Reading Guide for Goal 3 Civil War and Reconstruction
... Explain how soldiers’ misguided view of becoming “war heroes” quickly faded once they engaged in training and their first battles and duties. Explain how the South overestimated the importance of its “cotton diplomacy” and discuss its relationship with the British during the Civil War. What was the ...
... Explain how soldiers’ misguided view of becoming “war heroes” quickly faded once they engaged in training and their first battles and duties. Explain how the South overestimated the importance of its “cotton diplomacy” and discuss its relationship with the British during the Civil War. What was the ...
Freedmen. - Jessamine County Schools
... Amendments, granting African American males citizenship, equality under the law and the right to vote. In 1867 and 1868, voters in southern states chose delegates to draft new state constitutions. One quarter of the delegates elected were black. The new state constitutions guaranteed civil rights, ...
... Amendments, granting African American males citizenship, equality under the law and the right to vote. In 1867 and 1868, voters in southern states chose delegates to draft new state constitutions. One quarter of the delegates elected were black. The new state constitutions guaranteed civil rights, ...
In the course of the American Civil War, in four occupied southern
... policy was a proper one. The peculiarities of each state asked for differentiated handling. Louisiana and Arkansas were chosen for their abysmally different social, economic and political features yet common war experience. In terms of wealth, density of population, and share of slaves in its number ...
... policy was a proper one. The peculiarities of each state asked for differentiated handling. Louisiana and Arkansas were chosen for their abysmally different social, economic and political features yet common war experience. In terms of wealth, density of population, and share of slaves in its number ...
Reconstruction (1865-1876) - Mrs. Carnes
... • Northern Republicans were outraged at the South’s attempts to deny freedmen their rights. • This act guaranteed the rights of freedmen and blocked the Black Codes. • Freedmen’s Bureau was extended. • Congress passed the 14th Amendment, which guaranteed citizenship to all people born in the US, exc ...
... • Northern Republicans were outraged at the South’s attempts to deny freedmen their rights. • This act guaranteed the rights of freedmen and blocked the Black Codes. • Freedmen’s Bureau was extended. • Congress passed the 14th Amendment, which guaranteed citizenship to all people born in the US, exc ...
WAGING PEACE Part I - Scaliasworld
... Freedmen? If total emancipation were to be enacted after the cessation of hostilities what was the United States’ government’s role in accommodating four million human beings who were, by virtue of Dred Scott v Sandford, pieces of property? Dred Scott did provide legal precedence (in fact, the ONLY ...
... Freedmen? If total emancipation were to be enacted after the cessation of hostilities what was the United States’ government’s role in accommodating four million human beings who were, by virtue of Dred Scott v Sandford, pieces of property? Dred Scott did provide legal precedence (in fact, the ONLY ...
Ch. 22 PowerPoint - Jessamine County Schools
... Amendments, granting African American males citizenship, equality under the law and the right to vote. In 1867 and 1868, voters in southern states chose delegates to draft new state constitutions. One quarter of the delegates elected were black. The new state constitutions guaranteed civil rights, ...
... Amendments, granting African American males citizenship, equality under the law and the right to vote. In 1867 and 1868, voters in southern states chose delegates to draft new state constitutions. One quarter of the delegates elected were black. The new state constitutions guaranteed civil rights, ...
4 - Barren County Schools
... claiming it was much too lenient and did not safeguard Union gains. -- Feared southern planter aristocracy would regain power and possibly re-enslave African Americans. 2. Wade-Davis Bill (1864) a. Passed by Republicans b. Required 50% of state’s voters in 1860 election to take oath of allegiance an ...
... claiming it was much too lenient and did not safeguard Union gains. -- Feared southern planter aristocracy would regain power and possibly re-enslave African Americans. 2. Wade-Davis Bill (1864) a. Passed by Republicans b. Required 50% of state’s voters in 1860 election to take oath of allegiance an ...
Ch 4 S 4 Notes
... Southern Republicans-scalawags, carpetbaggers, and African Americans- have very different goals, especially regarding civil rights equality, leading to a lack of unity in the republican party. o Scalawags- White Southerners that joined Republican Party. Generally small farmers who wanted to improve ...
... Southern Republicans-scalawags, carpetbaggers, and African Americans- have very different goals, especially regarding civil rights equality, leading to a lack of unity in the republican party. o Scalawags- White Southerners that joined Republican Party. Generally small farmers who wanted to improve ...
