Lecture
... Hund’s rules - determine the energy levels for the same configuration (generally correct, but not absolutely right) (i) Among all the terms derived from the same configuration, those with the highest spin multiplicity are the lowest in energy. (ii) Of the terms with the same multiplicity, the lowes ...
... Hund’s rules - determine the energy levels for the same configuration (generally correct, but not absolutely right) (i) Among all the terms derived from the same configuration, those with the highest spin multiplicity are the lowest in energy. (ii) Of the terms with the same multiplicity, the lowes ...
Why is this a problem?
... This problem became known as the ultraviolet catastrophe and was one of the many effects classical physics couldn’t explain. ...
... This problem became known as the ultraviolet catastrophe and was one of the many effects classical physics couldn’t explain. ...
Quantum Mechanics
... Electron density goes away from the internuclear region! Destructive interference! ...
... Electron density goes away from the internuclear region! Destructive interference! ...
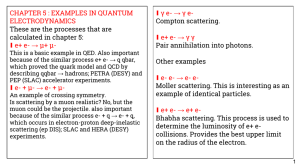
CHAPTER 5 : EXAMPLES IN QUANTUM γ e- → γ e- ∎ ELECTRODYNAMICS
... These were important experiments in the history of high-energy physics. From the particle data group, the figure shows the ratio R = σ ( e e → hadrons ) / σ ( e ebar → μ μbar) . The underlying process in hadron production is e- + e+ → q + qbar. Neglecting QCD interactions we would just have R = cons ...
... These were important experiments in the history of high-energy physics. From the particle data group, the figure shows the ratio R = σ ( e e → hadrons ) / σ ( e ebar → μ μbar) . The underlying process in hadron production is e- + e+ → q + qbar. Neglecting QCD interactions we would just have R = cons ...
Document
... Which of the following phenomena could be explained by classical physics and did not require a quantum hypothesis in order to make theory agree with experiment? ...
... Which of the following phenomena could be explained by classical physics and did not require a quantum hypothesis in order to make theory agree with experiment? ...
Relativity Problem Set 7 - Solutions Prof. J. Gerton October 24, 2011
... The energy spectrum is proportional to n2 as in the Hydrogen atom case, which is obvious because we are still treating a Coulomb field, but the number of the fundamental level E0 = 6.81 eV is different from the fundamental level of the Hydrogen system. Positronium has long being theoretically predic ...
... The energy spectrum is proportional to n2 as in the Hydrogen atom case, which is obvious because we are still treating a Coulomb field, but the number of the fundamental level E0 = 6.81 eV is different from the fundamental level of the Hydrogen system. Positronium has long being theoretically predic ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 SECTION - A ALL
... 2. A capacitor of capacity 20μF is charged to a potential of 1000 volt. Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor. 3. State Kirchhoff’s laws of distribution of currents in an electrical network. 4. Distinguish between Peltier effect and Joule effect. 5. What is meant by Lorentz force? 6. Define m ...
... 2. A capacitor of capacity 20μF is charged to a potential of 1000 volt. Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor. 3. State Kirchhoff’s laws of distribution of currents in an electrical network. 4. Distinguish between Peltier effect and Joule effect. 5. What is meant by Lorentz force? 6. Define m ...
Final Exam 2004
... result of this process. How does the atom quantum number M J change? Express the frequency of the emitted photon via W. [Hint: use conservation laws.] f) (2 points) Sulfur has the following electronic structure: (Ne) (3s)2 (3 p) 4 . Here (Ne) is shorthand notation for the filled neon-like core. Us ...
... result of this process. How does the atom quantum number M J change? Express the frequency of the emitted photon via W. [Hint: use conservation laws.] f) (2 points) Sulfur has the following electronic structure: (Ne) (3s)2 (3 p) 4 . Here (Ne) is shorthand notation for the filled neon-like core. Us ...
Renormalization

In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities.Renormalization specifies relationships between parameters in the theory when the parameters describing large distance scales differ from the parameters describing small distances. Physically, the pileup of contributions from an infinity of scales involved in a problem may then result in infinities. When describing space and time as a continuum, certain statistical and quantum mechanical constructions are ill defined. To define them, this continuum limit, the removal of the ""construction scaffolding"" of lattices at various scales, has to be taken carefully, as detailed below.Renormalization was first developed in quantum electrodynamics (QED) to make sense of infinite integrals in perturbation theory. Initially viewed as a suspect provisional procedure even by some of its originators, renormalization eventually was embraced as an important and self-consistent actual mechanism of scale physics in several fields of physics and mathematics. Today, the point of view has shifted: on the basis of the breakthrough renormalization group insights of Kenneth Wilson, the focus is on variation of physical quantities across contiguous scales, while distant scales are related to each other through ""effective"" descriptions. All scales are linked in a broadly systematic way, and the actual physics pertinent to each is extracted with the suitable specific computational techniques appropriate for each.