Reconstruction - Teaching American History: Freedom Project
... the South are making you nervous. Perhaps some guarantee that blacks will receive education and be left alone could be provided? ...
... the South are making you nervous. Perhaps some guarantee that blacks will receive education and be left alone could be provided? ...
HIST 112 -
... the Civil War, philanthropists established societies for self-improvement, purchase of land, building schools, and hiring teachers. In an effort to continue this process on a national scale, Congress, just before the conclusion of the Civil War in March 1865, created the Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen ...
... the Civil War, philanthropists established societies for self-improvement, purchase of land, building schools, and hiring teachers. In an effort to continue this process on a national scale, Congress, just before the conclusion of the Civil War in March 1865, created the Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen ...
3. Battles of the Civil War: Crash Course US History #19
... of 1850, the Kansas-Nebraska Act and the Dred Scott decision, but these ultimately failed to reduce sectional conflict. The second party system ended when the issues of slavery and anti-immigrant nativism weakened loyalties to the two major parties and fostered the emergence of sectional parties, mo ...
... of 1850, the Kansas-Nebraska Act and the Dred Scott decision, but these ultimately failed to reduce sectional conflict. The second party system ended when the issues of slavery and anti-immigrant nativism weakened loyalties to the two major parties and fostered the emergence of sectional parties, mo ...
Post Civil War Years
... would not have been possible without thousands of Irish and Chinese immigrants. Immigrants were often victims of racism and abuse because of their Asian features, cultural differences, and distinct dress. ...
... would not have been possible without thousands of Irish and Chinese immigrants. Immigrants were often victims of racism and abuse because of their Asian features, cultural differences, and distinct dress. ...
File - Mr Powell`s History Pages
... Northern Democrats supported popular sovereignty. They did not want federal slave code in the territories. The Democratic party could not agree on a candidate for the 1860 election. N. Democrats chose Stephen A. Douglas, who supported popular sovereignty. While the S. Democrats supported John ...
... Northern Democrats supported popular sovereignty. They did not want federal slave code in the territories. The Democratic party could not agree on a candidate for the 1860 election. N. Democrats chose Stephen A. Douglas, who supported popular sovereignty. While the S. Democrats supported John ...
guided notes - Henrico County Public Schools
... ________________________ to influence the process of Reconstruction in a manner much more _________________towards the former Confederate states. The states that seceded were not allowed back into the Union immediately, but were put under ____________________ occupation. 5. Radical ______________ ...
... ________________________ to influence the process of Reconstruction in a manner much more _________________towards the former Confederate states. The states that seceded were not allowed back into the Union immediately, but were put under ____________________ occupation. 5. Radical ______________ ...
Reading #6
... Republicans in Congress. Their leader, Thaddeus Stevens from Pennsylvania, hated the rich slave owners of the South and blamed them for the war. When Johnson changed course and began following a more lenient policy in the South, Stevens turned against Johnson and led the radical Republicans in l ...
... Republicans in Congress. Their leader, Thaddeus Stevens from Pennsylvania, hated the rich slave owners of the South and blamed them for the war. When Johnson changed course and began following a more lenient policy in the South, Stevens turned against Johnson and led the radical Republicans in l ...
Civil War and Reconstruction
... impact of geography on these battles. e. Describe the significance of the Emancipation Proclamation. SSUSH10 The student will identify legal, political, and social dimensions of Reconstruction. a. Compare and contrast Presidential Reconstruction with Radical Republican Reconstruction. b. Explain eff ...
... impact of geography on these battles. e. Describe the significance of the Emancipation Proclamation. SSUSH10 The student will identify legal, political, and social dimensions of Reconstruction. a. Compare and contrast Presidential Reconstruction with Radical Republican Reconstruction. b. Explain eff ...
Name: Date: Page #: ______ RECONSTRUCTION READING
... public school program for either blacks or whites in the state and set the stage for Georgia’s modern public school system. In addition, some of the schools created by the Freemen’s Bureau continue to this day throughout the South, including two of Atlanta’s historical black colleges: Clarke Atlanta ...