Reconstruction - Henry County Schools
... Southern governments resisted Reconstruction by passing more discriminatory black codes Black codes restricted blacks from serving on juries, testifying against whites in court, marrying whites, or owning land ...
... Southern governments resisted Reconstruction by passing more discriminatory black codes Black codes restricted blacks from serving on juries, testifying against whites in court, marrying whites, or owning land ...
Reconstruction: the period during which the United States began to
... society by granting them full citizenship and the right to vote. The second goal, necessary to ensure the success of the first, was to destroy the political power of former slaveholders. To achieve these goals, Congress began their Reconstruction plan by passing the Civil Rights Act of 1866. This la ...
... society by granting them full citizenship and the right to vote. The second goal, necessary to ensure the success of the first, was to destroy the political power of former slaveholders. To achieve these goals, Congress began their Reconstruction plan by passing the Civil Rights Act of 1866. This la ...
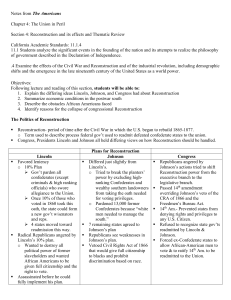
Chapter 2 Two Plans for Reconstruction
... Lincoln also required that the reconstructed states ratify the Thirteenth Amendment which abolished slavery. Congress opposed Lincoln’s generous policies. Led by Thaddeus Stevens of Pennsylvania and Charles Sumner of Massachusetts, Congress passed a bill calling for far harsher treatment of the rebe ...
... Lincoln also required that the reconstructed states ratify the Thirteenth Amendment which abolished slavery. Congress opposed Lincoln’s generous policies. Led by Thaddeus Stevens of Pennsylvania and Charles Sumner of Massachusetts, Congress passed a bill calling for far harsher treatment of the rebe ...
PowerPoint on Reconstruction
... How ex-Confederate states will be re-admitted into the Union How the Southern economy will recover from the war How the rights of Free Blacks will be protected How Whites and Blacks will relate to each other Whether the South will be transformed or back to the way it was before the Civil War Who wil ...
... How ex-Confederate states will be re-admitted into the Union How the Southern economy will recover from the war How the rights of Free Blacks will be protected How Whites and Blacks will relate to each other Whether the South will be transformed or back to the way it was before the Civil War Who wil ...
Reconstruction
... Lincoln was the first president to be assassinated Vice President Andrew Johnson became President ...
... Lincoln was the first president to be assassinated Vice President Andrew Johnson became President ...
Reconstruction
... amendment to the Constitution Allowed Southern states to reenter the Union if They formed new state governments They promised to treat former slaves fairly ...
... amendment to the Constitution Allowed Southern states to reenter the Union if They formed new state governments They promised to treat former slaves fairly ...
Reconstruction 1865–1877
... plan to restore the Union to include both the northern and southern states. The southern states were left in ruins, so rebuilding would ...
... plan to restore the Union to include both the northern and southern states. The southern states were left in ruins, so rebuilding would ...
Reconstruction and Segregation
... could no longer rely on free labor to help bring in the crops. Freed slaves had no skills other than farming. Sharecropping allowed plantation owners to retain their labor, by giving up farmland and using slave-housing, and gave slaves a chance to make a living by paying rent through a share of crop ...
... could no longer rely on free labor to help bring in the crops. Freed slaves had no skills other than farming. Sharecropping allowed plantation owners to retain their labor, by giving up farmland and using slave-housing, and gave slaves a chance to make a living by paying rent through a share of crop ...
Unit 6.1 Reconstruction - Dover Union Free School District
... claiming it was much too lenient and did not safeguard Union gains. -- Feared southern planter aristocracy would regain power and possibly re-enslave African Americans. 2. Wade-Davis Bill (1864) a. Passed by Republicans b. Required 50% of state’s voters in 1860 election to take oath of allegiance an ...
... claiming it was much too lenient and did not safeguard Union gains. -- Feared southern planter aristocracy would regain power and possibly re-enslave African Americans. 2. Wade-Davis Bill (1864) a. Passed by Republicans b. Required 50% of state’s voters in 1860 election to take oath of allegiance an ...
Civil War and Reconstruction – Period 5 – APUSH
... the mode of its formation subjects it to a third fundamental principle, namely: the law of compact. We maintain that in every compact between two or more parties, the obligation is mutual; that the failure of one of the contracting parties to perform a material part of the agreement, entirely releas ...
