File
... who owned property worth more than $20,000. • LARGE PLANTATION OWNERS ---- add in your notes!! ...
... who owned property worth more than $20,000. • LARGE PLANTATION OWNERS ---- add in your notes!! ...
Ch 20 Packet
... 10. arbitrary Governed by indeterminate preference or whim rather than by settled principle or law. “Jefferson Davis was less able than Lincoln to exercise arbitrary power. . . .” 11. quota The proportion or share of a larger number of things that a smaller group is assigned to contribute. “. . . wi ...
... 10. arbitrary Governed by indeterminate preference or whim rather than by settled principle or law. “Jefferson Davis was less able than Lincoln to exercise arbitrary power. . . .” 11. quota The proportion or share of a larger number of things that a smaller group is assigned to contribute. “. . . wi ...
Civil War Student Notes
... What were the underlying and immediate causes of the Civil War? Contrast the resources and strategies of the North and South. Describe the immediate outcomes and effects of the battles of the Civil War. What lasting impacts did the Civil War have on the North and the South? ...
... What were the underlying and immediate causes of the Civil War? Contrast the resources and strategies of the North and South. Describe the immediate outcomes and effects of the battles of the Civil War. What lasting impacts did the Civil War have on the North and the South? ...
The Civil War
... S.C. Curriculum Standards • 4.1.15 Compare and contrast the ways of life in the North and South; • 4.1.16 State the causes and events leading up to the Civil War; • 4.1.17 Identify the notable figures of the Civil War and the roles they played; • 4.1.18 Describe the Civil War and its effects on the ...
... S.C. Curriculum Standards • 4.1.15 Compare and contrast the ways of life in the North and South; • 4.1.16 State the causes and events leading up to the Civil War; • 4.1.17 Identify the notable figures of the Civil War and the roles they played; • 4.1.18 Describe the Civil War and its effects on the ...
Chapter 19
... • Why was Gen. Stonewall Jackson not at Gettysburg? – May 1863, • Gen. Lee defeated a much larger Union force in Chancellorsville, Virginia. – Lee’s most trusted General, Stonewall Jackson, was accidentally shot by his own troops. ...
... • Why was Gen. Stonewall Jackson not at Gettysburg? – May 1863, • Gen. Lee defeated a much larger Union force in Chancellorsville, Virginia. – Lee’s most trusted General, Stonewall Jackson, was accidentally shot by his own troops. ...
causes of the Civil War
... border states or to places that were already under Union military control; Didn’t free ALL slaves! So, it received a mixed reaction (both positive and negative) ...
... border states or to places that were already under Union military control; Didn’t free ALL slaves! So, it received a mixed reaction (both positive and negative) ...
Good Morning!!!!!!!!!!
... proclamation in areas where it actually applied. The Proclamation did not stop slavery in border states, where the government had the power to enforce it. The words written were powerful but more symbolic than realistic. The proclamation defined what the Union was fighting against, and discouraged B ...
... proclamation in areas where it actually applied. The Proclamation did not stop slavery in border states, where the government had the power to enforce it. The words written were powerful but more symbolic than realistic. The proclamation defined what the Union was fighting against, and discouraged B ...
Civil War - Point Loma High School
... community and a civilized community can constitute one state.” (Northern View) ...
... community and a civilized community can constitute one state.” (Northern View) ...
Faces of the Civil War
... During the Civil war Tubman was a spy, a nurse, and a cook for the Union Army. She gained knowledge of the land from running the Underground Railroad which she used to spy on the Cofederate troops. She ...
... During the Civil war Tubman was a spy, a nurse, and a cook for the Union Army. She gained knowledge of the land from running the Underground Railroad which she used to spy on the Cofederate troops. She ...
“The North Vs. the South: The Furnace of Civil War” Outline The
... IV. Civil War Strategy and Diplomacy 1861-1865 a. Why did the North need to take “military initiative” in the war? (22) i. Who was the Union’s most important military commander? (22) ...
... IV. Civil War Strategy and Diplomacy 1861-1865 a. Why did the North need to take “military initiative” in the war? (22) i. Who was the Union’s most important military commander? (22) ...
Science 6 - Study Guide Home Page
... a. smuggle illegal goods into the country b. help runaway slaves escape to freedom* c. provide a form of inexpensive transportation d. stop illegal aliens from entering the country 5. Which event was the immediate cause of the secession of several Southern states from the Union in 1860? a. the Dred ...
... a. smuggle illegal goods into the country b. help runaway slaves escape to freedom* c. provide a form of inexpensive transportation d. stop illegal aliens from entering the country 5. Which event was the immediate cause of the secession of several Southern states from the Union in 1860? a. the Dred ...
