AI research succeeds in developing an agent that can be usefully modeled as rational (perhaps more s ...
... and economics. We start this review by describing progress on the question of how to operationalize rationality, and how to construct AI agents that are able to reason about other AIs. Supposing that AI research succeeds in developing an agent that can be usefully modeled as rational (perhaps more s ...
Swarm Intelligence
... the swarm as a whole can show an intelligent behavior. • This is the result of the interaction of spatially neighboring individuals that act on the basis of simple rules. • Most often, the behavior of each individual of the swarm is described in probabilistic terms: – Each individual has a st ...
... the swarm as a whole can show an intelligent behavior. • This is the result of the interaction of spatially neighboring individuals that act on the basis of simple rules. • Most often, the behavior of each individual of the swarm is described in probabilistic terms: – Each individual has a st ...
Chapter 1 The Architecture of Human
... Part of the reason why global human cognitive architecture diagrams are not so common is, of course, a lack of agreement in the field regarding all the relevant issues. Since there are multiple opinions regarding nearly every aspect of human intelligence, it would be difficult to get two cognitive s ...
... Part of the reason why global human cognitive architecture diagrams are not so common is, of course, a lack of agreement in the field regarding all the relevant issues. Since there are multiple opinions regarding nearly every aspect of human intelligence, it would be difficult to get two cognitive s ...
ISM 622 – Midterm Exam Questions
... 22. Describe computerized knowledge acquisition (rule induction), and discuss its advantages and disadvantages. 23. What are the major knowledge representation methods? Describe any two of them in greater detail? 24. List some reasoning methods. What are approaches used in inferencing with rules? 25 ...
... 22. Describe computerized knowledge acquisition (rule induction), and discuss its advantages and disadvantages. 23. What are the major knowledge representation methods? Describe any two of them in greater detail? 24. List some reasoning methods. What are approaches used in inferencing with rules? 25 ...
A Preliminary Investigation of Alien Presence
... Interpretation is the process by which people assign meaning to events or objects in order to make them relevant in the context of their lives. Assigning meaning to an artifact is a complex process that involves at least two elements besides the artifact and its producer: (1) how viewers interpret o ...
... Interpretation is the process by which people assign meaning to events or objects in order to make them relevant in the context of their lives. Assigning meaning to an artifact is a complex process that involves at least two elements besides the artifact and its producer: (1) how viewers interpret o ...
The Symbol Grounding Problem has been solved. So
... But one part of the criticism was justified: all was programmed by human designers. The semiotic relations were not autonomously established by the artificial agent but carefully mapped out and then coded by human programmers. In the case of natural intelligence, this is clearly not the case. The mi ...
... But one part of the criticism was justified: all was programmed by human designers. The semiotic relations were not autonomously established by the artificial agent but carefully mapped out and then coded by human programmers. In the case of natural intelligence, this is clearly not the case. The mi ...
Could a machine think? - Alan M. Turing vs. John R. Searle
... The PSSH dictates that symbol manipulation and thinking are processes of a fundamentally alike type. They are both physically realised and governed by rules and representations. 6 A computer is a physical apparatus. Therefore, the performance of a computer can be described by the causal structure of ...
... The PSSH dictates that symbol manipulation and thinking are processes of a fundamentally alike type. They are both physically realised and governed by rules and representations. 6 A computer is a physical apparatus. Therefore, the performance of a computer can be described by the causal structure of ...
Lecture#1 slides - Computer Science
... The preys emit a signal whose intensity decreases in proportion to distance - plays the role of attractor for the predators Hunters emit a signal which acts as a repellant for other hunters, so as not to find themselves at the same place Each hunter is each attracted by the pray and (weakly) repe ...
... The preys emit a signal whose intensity decreases in proportion to distance - plays the role of attractor for the predators Hunters emit a signal which acts as a repellant for other hunters, so as not to find themselves at the same place Each hunter is each attracted by the pray and (weakly) repe ...
ELIZA/DOCTOR PROGRAM Introduction Working
... can choose to decide against something which is computationally the right decision by using non-quantifiable factors like judgement and emotions, and alter these decisions as they see fit, a computational system cannot do so. While a human can choose a different decision for the same input parameter ...
... can choose to decide against something which is computationally the right decision by using non-quantifiable factors like judgement and emotions, and alter these decisions as they see fit, a computational system cannot do so. While a human can choose a different decision for the same input parameter ...
ppt
... differently. Plug in a laptop, make movie on the fly. Similar to video games. Each frame requires 2 hrs on 2.4 GHz Pentium processor. At 30 fps, 2 hr movie – 216,000 computers’ power required – so present computational capability is under equipped. ...
... differently. Plug in a laptop, make movie on the fly. Similar to video games. Each frame requires 2 hrs on 2.4 GHz Pentium processor. At 30 fps, 2 hr movie – 216,000 computers’ power required – so present computational capability is under equipped. ...
Document
... Show how an artificial agent can be used to simulate mundane tasks performed by human beings. Show how expert systems and mundane systems can use different search techniques to solve problems. Show how the learning process in humans can be simulated, to some extent, using neural networks that ...