... the mode of its formation subjects it to a third fundamental principle, namely: the law of compact. We maintain that in every compact between two or more parties, the obligation is mutual; that the failure of one of the contracting parties to perform a material part of the agreement, entirely releas ...
Lincoln Plans for Reconstruction http://civilwar150.longwood.edu
... proposal being commonly referred to as the Ten Percent Plan. In the aftermath of Lincoln’s Proclamation, Unionists in Arkansas, Virginia, Louisiana, and Florida began to reorganize. Many in Lincoln’s own party however, criticized the plan as too lenient. The so-called Radical Republicans wanted to r ...
... proposal being commonly referred to as the Ten Percent Plan. In the aftermath of Lincoln’s Proclamation, Unionists in Arkansas, Virginia, Louisiana, and Florida began to reorganize. Many in Lincoln’s own party however, criticized the plan as too lenient. The so-called Radical Republicans wanted to r ...
Unit 2 Class Notes- The Civil War and Reconstruction
... ***The Freedmen’s Bureau had its greatest success in education, teaching an estimated 200,000 blacks how to read Following Lincoln’s assassination in April 1865, President Andrew Johnson announced his own plan for Reconstruction His plan differed little from Lincoln’s The difference was that J ...
... ***The Freedmen’s Bureau had its greatest success in education, teaching an estimated 200,000 blacks how to read Following Lincoln’s assassination in April 1865, President Andrew Johnson announced his own plan for Reconstruction His plan differed little from Lincoln’s The difference was that J ...
United States History I
... Black Codes – a series of laws passed by Southern legislatures, which severely limited African Americans’ rights in the South. Civil Rights Act – 1866 law that granted citizenship to all persons born in the United States except Native Americans. Fourteenth Amendment – Amendment to the Constitution t ...
... Black Codes – a series of laws passed by Southern legislatures, which severely limited African Americans’ rights in the South. Civil Rights Act – 1866 law that granted citizenship to all persons born in the United States except Native Americans. Fourteenth Amendment – Amendment to the Constitution t ...
United States History I
... Black Codes – a series of laws passed by Southern legislatures, which severely limited African Americans’ rights in the South. Civil Rights Act – 1866 law that granted citizenship to all persons born in the United States except Native Americans. Fourteenth Amendment – Amendment to the Constitution t ...
... Black Codes – a series of laws passed by Southern legislatures, which severely limited African Americans’ rights in the South. Civil Rights Act – 1866 law that granted citizenship to all persons born in the United States except Native Americans. Fourteenth Amendment – Amendment to the Constitution t ...
RECONSTRUCTION
... I. Context Setter: Four main questions vis-à-vis the post-Civil War South: 1. Rebuilding the South after its destruction and the emancipation of slavery 2. The condition of African Americans in the South 3. How would the South be reintegrated into the Union? 4. Who would control process of Reconstru ...
... I. Context Setter: Four main questions vis-à-vis the post-Civil War South: 1. Rebuilding the South after its destruction and the emancipation of slavery 2. The condition of African Americans in the South 3. How would the South be reintegrated into the Union? 4. Who would control process of Reconstru ...
Radical Republican

The Radical Republicans were a faction of American politicians within the Republican Party from about 1854 (before the American Civil War) until the end of Reconstruction in 1877. They called themselves ""Radicals"" and were opposed during the war by the Moderate Republicans (led by Abraham Lincoln), by the Conservative Republicans, and by the pro-slavery Democratic Party. After the war, the Radicals were opposed by self-styled ""conservatives"" (in the South) and ""liberals"" (in the North). Radicals strongly opposed slavery during the war and after the war distrusted ex-Confederates, demanding harsh policies for the former rebels, and emphasizing civil rights and voting rights for freedmen (recently freed slaves).During the war, Radical Republicans often opposed Lincoln in terms of selection of generals (especially his choice of Democrat George B. McClellan for top command) and his efforts to bring states back into the Union. The Radicals passed their own reconstruction plan through Congress in 1864, but Lincoln vetoed it and was putting his own policies in effect when he was assassinated in 1865. Radicals pushed for the uncompensated abolition of slavery, while Lincoln wanted to pay slave owners who were loyal to the Union. After the war, the Radicals demanded civil rights for freedmen, such as measures ensuring suffrage. They initiated the Reconstruction Acts, and limited political and voting rights for ex-Confederates. They bitterly fought President Andrew Johnson; they weakened his powers and attempted to remove him from office through impeachment, which failed by one vote. The Radicals were vigorously opposed by the Democratic Party and often by moderate and Liberal Republicans as well.