Lauren Ritter Abraham Lincoln ppt
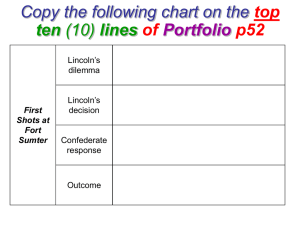
... April 12, 1861,Confederate South Carolina troops fired on Fort Sumner and thus the Civil War began. The Union and Confederacy went on to fight for 4 years. The war ended on April 9, 1865. About 620,000 people were lost in all. ...
... April 12, 1861,Confederate South Carolina troops fired on Fort Sumner and thus the Civil War began. The Union and Confederacy went on to fight for 4 years. The war ended on April 9, 1865. About 620,000 people were lost in all. ...
Union and Confederate Resources Main Idea: As the
... Resources, Strategies, and Early Battles Union and Confederate Resources Main Idea: As the Civil War began, each side possessed significant strengths and notable weaknesses. At first glance, most advantages appeared to add up in favor of the Union. Confederate and Union Strategies Main Idea: As the ...
... Resources, Strategies, and Early Battles Union and Confederate Resources Main Idea: As the Civil War began, each side possessed significant strengths and notable weaknesses. At first glance, most advantages appeared to add up in favor of the Union. Confederate and Union Strategies Main Idea: As the ...
Lesson 16.1: War Erupts
... expect the house to fall — but I do expect it will cease to be divided. • It will become all one thing, or all the other.” ...
... expect the house to fall — but I do expect it will cease to be divided. • It will become all one thing, or all the other.” ...
The Civil War
... considered the battle of Antietam a victory since the Confederate army retreated back into Virginia. After the battle, Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation to try to rebuild northern support for the war. The Proclamation ordered that all slaves in Confederate states would be free if the ...
... considered the battle of Antietam a victory since the Confederate army retreated back into Virginia. After the battle, Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation to try to rebuild northern support for the war. The Proclamation ordered that all slaves in Confederate states would be free if the ...
Uncle Tom`s Cabin
... During the campaign of 1860, Abraham Lincoln and the Republican party a) Opposed the expansion of slavery but did not threaten to attack slavery in the South b) Promised, if elected, to seek peaceful, compensated abolition of slavery in the South c) Were forced to be cautious about limiting the exp ...
... During the campaign of 1860, Abraham Lincoln and the Republican party a) Opposed the expansion of slavery but did not threaten to attack slavery in the South b) Promised, if elected, to seek peaceful, compensated abolition of slavery in the South c) Were forced to be cautious about limiting the exp ...
reconstruction powerpoint - Pottsgrove School District
... Louisiana gained a black governor Hiram Revels of Mississippi became the first African American elected to the Senate. ...
... Louisiana gained a black governor Hiram Revels of Mississippi became the first African American elected to the Senate. ...
eoc - TeacherWeb
... peacefully; would not start a war; would not allow slavery to spread Declared slaves in the Confederacy free; turned Europe against the South; African Americans now could fight in the Union army Dedicated a cemetery; told the nation that the purpose of the war was to save our democratic government T ...
... peacefully; would not start a war; would not allow slavery to spread Declared slaves in the Confederacy free; turned Europe against the South; African Americans now could fight in the Union army Dedicated a cemetery; told the nation that the purpose of the war was to save our democratic government T ...
The Civil War
... army when they were separated. • The battle was the deadliest battle in American History. Over 26,000 troops died in one day (more than the Mexican American War and the War of 1812 combined!!) • Confederate Army was almost destroyed, they retreated back to the South. McClellan could have followed an ...
... army when they were separated. • The battle was the deadliest battle in American History. Over 26,000 troops died in one day (more than the Mexican American War and the War of 1812 combined!!) • Confederate Army was almost destroyed, they retreated back to the South. McClellan could have followed an ...
Hampton Roads Conference

The Hampton Roads Conference was a peace conference held between the United States and the Confederate States on February 3, 1865, aboard the steamboat River Queen in Hampton Roads, Virginia, to discuss terms to end the American Civil War. President Abraham Lincoln and Secretary of State William H. Seward, representing the Union, met with three commissioners from the Confederacy: Vice President Alexander H. Stephens, Senator Robert M. T. Hunter, and Assistant Secretary of War John A. Campbell.The representatives discussed a possible alliance against France, the possible terms of surrender, the question of whether slavery might persist after the war, and the question of whether the South would be compensated for property lost through emancipation. Lincoln and Seward reportedly offered some possibilities for compromise on the issue of slavery. The only concrete agreement reached was over prisoner-of-war exchanges.The Confederate commissioners immediately returned to Richmond at the conclusion of the conference. Confederate President Jefferson Davis announced that the North would not compromise. Lincoln drafted an amnesty agreement based on terms discussed at the Conference, but met with opposition from his Cabinet. John Campbell continued to advocate for a peace agreement and met again with Lincoln after the fall of Richmond on April 2. The war continued until April 9, 1865.