... Show how an artificial agent can be used to simulate mundane tasks performed by human beings. Show how expert systems and mundane systems can use different search techniques to solve problems. Show how the learning process in humans can be simulated, to some extent, using neural networks that ...
Strategic Decision Making
... length. This was the first cartoon that synchronized sound and action. Like all great inventions, Mickey Mouse began his life in a garage. After going bankrupt with the failure of his Laugh O Gram Company, Walt Disney decided to rent a camera, assemble an animation stand, and set up a studio in his ...
... length. This was the first cartoon that synchronized sound and action. Like all great inventions, Mickey Mouse began his life in a garage. After going bankrupt with the failure of his Laugh O Gram Company, Walt Disney decided to rent a camera, assemble an animation stand, and set up a studio in his ...
Beneficial AI 2017 - Future of Life Institute
... and a Research Advisor at the Centre for Effective Altruism. He has a PhD in pure mathematics. His research interests are centred on how to prioritise actions in situations of great uncertainty, with a focus on the value of research and understanding the long-term effects of actions today. Owen is t ...
... and a Research Advisor at the Centre for Effective Altruism. He has a PhD in pure mathematics. His research interests are centred on how to prioritise actions in situations of great uncertainty, with a focus on the value of research and understanding the long-term effects of actions today. Owen is t ...
Lecture notes for week 5
... For SAT problems, COMPLETE algorithms based on DFS search are commonly referred to as Davis-Putnam (DP) or Davis-Putnam Logemann Loveland (DPLL) ...
... For SAT problems, COMPLETE algorithms based on DFS search are commonly referred to as Davis-Putnam (DP) or Davis-Putnam Logemann Loveland (DPLL) ...
14.FARS 3.Synthetic PET(2001) - University of Southern California
... simulated activity of the neurons in models of interacting brain regions based on, say, single-cell recordings in behaving monkeys ...
... simulated activity of the neurons in models of interacting brain regions based on, say, single-cell recordings in behaving monkeys ...
From NARS to a Thinking Machine
... When the system is running, usually there are many tasks under processing in parallel. The system assigns a priority-value to every concept, task, and belief. At each inference step, a concept is selected, and then a task and a belief are selected within the concept. All these selections are probabi ...
... When the system is running, usually there are many tasks under processing in parallel. The system assigns a priority-value to every concept, task, and belief. At each inference step, a concept is selected, and then a task and a belief are selected within the concept. All these selections are probabi ...
Artificial Intelligence
... “How to pass the Turing test by cheating” ! “Turing’s imitation game in general is inadequate as a test of intelligence, as it relies solely on the ability to fool people, and this can be very easy to achieve, as Weizenbaum found.” ...
... “How to pass the Turing test by cheating” ! “Turing’s imitation game in general is inadequate as a test of intelligence, as it relies solely on the ability to fool people, and this can be very easy to achieve, as Weizenbaum found.” ...
beekman7_ppt_15
... Involves two people and a computer One person, the interrogator, sits at a terminal and types questions The questions can be about anything—math, science, politics, sports, entertainment, art, human relationships, emotions, etc. As answers to the questions asked appear on the screen, the interrogato ...
... Involves two people and a computer One person, the interrogator, sits at a terminal and types questions The questions can be about anything—math, science, politics, sports, entertainment, art, human relationships, emotions, etc. As answers to the questions asked appear on the screen, the interrogato ...
Multi-Agent Systems - AI-MAS
... simple but are actually quite complex. For example, one mission goal handled by autonomous agents is simply to not waste fuel. But accomplishing that means balancing multiple demands, such as staying on course and keeping experiments running, as well as dealing with the unexpected. "What happens if ...
... simple but are actually quite complex. For example, one mission goal handled by autonomous agents is simply to not waste fuel. But accomplishing that means balancing multiple demands, such as staying on course and keeping experiments running, as well as dealing with the unexpected. "What happens if ...
Curriculum Vitae, September 2008
... Ph.D. in Computer Science, Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge, July 1992. Appointments Held April 1990 – February 1997: Research Associate (AR1A), Department of Artificial Intelligence, University of Edinburgh. February 1997 – April 2004: Research Fellow (AR2), Centre for Intelligent Syste ...
... Ph.D. in Computer Science, Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge, July 1992. Appointments Held April 1990 – February 1997: Research Associate (AR1A), Department of Artificial Intelligence, University of Edinburgh. February 1997 – April 2004: Research Fellow (AR2), Centre for Intelligent Syste ...
3.4 An Architecture of Network Artificial Intelligence(NAI)
... key component: – 1. Central Controller: Centralized controller is the core component of Network Artificial Intelligence which can be called as 'Network Brain'. It man collect huge data of network states, store the data based on the big data platform, and carry on the machine learning, to achieve net ...
... key component: – 1. Central Controller: Centralized controller is the core component of Network Artificial Intelligence which can be called as 'Network Brain'. It man collect huge data of network states, store the data based on the big data platform, and carry on the machine learning, to achieve net ...