... public school program for either blacks or whites in the state and set the stage for Georgia’s modern public school system. In addition, some of the schools created by the Freemen’s Bureau continue to this day throughout the South, including two of Atlanta’s historical black colleges: Clarke Atlanta ...
Reconstruction sec.1
... • States were required to revise their constitutions and declare that secession was illegal. • States had to ratify the Thirteenth Amendment and refuse to pay Confederate debts. • All southern states except Texas had created new governments by 1865. • Johnson declared the Union to be restored, bu ...
... • States were required to revise their constitutions and declare that secession was illegal. • States had to ratify the Thirteenth Amendment and refuse to pay Confederate debts. • All southern states except Texas had created new governments by 1865. • Johnson declared the Union to be restored, bu ...
Period 5 Packet
... of 1850, the Kansas-‐Nebraska Act and the Dred Scott decision, but these ultimately failed to reduce sectional conflict. • The second party system ended when the issues of slavery and anti-‐immigrant nativis ...
... of 1850, the Kansas-‐Nebraska Act and the Dred Scott decision, but these ultimately failed to reduce sectional conflict. • The second party system ended when the issues of slavery and anti-‐immigrant nativis ...
In Andrew Johnson’s Shoes
... • Since the Constitution did not state who should be in charge of reconstruction, Andrew Johnson and the Republican members of Congress agreed that they would work together to solve the many problems facing the nation after the Civil War. Congress ended their session and left Washington in the summ ...
... • Since the Constitution did not state who should be in charge of reconstruction, Andrew Johnson and the Republican members of Congress agreed that they would work together to solve the many problems facing the nation after the Civil War. Congress ended their session and left Washington in the summ ...
Tale of the Tape: Civil War - Mr. Fields Social Studies
... The clash was not over slavery as a moral institution-most northerners did not care enough about slavery to make sacrifices for it, certainly not the sacrifice of war. It was not a clash of peoples (most northern whites were not economically favored, not politically powerful; most southern whites we ...
... The clash was not over slavery as a moral institution-most northerners did not care enough about slavery to make sacrifices for it, certainly not the sacrifice of war. It was not a clash of peoples (most northern whites were not economically favored, not politically powerful; most southern whites we ...
Unit 6 Learning Targets and Calendar
... government. After Abraham Lincoln was assassinated, Johnson became president and announced his plan of “Restoration.” 14.2: Radicals in Control- (pgs 629- 634) When Northerners realized that African Americans in the South were still being mistreated Congress worked to find a solution. Radical Republ ...
... government. After Abraham Lincoln was assassinated, Johnson became president and announced his plan of “Restoration.” 14.2: Radicals in Control- (pgs 629- 634) When Northerners realized that African Americans in the South were still being mistreated Congress worked to find a solution. Radical Republ ...
Unit 5 Book Notes - Caldwell County Schools
... By 1857, Kansas had enough people to apply for statehood, and those for slavery devised the Lecompton Constitution, which provided that the people were only allowed to vote for the constitution “with slavery” or “without slavery.” o However, even if the constitution was passed “without slavery,” tho ...
... By 1857, Kansas had enough people to apply for statehood, and those for slavery devised the Lecompton Constitution, which provided that the people were only allowed to vote for the constitution “with slavery” or “without slavery.” o However, even if the constitution was passed “without slavery,” tho ...
Reconstruction - Cobb Learning
... All southerners were to take an oath of allegiance to the U.S. (exclude high ranking military officials & Confederate government officials) After 10% of the voters in a state took the oath, the state could form a government and ask to be readmitted to the Union ...
... All southerners were to take an oath of allegiance to the U.S. (exclude high ranking military officials & Confederate government officials) After 10% of the voters in a state took the oath, the state could form a government and ask to be readmitted to the Union ...
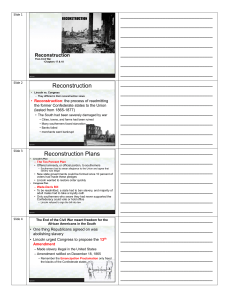
Reconstruction Reconstruction Plans
... • Families searched for members who had been sold away • Many moved from mostly white counties to places with more African Americans • Freed people demanded same economic and political rights as white citizens • Many former slaves wanted their own land to farm • Many white planters refused to surren ...
... • Families searched for members who had been sold away • Many moved from mostly white counties to places with more African Americans • Freed people demanded same economic and political rights as white citizens • Many former slaves wanted their own land to farm • Many white planters refused to surren ...
s Reconstruction Plan
... 8-5.1 Analyze the development of Reconstruction Policy and its impact in South Carolina including, the presidential and congressional reconstruction plans ...
... 8-5.1 Analyze the development of Reconstruction Policy and its impact in South Carolina including, the presidential and congressional reconstruction plans ...
Reconstruction - Cobb Learning
... All southerners were to take an oath of allegiance to the U.S. (exclude high ranking military officials & Confederate government officials) After 10% of the voters in a state took the oath, the state could form a government and ask to be readmitted to the Union ...
... All southerners were to take an oath of allegiance to the U.S. (exclude high ranking military officials & Confederate government officials) After 10% of the voters in a state took the oath, the state could form a government and ask to be readmitted to the Union ...
Nov. 18 From Presidential to Radical reconstruction
... such system as that contemplated by the details of this bill has ever before been proposed or adopted. They establish for the security of the colored race safeguards which go infinitely beyond any that the General Government has ever provided for the white race. In fact, the distinction of race and ...
... such system as that contemplated by the details of this bill has ever before been proposed or adopted. They establish for the security of the colored race safeguards which go infinitely beyond any that the General Government has ever provided for the white race. In fact, the distinction of race and ...
Unit 7 Study Guide
... What were “black codes?” Describe the relationship between Andrew Johnson and the Radical Republicans in Congress. Describe the Radical Republican plan for Reconstruction. What was the purpose of Andrew Johnson’s impeachment? What precedent was set by the fact that Andrew Johnson was voted “not guil ...
... What were “black codes?” Describe the relationship between Andrew Johnson and the Radical Republicans in Congress. Describe the Radical Republican plan for Reconstruction. What was the purpose of Andrew Johnson’s impeachment? What precedent was set by the fact that Andrew Johnson was voted “not guil ...
Radical Republican

The Radical Republicans were a faction of American politicians within the Republican Party from about 1854 (before the American Civil War) until the end of Reconstruction in 1877. They called themselves ""Radicals"" and were opposed during the war by the Moderate Republicans (led by Abraham Lincoln), by the Conservative Republicans, and by the pro-slavery Democratic Party. After the war, the Radicals were opposed by self-styled ""conservatives"" (in the South) and ""liberals"" (in the North). Radicals strongly opposed slavery during the war and after the war distrusted ex-Confederates, demanding harsh policies for the former rebels, and emphasizing civil rights and voting rights for freedmen (recently freed slaves).During the war, Radical Republicans often opposed Lincoln in terms of selection of generals (especially his choice of Democrat George B. McClellan for top command) and his efforts to bring states back into the Union. The Radicals passed their own reconstruction plan through Congress in 1864, but Lincoln vetoed it and was putting his own policies in effect when he was assassinated in 1865. Radicals pushed for the uncompensated abolition of slavery, while Lincoln wanted to pay slave owners who were loyal to the Union. After the war, the Radicals demanded civil rights for freedmen, such as measures ensuring suffrage. They initiated the Reconstruction Acts, and limited political and voting rights for ex-Confederates. They bitterly fought President Andrew Johnson; they weakened his powers and attempted to remove him from office through impeachment, which failed by one vote. The Radicals were vigorously opposed by the Democratic Party and often by moderate and Liberal Republicans as well.